
Which of the following is oxetane?
A. 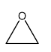
B. 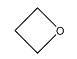
C. 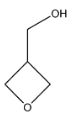
D. 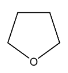
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The compound oxetane, is a more commonly used name for the compound oxacyclobutane. From this we can determine that the required compound has 4 carbon cyclic structures where one of the carbon atoms has been substituted by an oxygen atom.
Complete Step-by-Step Solution:
While naming cyclic organic compounds, certain nomenclature rules need to be followed:
1. Determine the cyclic organic compound or the cycloalkane to be used as the parent chain. This can be determined by finding the cycloalkane with the highest number of carbon atoms.
2. In a situation where the compound contains an alkyl group, in case the alkyl group has a higher number of carbon atoms, then it would be treated as the parent chain. Otherwise, the cycloalkane would be the parent chain.
3. Next, we need to name the functional groups in their alphabetical order.
4. The naming should be done in such a way that the carbon on which the functional group is attached should have the lowest number in nomenclature.
5. If the same functional group is repeated more than once, then corresponding prefixes along with the correct position numbering of the functional group must be mentioned.
6. After all these functional groups are named, then the name of the cycloalkane can be written in the end. The name of the cycloalkane depends on the number of carbon atoms present in the cyclic compound.
The given compound is oxetane. This is a more commonly used name for the compound oxacyclobutane.
From this we can determine that the required compound has 4 carbon cyclic structure where one of the carbon atoms has been substituted by an oxygen atom.
Hence, Option B is the correct option.
Note: On the basis of the IUPAC rules mentioned in the solution, we can determine the names of the other compounds as well. Their corresponding IUPAC names are: A. Oxacyclopropane; C. methanoloxacyclobutane; D. Oxapenatne.
Complete Step-by-Step Solution:
While naming cyclic organic compounds, certain nomenclature rules need to be followed:
1. Determine the cyclic organic compound or the cycloalkane to be used as the parent chain. This can be determined by finding the cycloalkane with the highest number of carbon atoms.
2. In a situation where the compound contains an alkyl group, in case the alkyl group has a higher number of carbon atoms, then it would be treated as the parent chain. Otherwise, the cycloalkane would be the parent chain.
3. Next, we need to name the functional groups in their alphabetical order.
4. The naming should be done in such a way that the carbon on which the functional group is attached should have the lowest number in nomenclature.
5. If the same functional group is repeated more than once, then corresponding prefixes along with the correct position numbering of the functional group must be mentioned.
6. After all these functional groups are named, then the name of the cycloalkane can be written in the end. The name of the cycloalkane depends on the number of carbon atoms present in the cyclic compound.
The given compound is oxetane. This is a more commonly used name for the compound oxacyclobutane.
From this we can determine that the required compound has 4 carbon cyclic structure where one of the carbon atoms has been substituted by an oxygen atom.
Hence, Option B is the correct option.
Note: On the basis of the IUPAC rules mentioned in the solution, we can determine the names of the other compounds as well. Their corresponding IUPAC names are: A. Oxacyclopropane; C. methanoloxacyclobutane; D. Oxapenatne.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




