
Which of the following is a non-reducing sugar?
A. Glucose
B. Sucrose
C. Maltose
D. Lactose
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Non-reducing sugars does have a group attached to any of the anomeric carbon. Therefore, they are unable to reduce other compounds.
Complete step by step answer:
We can draw the structure of sucrose as follows:
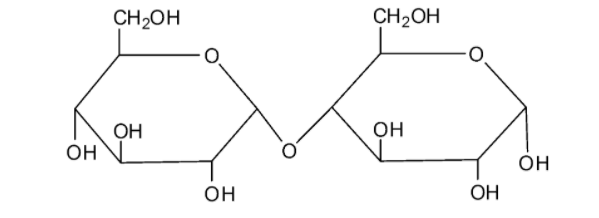
The molecule of sucrose is a disaccharide. From the structure, we can see that sucrose is a combination of the monosaccharides fructose and glucose with the formula ${{\rm{C}}_{{\rm{12}}}}{{\rm{H}}_{{\rm{22}}}}{{\rm{O}}_{{\rm{11}}}}$. It is a non-reducing sugar as this molecule does not have characteristics of the reducing sugars. The two monosaccharide units are connected by a glycosidic linkage between ${{\rm{C}}_{\rm{1}}}$ of ${\rm{\alpha }} - $ glucose and ${{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}$ of ${\rm{\beta }} - $ fructose. As the reducing groups of the glucose molecule and fructose molecules are involved in the formation of the glycosidic, sucrose is considered a non-reducing sugar.
Therefore, Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar.
So, out of the given four options, B is the correct option.
Additional information:
We can draw the structure of glucose as follows:
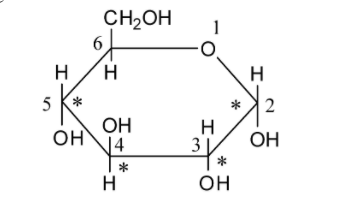
Glucose is a monosaccharide. As glucose acts as a reducing agent, it is reconsidered as a reducing sugar.
We can draw the structure of maltose as follows:
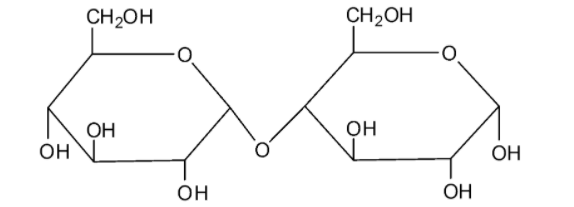
Maltose is made by the combination of two glucose molecules. Maltose undergoes mutarotation. Because of this reason, maltose is considered as a reducing sugar.
We can draw the structure of lactose as follows:
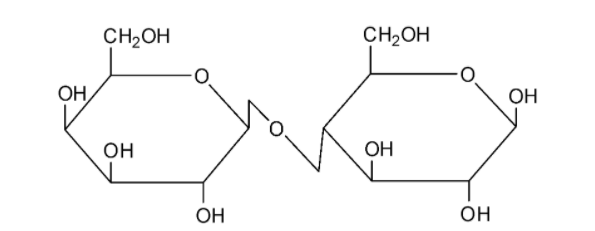
Lactose is composed by the combination of a glucose and a galactose molecule. Lactose undergoes mutarotation and it is hence a reducing sugar.
Note:
Monosaccharides are considered as reducing sugars. Then sugar that cannot act as a reducing agent are non-reducing agents. Out of disaccharides, sucrose is a well-known non-reducing sugar.
Complete step by step answer:
We can draw the structure of sucrose as follows:

The molecule of sucrose is a disaccharide. From the structure, we can see that sucrose is a combination of the monosaccharides fructose and glucose with the formula ${{\rm{C}}_{{\rm{12}}}}{{\rm{H}}_{{\rm{22}}}}{{\rm{O}}_{{\rm{11}}}}$. It is a non-reducing sugar as this molecule does not have characteristics of the reducing sugars. The two monosaccharide units are connected by a glycosidic linkage between ${{\rm{C}}_{\rm{1}}}$ of ${\rm{\alpha }} - $ glucose and ${{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}$ of ${\rm{\beta }} - $ fructose. As the reducing groups of the glucose molecule and fructose molecules are involved in the formation of the glycosidic, sucrose is considered a non-reducing sugar.
Therefore, Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar.
So, out of the given four options, B is the correct option.
Additional information:
We can draw the structure of glucose as follows:

Glucose is a monosaccharide. As glucose acts as a reducing agent, it is reconsidered as a reducing sugar.
We can draw the structure of maltose as follows:

Maltose is made by the combination of two glucose molecules. Maltose undergoes mutarotation. Because of this reason, maltose is considered as a reducing sugar.
We can draw the structure of lactose as follows:

Lactose is composed by the combination of a glucose and a galactose molecule. Lactose undergoes mutarotation and it is hence a reducing sugar.
Note:
Monosaccharides are considered as reducing sugars. Then sugar that cannot act as a reducing agent are non-reducing agents. Out of disaccharides, sucrose is a well-known non-reducing sugar.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




