
Which metal is used in Wurtz synthesis:
A. Ba
B. Al
C. Na
D. Fe
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Wurtz synthesis is a coupling reaction between two alkyl halides resulting in the formation of an alkane. The reaction proceeds via a free radical intermediate. A metal that can generate free radicals from alkyl halides is used as the catalyst.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In the Wurtz reaction, alkyl halides undergo a coupling reaction which results in the formation of an alkane. The alkane is formed out of the alkyl groups of the reactant alkyl halides being attached via a carbon-carbon bond.
This reaction can occur with two different alkyl halide molecules and with two molecules of the same alkyl halide, in which case, the resulting alkane will have twice the number of carbon atoms. The general scheme of this reaction is shown below:
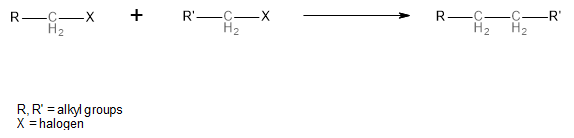
Image: The general scheme of the Wurtz reaction
The first step of the Wurtz reaction involves the formation of an alkyl radical from one of the alkyl halides. For this process to happen, there must be a metal catalyst that can donate a single electron and not become unstable. The metals of Group 1 (alkali metals) are perfect for this purpose because they have only 1 electron in their valence orbitals. When that electron is lost, the alkali metal cations attain a stable noble gas configuration.
The alkali metal used in the Wurtz reaction is sodium (\[Na\]). Shown below is the formation of an alkyl radical by sodium.

Image: Formation of the alkyl radical from an alkyl halide
Thus, option C is correct.
Note: The alkyl halide which gets converted into its radical is decided by the stability of the alkyl radical. It is advised that the student learns about the various factors governing the stability of reactive intermediates.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In the Wurtz reaction, alkyl halides undergo a coupling reaction which results in the formation of an alkane. The alkane is formed out of the alkyl groups of the reactant alkyl halides being attached via a carbon-carbon bond.
This reaction can occur with two different alkyl halide molecules and with two molecules of the same alkyl halide, in which case, the resulting alkane will have twice the number of carbon atoms. The general scheme of this reaction is shown below:
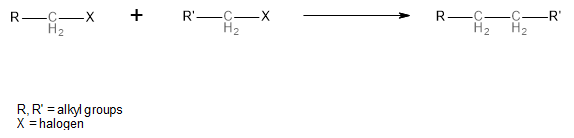
Image: The general scheme of the Wurtz reaction
The first step of the Wurtz reaction involves the formation of an alkyl radical from one of the alkyl halides. For this process to happen, there must be a metal catalyst that can donate a single electron and not become unstable. The metals of Group 1 (alkali metals) are perfect for this purpose because they have only 1 electron in their valence orbitals. When that electron is lost, the alkali metal cations attain a stable noble gas configuration.
The alkali metal used in the Wurtz reaction is sodium (\[Na\]). Shown below is the formation of an alkyl radical by sodium.

Image: Formation of the alkyl radical from an alkyl halide
Thus, option C is correct.
Note: The alkyl halide which gets converted into its radical is decided by the stability of the alkyl radical. It is advised that the student learns about the various factors governing the stability of reactive intermediates.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




