
Which of the following alkyl halides undergo rearrangement in ${{S}_{{{N}^{1}}}}$ reaction?
A.
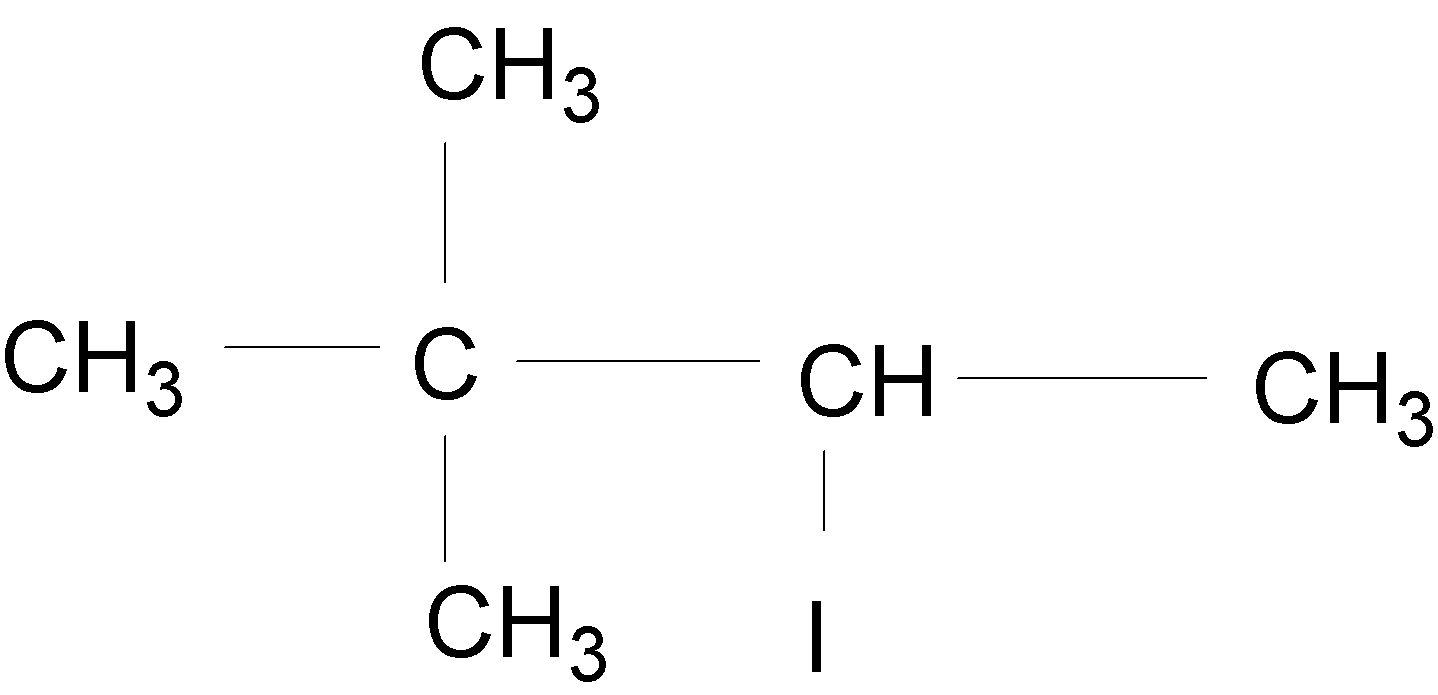
B.
