
Which of the following is not a fatty acid [CPMT $1978$]
A.Stearic acid
B.Palmitic acid
C.Oleic acid
D.Phenyl acetic acid
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: Fatty acids are very essential to human body systems as they are building blocks of the fat in our body. These compounds consist of carboxylic acids with long aliphatic chains with saturated or unsaturated bonds. The number of carbon atoms in most fatty acids may vary from $2$to $30$.
Complete answer: In lipids, fatty acids are an important component found in animals, plants, and microorganisms. Fatty acids consist of a straight chain of an even number of carbon atoms or a straight aliphatic chain and a carboxyl group at one end of the compound. Few fatty acids have branched chains and ring structures.
If in a fatty acid all the carbon-carbon bonds are single then it is called saturated fatty acid such as stearic acid, palmitic acid, lauric acid, etc. When any of the bonds is double or triple then it is called unsaturated fatty acid. For example oleic acid, linolenic acid, arachidonic acid, etc.
Therefore from the options, we can see that stearic acid, palmitic acid, and oleic acid are examples of fatty acids. Stearic acid and palmitic acid are saturated fatty acids with $16$and 18 carbon atoms while oleic acid is an unsaturated fatty acid with $18$carbon atoms. Their structures are shown below:
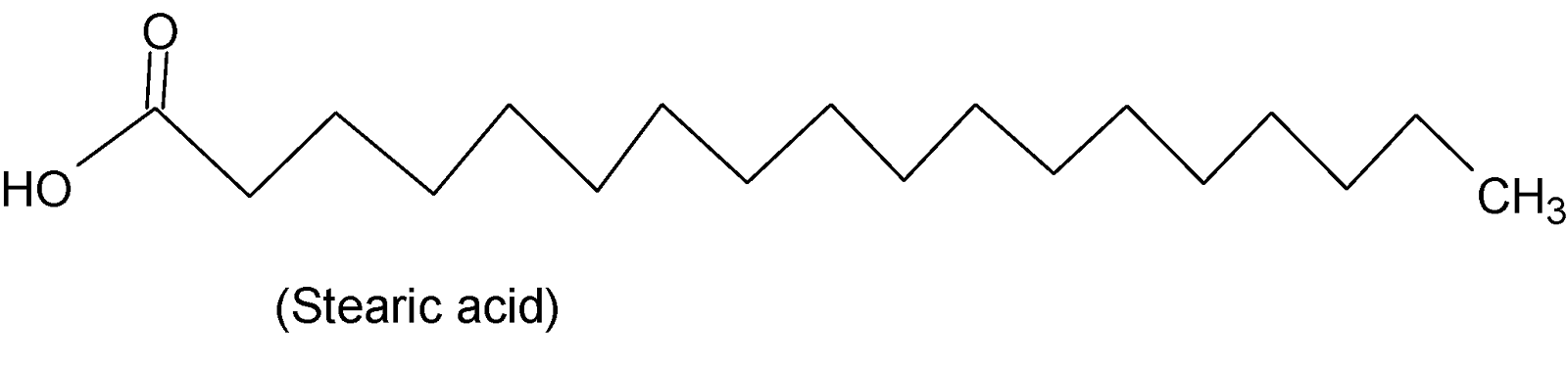
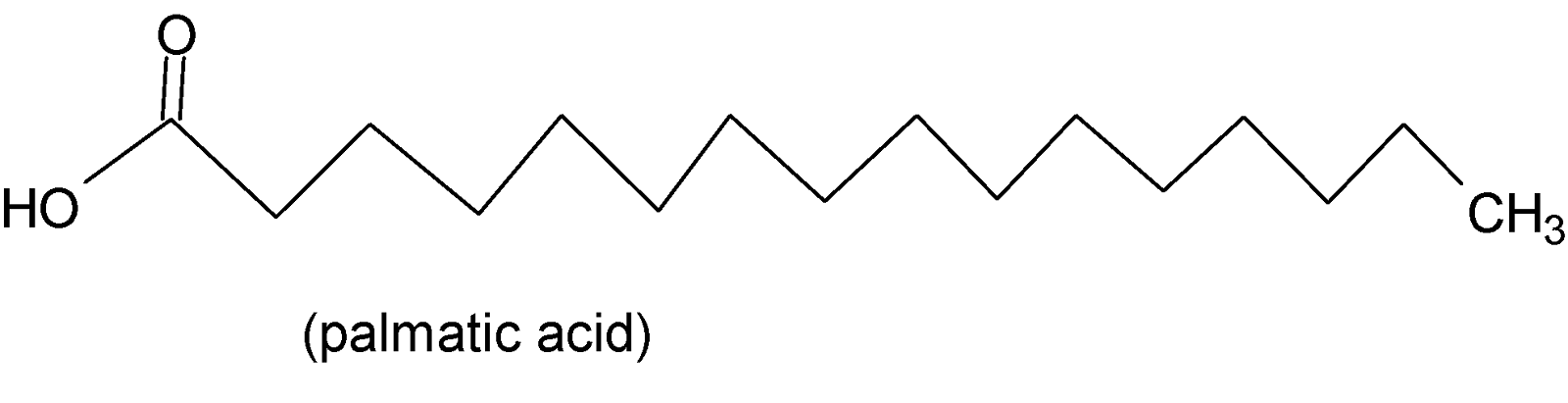
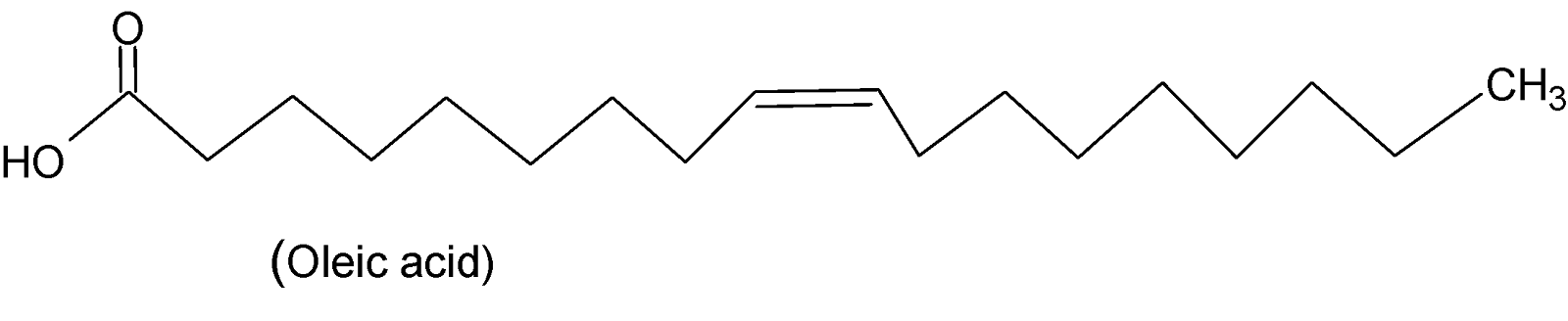
Phenylacetic acid is an organic compound that has a phenyl group and a carboxylic acid group. But it is not a fatty acid.
