
Which contains hydrogen bonds?
(a) \[HF\]
(b) \[HCl\]
(c) \[HBr\] \[\]
(d) \[HI\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The hydrogen bond is formed between more electronegative elements and hydrogen atoms such as fluorine, oxygen, nitrogen, etc.,
Complete Step by Step Solution:
When a hydrogen atom is connected to highly electronegative elements then the formation of a hydrogen bond occurs. During the formation of hydrogen bonds, the electronegative atom has a partial negative charge whereas the hydrogen atom possesses a partial positive charge.
The main reason for the hydrogen bond is dipole-dipole interaction.
Type of hydrogen bond
Intermolecular hydrogen bond
When the hydrogen bond exists between two molecules is called an intermolecular hydrogen bond. Such a type of hydrogen bond is found in a carboxylic acid (Image 1).
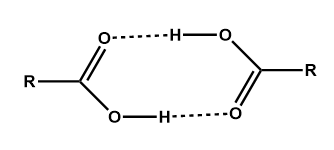
Image: Intermolecular hydrogen bond in a carboxylic acid.
Intramolecular hydrogen bond: When the formation of a hydrogen bond occurs in the same molecule then it is called an intramolecular hydrogen bond. Such a type of hydrogen bonding can be seen in nitro phenol (Image 2).
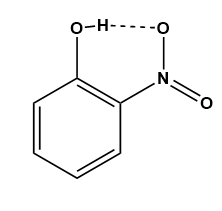
Image: Intramolecular hydrogen bond in nitrophenol.
As to the definition hydrogen bond is formed between the hydrogen atom and a more electronegative atom. Therefore, in the question, the fluorine atom is more electronegative than chlorine, bromine, and iodine. Hence the \[HF\] will contain a hydrogen bond.
Note: The hydrogen bond also increases the melting and boiling points of the compounds. The hydrogen bond also increases the solubility of compounds. The hydrogen bonding also increases the viscosity of the compounds. Hydrogen bonding is also present in nucleic acids. Which helps to bind two strands together. The folding in protein is arise due to hydrogen bonding.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
When a hydrogen atom is connected to highly electronegative elements then the formation of a hydrogen bond occurs. During the formation of hydrogen bonds, the electronegative atom has a partial negative charge whereas the hydrogen atom possesses a partial positive charge.
The main reason for the hydrogen bond is dipole-dipole interaction.
Type of hydrogen bond
Intermolecular hydrogen bond
When the hydrogen bond exists between two molecules is called an intermolecular hydrogen bond. Such a type of hydrogen bond is found in a carboxylic acid (Image 1).

Image: Intermolecular hydrogen bond in a carboxylic acid.
Intramolecular hydrogen bond: When the formation of a hydrogen bond occurs in the same molecule then it is called an intramolecular hydrogen bond. Such a type of hydrogen bonding can be seen in nitro phenol (Image 2).

Image: Intramolecular hydrogen bond in nitrophenol.
As to the definition hydrogen bond is formed between the hydrogen atom and a more electronegative atom. Therefore, in the question, the fluorine atom is more electronegative than chlorine, bromine, and iodine. Hence the \[HF\] will contain a hydrogen bond.
Note: The hydrogen bond also increases the melting and boiling points of the compounds. The hydrogen bond also increases the solubility of compounds. The hydrogen bonding also increases the viscosity of the compounds. Hydrogen bonding is also present in nucleic acids. Which helps to bind two strands together. The folding in protein is arise due to hydrogen bonding.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




