
What are the two types of flux?
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: A set of imaginary lines across which a physical substance travels is known as flux. In physics, there are two forms of important flux named as electric and magnetic flux.
Complete step by step solution:
(i) Electric flux: The Electric Flux is defined as the rate at which the electric field flows over a specific region, and it is proportional to the number of electric field lines that pass through a virtual surface. It is denoted by \[{\Phi _E}\]. When you turn on the mosquito repellent, you'll notice the scent after a while. As a result, the electric flux is represented by lines (electric field lines) of fragrance moving through the area of the room.
The following are some key terms in the concept of electric flux:
Some of the key phrases that are utilised in the notion of electric flux, and which must be understood in order to grasp the concept of electric flux. The following are the terms:
Electric Field: A field or area around a steady or moving charge in the form of a charged particle, or between two voltages, is known as an electric field. Other charged objects or particles in this space are also subjected to some force from this field, the intensity and type of which is determined by the charge a particle bears.
Electric Charge: In an electromagnetic field, it is a physical property of matter that leads it to experience a force. It also allows the particle to have its own electric field. The charge of an electron is -1, while the charge of a proton is +1. Neutrons have a charge of 0 and do not interfere with other electric charges.
Electric displacement field: The phrase electric displacement field, often known as electric induction, is a vector field that appears in Maxwell's equation and is symbolised by the letter 'D' in physics.
(ii) Magnetic flux: Magnetic flux is the total number of magnetic field lines travelling through a particular area normal to it.
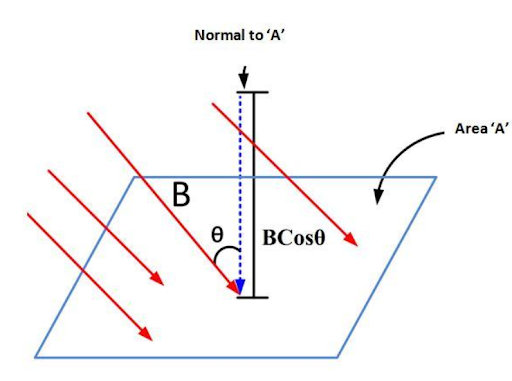
The dot product of the magnetic field 'B' and the Area vector 'A' is the magnetic flux.
\[{\Phi _M} = \overrightarrow B \cdot \overrightarrow A \]
Here, \[\overrightarrow B \] is the magnetic field vector and \[\overrightarrow A \] is the area vector.
In terms of magnitude, it is given as
\[{\Phi _M} = B\,A\,\,\cos \theta \]
Here, \[\theta \] is the angle between the magnetic field vector and the area vector.
Hence, the two types of flux are electric and magnetic flux.
Note: The magnetic flux has physical significance since it represents the entire amount of magnetic field that may pass through a certain area. It's a helpful tool for describing the effects of magnetic force on things in a specific location.
Complete step by step solution:
(i) Electric flux: The Electric Flux is defined as the rate at which the electric field flows over a specific region, and it is proportional to the number of electric field lines that pass through a virtual surface. It is denoted by \[{\Phi _E}\]. When you turn on the mosquito repellent, you'll notice the scent after a while. As a result, the electric flux is represented by lines (electric field lines) of fragrance moving through the area of the room.
The following are some key terms in the concept of electric flux:
Some of the key phrases that are utilised in the notion of electric flux, and which must be understood in order to grasp the concept of electric flux. The following are the terms:
Electric Field: A field or area around a steady or moving charge in the form of a charged particle, or between two voltages, is known as an electric field. Other charged objects or particles in this space are also subjected to some force from this field, the intensity and type of which is determined by the charge a particle bears.
Electric Charge: In an electromagnetic field, it is a physical property of matter that leads it to experience a force. It also allows the particle to have its own electric field. The charge of an electron is -1, while the charge of a proton is +1. Neutrons have a charge of 0 and do not interfere with other electric charges.
Electric displacement field: The phrase electric displacement field, often known as electric induction, is a vector field that appears in Maxwell's equation and is symbolised by the letter 'D' in physics.
(ii) Magnetic flux: Magnetic flux is the total number of magnetic field lines travelling through a particular area normal to it.

The dot product of the magnetic field 'B' and the Area vector 'A' is the magnetic flux.
\[{\Phi _M} = \overrightarrow B \cdot \overrightarrow A \]
Here, \[\overrightarrow B \] is the magnetic field vector and \[\overrightarrow A \] is the area vector.
In terms of magnitude, it is given as
\[{\Phi _M} = B\,A\,\,\cos \theta \]
Here, \[\theta \] is the angle between the magnetic field vector and the area vector.
Hence, the two types of flux are electric and magnetic flux.
Note: The magnetic flux has physical significance since it represents the entire amount of magnetic field that may pass through a certain area. It's a helpful tool for describing the effects of magnetic force on things in a specific location.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




