
Which of the following is not true about angle of contact?
A) The value of angle of contact for pure water and glass is zero.
B) Angle of contact increases with increase in temperature of liquid.
C) If the angle of contact of a liquid and a solid surface is less than ${90^ \circ }$, then the liquid spreads on the surface of solid.
D) Angle of contact doesn’t depend upon the inclination of the solid surface to the liquid surface.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The angle of contact is actually the angle between the meniscus and the containing walls of a column of liquid measured from the vertical wall below the surface of the liquid to the position of the tangent to the meniscus at its point of contact with the wall. Angle of contact depends on the nature of liquid and solid, medium in which angle of contact is being made and purity of liquids and solids.
Complete solution:
The problem is asking for the correct statements regarding the angle of contact. So we will consider each statement and then find which of the options is correct.
Let us consider the option A.
For pure water and pure glass, the angle of contact is$0^\circ $. For ordinary water and glass, it lies between \[8^\circ \] and\[18^\circ \]. Hence this statement is true.
Consider option B.
With the increase in temperature, the surface tension of liquid decreases. Due to this the liquid surface on the solid surface becomes more flat so the angle of contact of a liquid increases with the increase in temperature. So the statement in option B is true.
Consider option C.
If the angle of contact of a liquid and a solid surface is less than ${90^ \circ }$, then the liquid spreads on the surface of solid, this statement is also true because for contact angle less than ${90^ \circ }$ the difference in the surface tensions of air-solid interface and liquid-solid interface is less than the air-liquid interface.
The diagram for the angle of contact for less than ${90^ \circ }$.
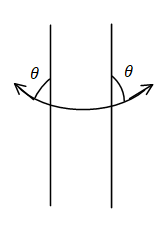
The diagram for the angle of contact more than ${90^ \circ }$.
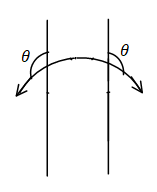
Consider option D.
Angle of contact doesn’t depend upon the inclination of the solid surface to the liquid surface. Angle of contact actually depends on the inclination of the solid surface so this statement for option D is not true.
The correct answer for this problem is option D.
Note: Keep in mind that the shape of meniscus is decided by the angle of contact which depends on the surface tension. Glass and water always make a concave surface & glass and mercury always makes a convex surface.
Complete solution:
The problem is asking for the correct statements regarding the angle of contact. So we will consider each statement and then find which of the options is correct.
Let us consider the option A.
For pure water and pure glass, the angle of contact is$0^\circ $. For ordinary water and glass, it lies between \[8^\circ \] and\[18^\circ \]. Hence this statement is true.
Consider option B.
With the increase in temperature, the surface tension of liquid decreases. Due to this the liquid surface on the solid surface becomes more flat so the angle of contact of a liquid increases with the increase in temperature. So the statement in option B is true.
Consider option C.
If the angle of contact of a liquid and a solid surface is less than ${90^ \circ }$, then the liquid spreads on the surface of solid, this statement is also true because for contact angle less than ${90^ \circ }$ the difference in the surface tensions of air-solid interface and liquid-solid interface is less than the air-liquid interface.
The diagram for the angle of contact for less than ${90^ \circ }$.

The diagram for the angle of contact more than ${90^ \circ }$.

Consider option D.
Angle of contact doesn’t depend upon the inclination of the solid surface to the liquid surface. Angle of contact actually depends on the inclination of the solid surface so this statement for option D is not true.
The correct answer for this problem is option D.
Note: Keep in mind that the shape of meniscus is decided by the angle of contact which depends on the surface tension. Glass and water always make a concave surface & glass and mercury always makes a convex surface.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