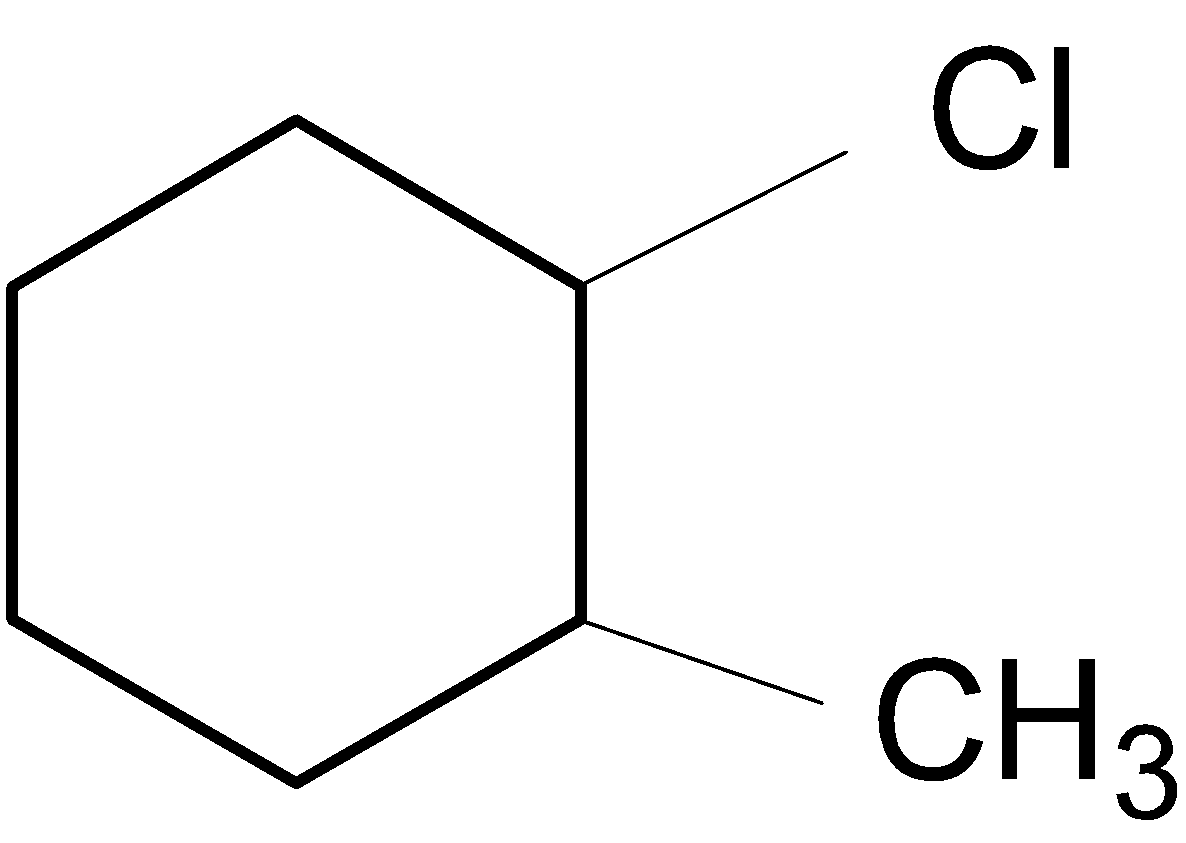
C.
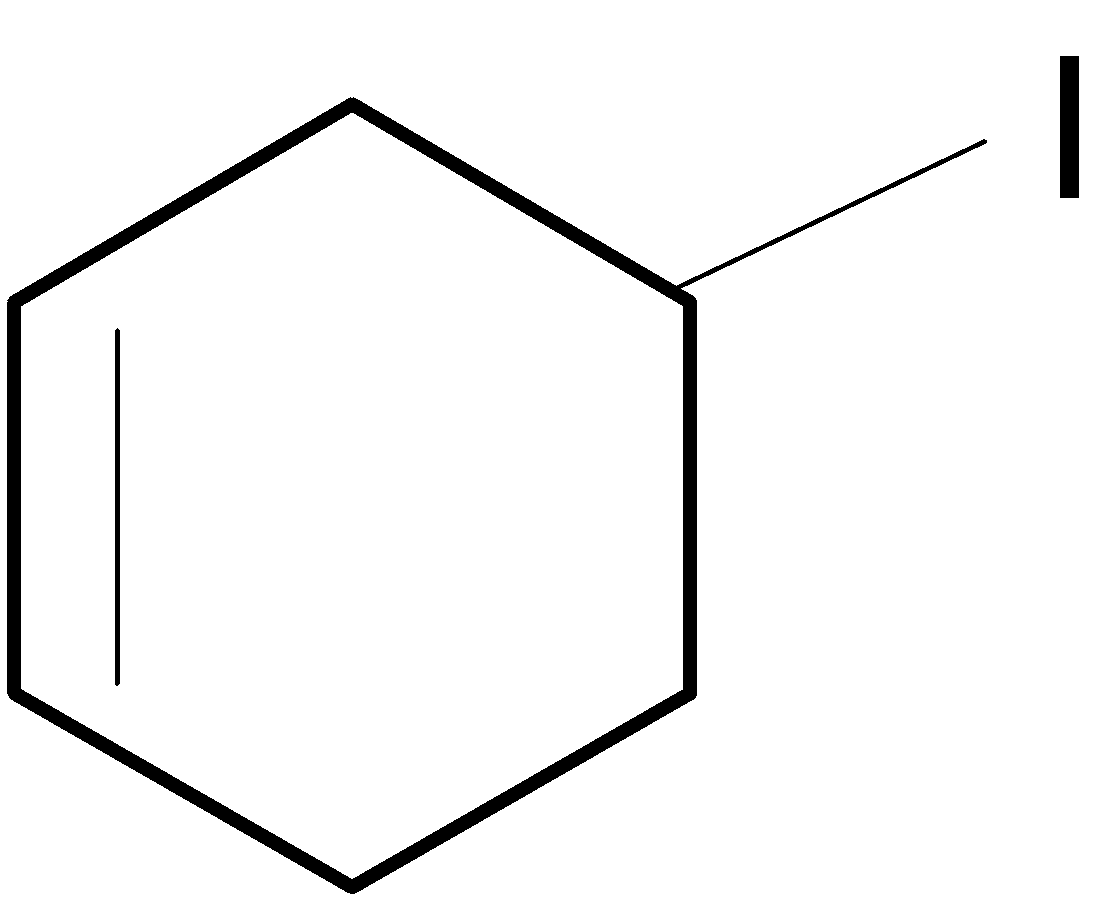
D. All of these
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: When reactants like alkyl halides undergo a reaction to form carbocation, carbocations are subject to a phenomenon named carbocation rearrangement. Carbocations are very reactive and consist of a positive charge on the central carbon atom with sextet instead of the octet. They are highly stabilised either by alkyl shift or hydride shift to form the most stable carbocation.
Complete step by step solution:
When the leaving group$(I)$ from the given alkyl halide, a carbocation is generated. A rearrangement can occur to form the most stable carbocation. Carbocation stability increases from tertiary to primary. These carbocations are stabilised by hyperconjugation and inductive effect. It is seen that a pair of electrons is transferred to the vacant p orbital on the carbocation through hydride or alkyl shift.