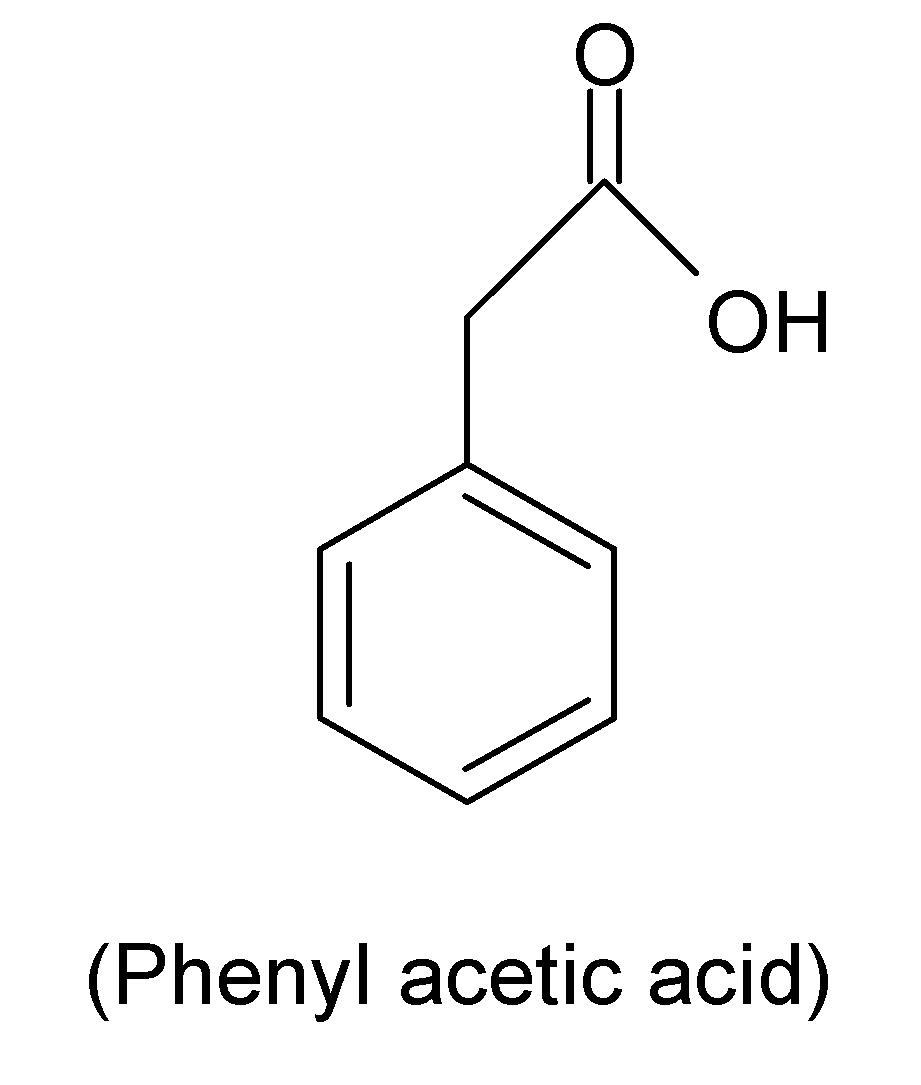
Thus, option (D) is correct.
Note: Generally fatty acids are not found in a free state in nature, They always exist in a combination of alcohol called glycerol in the form of triglyceride. When glucose is not available in our body for energy, the fatty acids are used to provide fuel to our cell organisms.
Complete answer: In lipids, fatty acids are an important component found in animals, plants, and microorganisms. Fatty acids consist of a straight chain of an even number of carbon atoms or a straight aliphatic chain and a carboxyl group at one end of the compound. Few fatty acids have branched chains and ring structures.
If in a fatty acid all the carbon-carbon bonds are single then it is called saturated fatty acid such as stearic acid, palmitic acid, lauric acid, etc. When any of the bonds is double or triple then it is called unsaturated fatty acid. For example oleic acid, linolenic acid, arachidonic acid, etc.
Therefore from the options, we can see that stearic acid, palmitic acid, and oleic acid are examples of fatty acids. Stearic acid and palmitic acid are saturated fatty acids with $16$and 18 carbon atoms while oleic acid is an unsaturated fatty acid with $18$carbon atoms. Their structures are shown below:



Phenylacetic acid is an organic compound that has a phenyl group and a carboxylic acid group. But it is not a fatty acid.

Thus, option (D) is correct.
Note: Generally fatty acids are not found in a free state in nature, They always exist in a combination of alcohol called glycerol in the form of triglyceride. When glucose is not available in our body for energy, the fatty acids are used to provide fuel to our cell organisms.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




