
Which of the following compounds is known as inorganic benzene?
A. ${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$
B. ${{C}_{5}}{{H}_{5}}B$
C. ${{C}_{3}}{{N}_{3}}{{H}_{3}}$
D. ${{B}_{3}}{{N}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Inorganic benzene is a cyclic compound, it is called as inorganic benzene because it is isoelectronic and also isostructural with benzene. It is actually a colourless liquid.
Step by step solution:
Borazine is called as the inorganic benzene, which is having chemical formula ${{B}_{3}}{{N}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}$. It is a cyclic compound , we can see the structure of borazine:
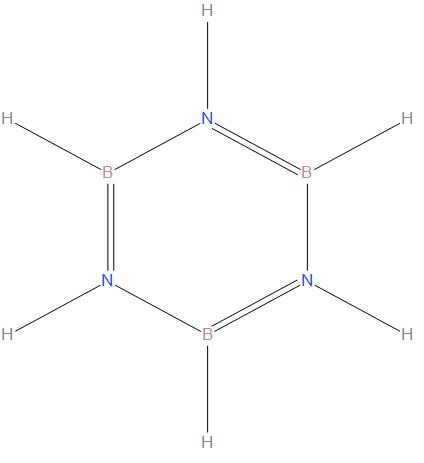
- The bond angle is found to be ${{117.1}^{\circ }}$ at the boron atoms and ${{122.9}^{\circ }}$ at the nitrogen, which will give the distinct symmetry to the molecule.
- There are several properties of borazine found like:
- It is isoelectronic and also isostructural with benzene, isoelectronic means those which have the same number of electrons around them and isostructural means those that are having the same hybridisation and shape as that of others.
-It is colourless and also has an aromatic smell.
- In borazine 12 sigma bonds and 3 pi bonds are found that are the same as in benzene.
- Now let’s see how borazine is being prepared: One of the main method of preparation of borazine is from diborane and ammonia, which are taken in a ratio of 1:2 at about temperature of ${{300}^{\circ }}C$. The reaction can be written as:
\[3{{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}+6N{{H}_{3}}\to 2{{B}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}{{N}_{3}}+12{{H}_{2}}\]
-The are several uses of borazine found like:
-It can be used as a precursor for growing boron nitride thin films on various surfaces.
- It is found that these are also used as a starting material for the various other ceramics like boron carbonitrides.
Hence, we can conclude that the correct option is (D) ,${{B}_{3}}{{N}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}$ is known as inorganic benzene.
Note:
We must remember that borazine is also called as borazole along with inorganic benzene, which is a polar compound, in which there are three BH units and three NH units are present alternate.
Step by step solution:
Borazine is called as the inorganic benzene, which is having chemical formula ${{B}_{3}}{{N}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}$. It is a cyclic compound , we can see the structure of borazine:

- The bond angle is found to be ${{117.1}^{\circ }}$ at the boron atoms and ${{122.9}^{\circ }}$ at the nitrogen, which will give the distinct symmetry to the molecule.
- There are several properties of borazine found like:
- It is isoelectronic and also isostructural with benzene, isoelectronic means those which have the same number of electrons around them and isostructural means those that are having the same hybridisation and shape as that of others.
-It is colourless and also has an aromatic smell.
- In borazine 12 sigma bonds and 3 pi bonds are found that are the same as in benzene.
- Now let’s see how borazine is being prepared: One of the main method of preparation of borazine is from diborane and ammonia, which are taken in a ratio of 1:2 at about temperature of ${{300}^{\circ }}C$. The reaction can be written as:
\[3{{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}+6N{{H}_{3}}\to 2{{B}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}{{N}_{3}}+12{{H}_{2}}\]
-The are several uses of borazine found like:
-It can be used as a precursor for growing boron nitride thin films on various surfaces.
- It is found that these are also used as a starting material for the various other ceramics like boron carbonitrides.
Hence, we can conclude that the correct option is (D) ,${{B}_{3}}{{N}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}$ is known as inorganic benzene.
Note:
We must remember that borazine is also called as borazole along with inorganic benzene, which is a polar compound, in which there are three BH units and three NH units are present alternate.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




