
Which chlorine atom is more electronegative in the following
A. \[C{H_3} - Cl\]
B. \[C{H_3} - C{H_2} - Cl\]
C. \[H - C Cl(C{H_3})_2\]
D. \[C{H_3} - C{H_2}C Cl(C{H_3})_2\]
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Electronegativity is defined as the tendency of an atom to attract the shared pair of electrons towards itself. If a more electronegative group is attached to $Cl$ then it will withdraw electron density from $Cl$ towards itself. For example, Fluorine. If a less electronegative element is attached to $Cl$ then $Cl$ will withdraw electron density from it. For example, metals
Complete step-by-step answer:Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract shared electrons toward itself and here in this problem chlorine, which is more electronegative than carbon is mentioned. Therefore with an increase in the number of the alkyl groups in the carbon center, the electron density increases gradually.
As we know $Cl$ tends to attract electrons from the attached bond with itself. From the four given options, we can see here the number of the alkyl group on the carbon center increases from compound A to D.
With increasing electron density on carbon chlorine attracts electron density towards itself, and as a result of electronegativity character also increases. In compound A, there is only one alkyl group, $-C{{H}_{3}}$ and in compound (B) only one $-{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}$ group is attached with carbon atom. so, here chlorine atom is not the most electronegative.
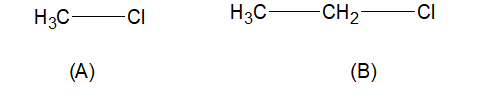
But compound (D) contains three alkyl groups (two $-C{{H}_{3}}$ and one $-{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}$ group) are attached with carbon atom, having (+I) effect, making it the most electronegative one than compound C (Containing two $-C{{H}_{3}}$ group).
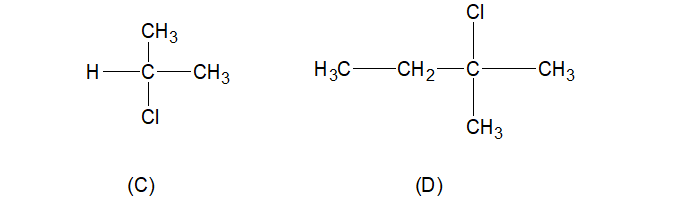
Option ‘D ’ is correct
Note: An element say X has some value of electronegativity say A. Then ${X^ + }$ will have a greater value of electronegativity than A. This is because the element X will pull more electron density to neutralize its positive charge. Contrary, ${X^ - }$ will have less electronegativity value than A because of the electron electron repulsion between the negative charge and the shared pair of electrons that the element will attract.
Complete step-by-step answer:Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract shared electrons toward itself and here in this problem chlorine, which is more electronegative than carbon is mentioned. Therefore with an increase in the number of the alkyl groups in the carbon center, the electron density increases gradually.
As we know $Cl$ tends to attract electrons from the attached bond with itself. From the four given options, we can see here the number of the alkyl group on the carbon center increases from compound A to D.
With increasing electron density on carbon chlorine attracts electron density towards itself, and as a result of electronegativity character also increases. In compound A, there is only one alkyl group, $-C{{H}_{3}}$ and in compound (B) only one $-{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}$ group is attached with carbon atom. so, here chlorine atom is not the most electronegative.
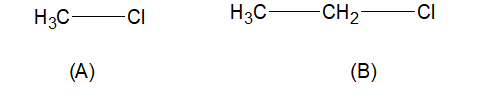
But compound (D) contains three alkyl groups (two $-C{{H}_{3}}$ and one $-{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}$ group) are attached with carbon atom, having (+I) effect, making it the most electronegative one than compound C (Containing two $-C{{H}_{3}}$ group).
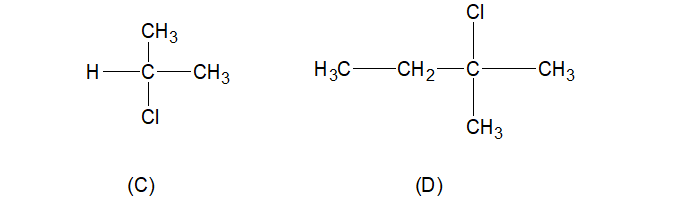
Option ‘D ’ is correct
Note: An element say X has some value of electronegativity say A. Then ${X^ + }$ will have a greater value of electronegativity than A. This is because the element X will pull more electron density to neutralize its positive charge. Contrary, ${X^ - }$ will have less electronegativity value than A because of the electron electron repulsion between the negative charge and the shared pair of electrons that the element will attract.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




