
Which of the following correctly show the way sound vibrations travel?
(A)
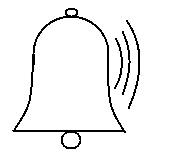
(B)
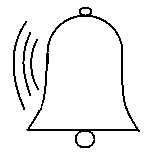
(C)
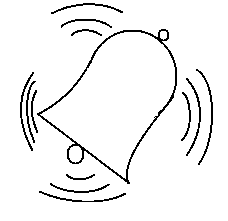
(D)
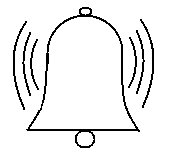
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Sound vibrations in air are formed when air molecules oscillate or vibrate and move at a direction away from the vibrating source. Sound vibrations travel in any material medium in the form of sound waves which are mechanical in nature.
Complete answer:
Sound waves in any material medium are mechanical waves. Sound waves travel in the form of longitudinal vibrations. Longitudinal vibrations have a distinctive property that they move in all directions. Longitudinal waves travel in any material medium in the form of a series of compressions and rarefactions.
Thus, sound waves travel outwards in all directions in the form of a series of compressions and rarefactions of the particles of the medium from the source. As the longitudinal sound waves travel, the energy they contain becomes dissipated or damped and as a result of which the intensity of the sound becomes weaker the farther it is from the source.
Thus, we can say that the shape of a longitudinal sound wave vibration with no obstacles in its direction of propagation would be spherical under approximation.
Since only the figure given in option (C) properly matches our description of a longitudinal sound wave vibration.
We can say that option (C) is the correct answer to this question.
Note: If we consider a sound wave to be moving at a direction from left to right through a medium of air, then in this condition the particles of the medium of air will be displaced at directions both rightward and leftward as the energy of the sound wave passes through it.
The motion of the particles of the medium is both, parallel and anti-parallel to the direction of the energy transport. This is what characterizes sound waves travelling in any material medium such as air as longitudinal waves.
Complete answer:
Sound waves in any material medium are mechanical waves. Sound waves travel in the form of longitudinal vibrations. Longitudinal vibrations have a distinctive property that they move in all directions. Longitudinal waves travel in any material medium in the form of a series of compressions and rarefactions.
Thus, sound waves travel outwards in all directions in the form of a series of compressions and rarefactions of the particles of the medium from the source. As the longitudinal sound waves travel, the energy they contain becomes dissipated or damped and as a result of which the intensity of the sound becomes weaker the farther it is from the source.
Thus, we can say that the shape of a longitudinal sound wave vibration with no obstacles in its direction of propagation would be spherical under approximation.
Since only the figure given in option (C) properly matches our description of a longitudinal sound wave vibration.
We can say that option (C) is the correct answer to this question.
Note: If we consider a sound wave to be moving at a direction from left to right through a medium of air, then in this condition the particles of the medium of air will be displaced at directions both rightward and leftward as the energy of the sound wave passes through it.
The motion of the particles of the medium is both, parallel and anti-parallel to the direction of the energy transport. This is what characterizes sound waves travelling in any material medium such as air as longitudinal waves.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




