
Which of the following is a set of enamine?
I.
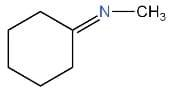
II.
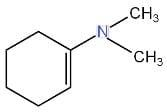
III.
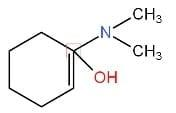
IV.
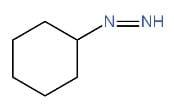
V.
(A) I and II
(B) II, III and IV
(C) II, IV and V
(D) Only II
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: An enamine is a compound formed by the condensation of an aldehyde or a ketone with a secondary amine (like pyrrolidine, piperidine, and morpholine). It can act as a good nucleophile as well as a good base. It contains a carbon – nitrogen single bond. These are labile in nature. The α, β-unsaturated amines are known as enamines.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
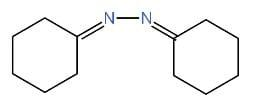
We have to identify which of the given compounds are α, β-unsaturated amines. The compounds I and V contain carbon-nitrogen double bonds. So, the compounds I and V are not enamines. The compound IV is not an α, β-unsaturated amine. Thus, it is also an enamine. As compound III contains a hydroxyl group. Hence, it is not an enamine.
Only compound II is an α, β-unsaturated amines and contains a carbon-nitrogen single bond. Hence, it is an enamine.
Correct Option: (D) Only II.
Additional Information: The enamines can be used to synthesise β-ketonitriles. It can also react with an acid halide to form β-dicarbonyls. These get reduced to saturated amines by catalytic hydrogenation. The primary and secondary enamines are thermodynamically unstable. It exists in an unfavourable equilibrium with their imine tautomer.
Note: For a compound to be enamine, it is necessary that it should be an α, β-unsaturated amines and must contain a carbon–nitrogen single bond.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
We have to identify which of the given compounds are α, β-unsaturated amines. The compounds I and V contain carbon-nitrogen double bonds. So, the compounds I and V are not enamines. The compound IV is not an α, β-unsaturated amine. Thus, it is also an enamine. As compound III contains a hydroxyl group. Hence, it is not an enamine.
Only compound II is an α, β-unsaturated amines and contains a carbon-nitrogen single bond. Hence, it is an enamine.
Correct Option: (D) Only II.
Additional Information: The enamines can be used to synthesise β-ketonitriles. It can also react with an acid halide to form β-dicarbonyls. These get reduced to saturated amines by catalytic hydrogenation. The primary and secondary enamines are thermodynamically unstable. It exists in an unfavourable equilibrium with their imine tautomer.
Note: For a compound to be enamine, it is necessary that it should be an α, β-unsaturated amines and must contain a carbon–nitrogen single bond.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Understanding Elastic Collisions in Two Dimensions

AssertionIn electrolytic refining of metal impure metal class 12 chemistry JEE_Main

JEE Main Syllabus 2026: Download Detailed Subject-wise PDF

Other Pages
Alcohol Phenol and Ether Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Solutions Hindi Medium (2025-26)

CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Set 1 56/2/1 2025: Question Paper, Answers & Analysis

CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Set 3 2025 with Answers

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students