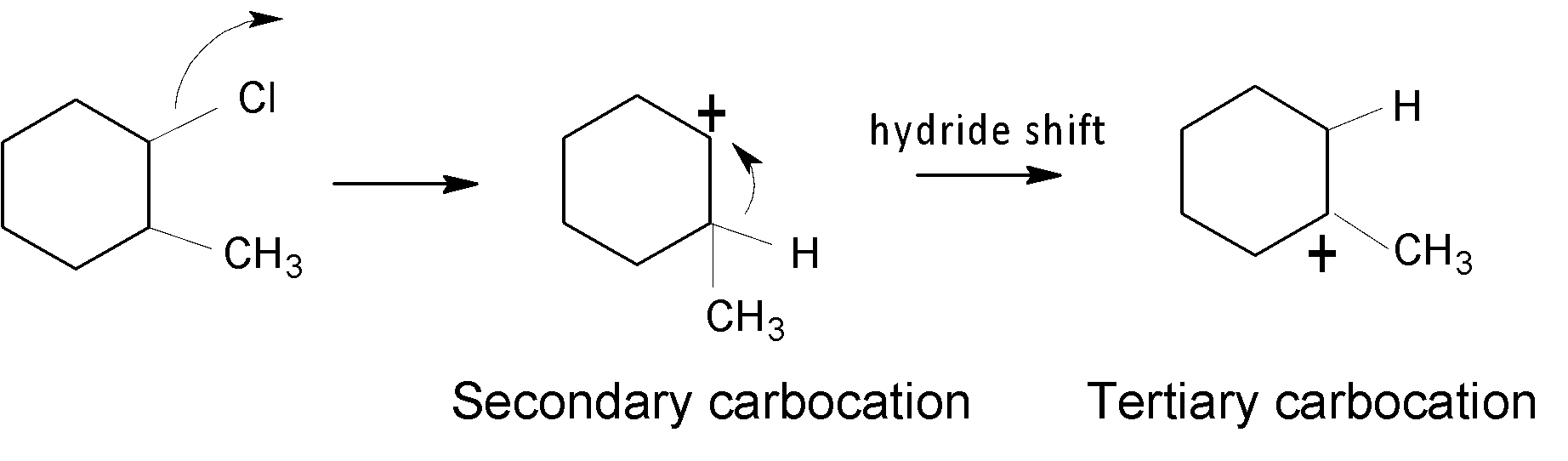
In the case of A, an alkyl group ($-C{{H}_{3}}$) is shifted to form a tertiary $({{3}^{{\mathrm O}}})$ carbocation, which is shown below:
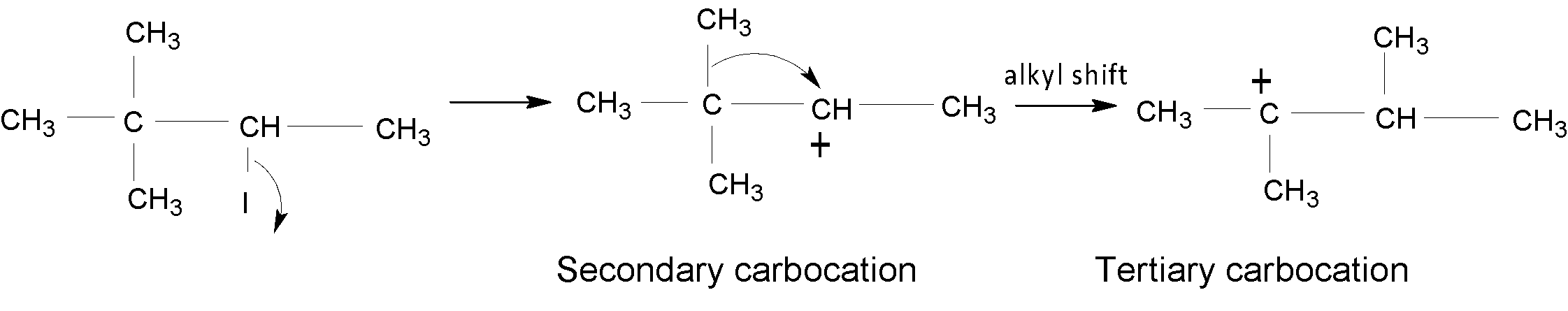
In the case of B, a hydride shift$(-H)$ takes place to form a stable ${{3}^{{\mathrm O}}}$ carbocation.
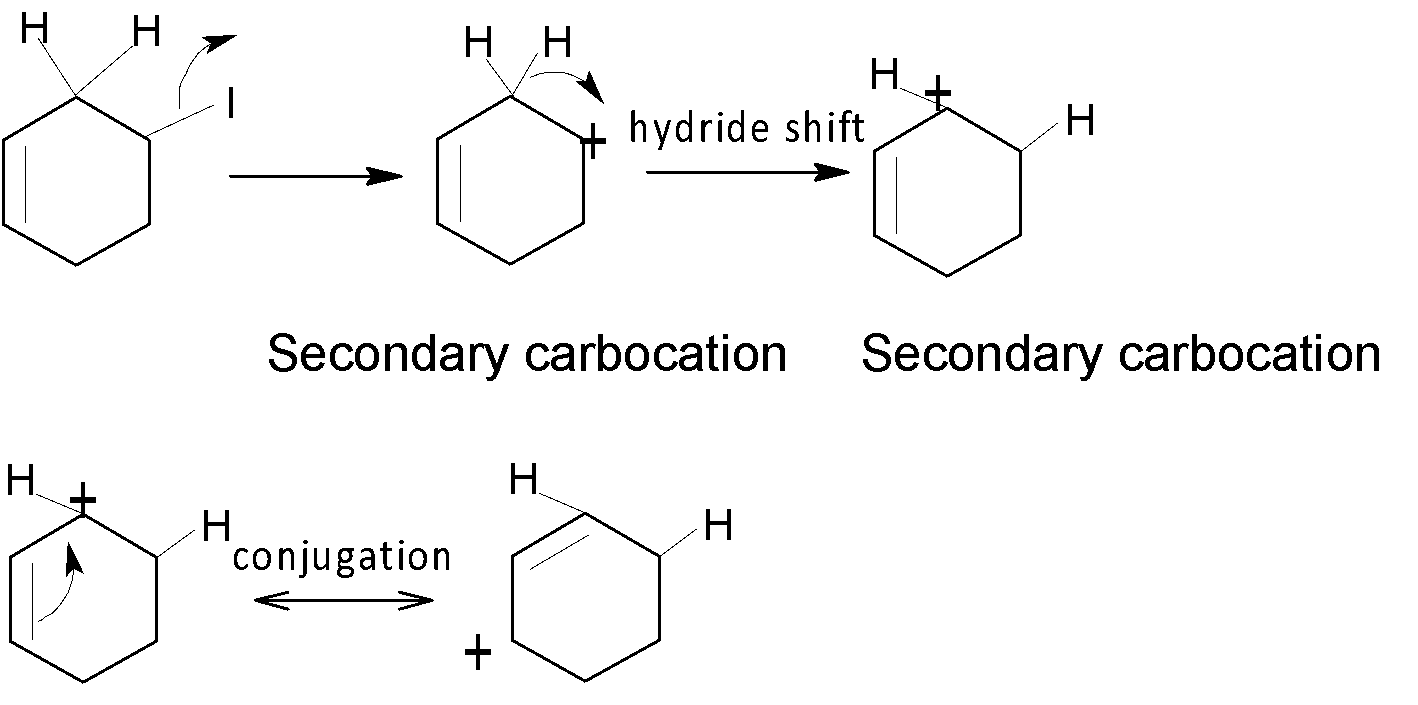
In the case of C, after shifting of the hydride group a secondary carbocation is generated which is then further stabilised by a nearest double bond and forms a most stable carbocation one which undergoes a rapid rearrangement reaction.
So, all of these compounds undergo rearrangement reactions via ${{S}_{{{N}^{1}}}}$
Hence, Option (D) is correct.
