
Two stars of masses $m_1$ and $m_2$ are in mutual interaction and revolving in orbits of radii $r_1$ and $r_2$ respectively. The time period of revolution for this system will be?
a. $2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{{{({{r}_{1}}-{{r}_{2}})}^{3}}}{G({{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}})}}$
b. $2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{{{({{r}_{1}}+{{r}_{2}})}^{3}}}{G({{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}})}}$
c. $2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{{{({{r}_{1}}-{{r}_{2}})}^{3}}}{G({{m}_{1}}-{{m}_{2}})}}$
d.$2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{{{({{r}_{1}}+{{r}_{2}})}^{3}}}{G({{m}_{1}}-{{m}_{2}})}}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The binary star system's mass is concentrated at the point around which the masses move. The mass and radius of one star in a binary star system are equal because of the centre of mass's property, which also states that the mass and radius of the other star are identical. Additionally, the centripetal force exerted on each star by the other star in the binary star system is equal to the gravitational force between the two stars.
Complete answer:
Kepler’s laws of planetary motion
“Each planet travels in an elliptical orbit around the sun, which is at one of the ellipse's foci.”
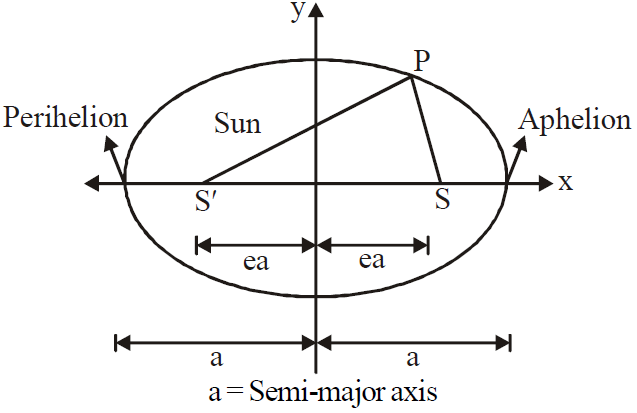
A planet with mass m orbiting the sun in an elliptical pattern. At one of the ellipse's foci, S′, is the mass M sun. S is the other emphasis, and it's in a blank area. A semi major axis of the ellipse, the perihelion (the distance closest to the sun) distance rmin., and the aphelion (the distance farthest from the sun) distance $r_{max}$. are also displayed. Each focus is at a distance 'ea' from the ellipse's centre.
${r_{max}} = a + e a = \left(1 + e\right) a$
${r_{min}} = a – e a = \left(1 – e\right) a$
Each focus's separation from the ellipse's centre is measured in units of ea, where e is the eccentricity, a dimensionless quantity that ranges from 0 to 1. The ellipse is a circle if e = 0.
E = 0.017 for the earth.
Let ${{r}_{1}}$and ${{r}_{2}}$ be the distances of the stars from the center of mass.
We can write,
$({{r}_{1}}+{{r}_{2}})=r$,
The gravitational force of attraction provides the centripetal force for revolution about the centre.
$\dfrac{G{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}={{m}_{1}}{{r}_{1}}{{\omega }^{2}}$
And
$\dfrac{G{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}={{m}_{2}}{{r}_{2}}{{\omega }^{2}}$
So, the angular velocities can be expressed as follows:
${{\omega }^{2}}=\dfrac{G{{m}_{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}{{r}_{1}}}=\dfrac{G{{m}_{1}}}{{{r}^{2}}{{r}_{2}}}$
for the entire system:
$\omega =\dfrac{G({{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}})}{{{r}^{2}}({{r}_{1}}+{{r}_{2}})}=\dfrac{G({{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}})}{{{r}^{3}}}$
This is where the expression of the revolutionary era can be found.
$T=\dfrac{2\pi }{\omega }=2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{{{r}^{3}}}{G({{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}})}}$
$T=2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{{{r}^{3}}}{G({{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}})}}$
$T=2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{{{({{r}_{1}}+{{r}_{2}})}^{3}}}{G({{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}})}}$
Hence, option (b) is correct.
Note: A major turning point in the evolution from geocentrism to heliocentrism is represented by Kepler's laws of planetary motion. The first quantifiable link between the planets, including earth, is provided by them. They also represent a period when the big issues of the day were changing.
Complete answer:
Kepler’s laws of planetary motion
“Each planet travels in an elliptical orbit around the sun, which is at one of the ellipse's foci.”

A planet with mass m orbiting the sun in an elliptical pattern. At one of the ellipse's foci, S′, is the mass M sun. S is the other emphasis, and it's in a blank area. A semi major axis of the ellipse, the perihelion (the distance closest to the sun) distance rmin., and the aphelion (the distance farthest from the sun) distance $r_{max}$. are also displayed. Each focus is at a distance 'ea' from the ellipse's centre.
${r_{max}} = a + e a = \left(1 + e\right) a$
${r_{min}} = a – e a = \left(1 – e\right) a$
Each focus's separation from the ellipse's centre is measured in units of ea, where e is the eccentricity, a dimensionless quantity that ranges from 0 to 1. The ellipse is a circle if e = 0.
E = 0.017 for the earth.
Let ${{r}_{1}}$and ${{r}_{2}}$ be the distances of the stars from the center of mass.
We can write,
$({{r}_{1}}+{{r}_{2}})=r$,
The gravitational force of attraction provides the centripetal force for revolution about the centre.
$\dfrac{G{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}={{m}_{1}}{{r}_{1}}{{\omega }^{2}}$
And
$\dfrac{G{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}={{m}_{2}}{{r}_{2}}{{\omega }^{2}}$
So, the angular velocities can be expressed as follows:
${{\omega }^{2}}=\dfrac{G{{m}_{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}{{r}_{1}}}=\dfrac{G{{m}_{1}}}{{{r}^{2}}{{r}_{2}}}$
for the entire system:
$\omega =\dfrac{G({{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}})}{{{r}^{2}}({{r}_{1}}+{{r}_{2}})}=\dfrac{G({{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}})}{{{r}^{3}}}$
This is where the expression of the revolutionary era can be found.
$T=\dfrac{2\pi }{\omega }=2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{{{r}^{3}}}{G({{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}})}}$
$T=2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{{{r}^{3}}}{G({{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}})}}$
$T=2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{{{({{r}_{1}}+{{r}_{2}})}^{3}}}{G({{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}})}}$
Hence, option (b) is correct.
Note: A major turning point in the evolution from geocentrism to heliocentrism is represented by Kepler's laws of planetary motion. The first quantifiable link between the planets, including earth, is provided by them. They also represent a period when the big issues of the day were changing.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