Note: The rate of ${{S}_{{{N}^{1}}}}$ reaction affects the stability of intermediate,strong leaving group and dielectric constants of solvent. The first step is ${{S}_{{{N}^{1}}}}$ reaction is carbocation formation and the rate of ${{S}_{{{N}^{1}}}}$ reaction is faster when the most stable carbocation is formed.
Complete step by step solution:
When the leaving group$(I)$ from the given alkyl halide, a carbocation is generated. A rearrangement can occur to form the most stable carbocation. Carbocation stability increases from tertiary to primary. These carbocations are stabilised by hyperconjugation and inductive effect. It is seen that a pair of electrons is transferred to the vacant p orbital on the carbocation through hydride or alkyl shift.
In the case of A, an alkyl group ($-C{{H}_{3}}$) is shifted to form a tertiary $({{3}^{{\mathrm O}}})$ carbocation, which is shown below:

In the case of B, a hydride shift$(-H)$ takes place to form a stable ${{3}^{{\mathrm O}}}$ carbocation.

In the case of C, after shifting of the hydride group a secondary carbocation is generated which is then further stabilised by a nearest double bond and forms a most stable carbocation one which undergoes a rapid rearrangement reaction.

So, all of these compounds undergo rearrangement reactions via ${{S}_{{{N}^{1}}}}$
Hence, Option (D) is correct.
Note: The rate of ${{S}_{{{N}^{1}}}}$ reaction affects the stability of intermediate,strong leaving group and dielectric constants of solvent. The first step is ${{S}_{{{N}^{1}}}}$ reaction is carbocation formation and the rate of ${{S}_{{{N}^{1}}}}$ reaction is faster when the most stable carbocation is formed.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




