
Two similar bar Magnets $P$ and $Q$ each of magnetic moment $M$ are taken. If $P$ is cut along its axial line and $Q$ along its equatorial line all the four pieces obtained have each of
A. Equal pole strength
B. Magnetic Moment $\dfrac{M}{4}$
C. Magnetic Moment $\dfrac{M}{2}$
D. Magnetic Moment $M$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint:
When a bar magnet is cut into two equal halves, each tiny magnet behaves like a magnet and has both the north and south pole. It is found that the magnetic field due to a tiny bar magnet at any point along its axial line is twice the magnetic field at a point along the equatorial line with the same distance.
Formula used:
The formula used to solve this question is given as follows: -
Magnetic dipole moment, $M = ml$
Complete step by step solution:
Initially, the magnetic moment of $P$ and $Q$ is $M$ (given)
We know that $M = ml$ is the magnetic dipole moment of a bar magnet.
Where m = pole strength and l = length of a bar magnet
Now, for magnet $P$, when it is cut along its axial line length remains the same but pole strength becomes halved as: -
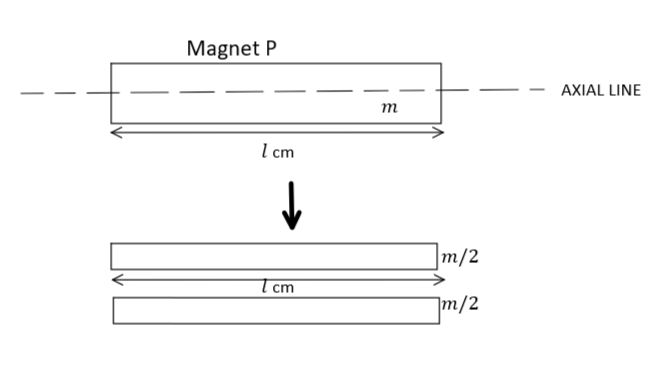
Therefore, in this case, magnetic moment will be: ${M_P} = \left( {\dfrac{m}{2}} \right)l = \dfrac{{ml}}{2} = \dfrac{M}{2}$ $\left( {\therefore M = ml} \right)$
Now, for magnet $Q$, when it is cut along its equatorial line pole strength remains the same but length becomes halved as: -
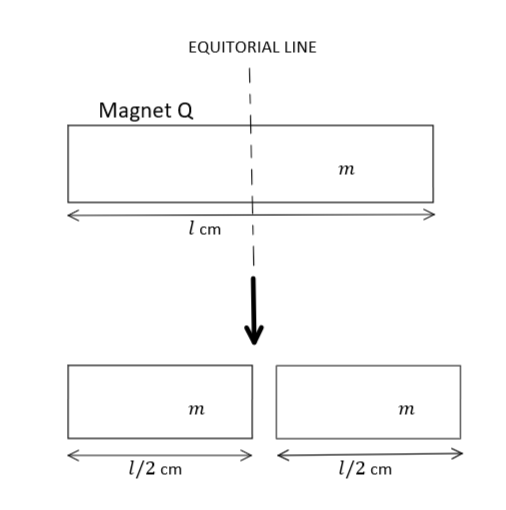
Therefore, in this case, magnetic moment will be: ${M_Q} = m\left( {\dfrac{l}{2}} \right) = \dfrac{{ml}}{2} = \dfrac{M}{2}$
Thus, when the two magnets $P$ and $Q$ is cut according to the question, the resulting magnetic moment of both the magnets will become ${M_P} = {M_Q} = \dfrac{M}{2}$.
Hence, the correct option is (C) Magnetic Moment $\dfrac{M}{2}$.
Therefore, the correct option is C.
Note:
Since this is a problem related to a uniform magnetic field and magnetic dipole moment hence, we should always remember that the direction of magnetic field is the same direction as that of magnetic dipole moment vector due to tiny bar magnet.
When a bar magnet is cut into two equal halves, each tiny magnet behaves like a magnet and has both the north and south pole. It is found that the magnetic field due to a tiny bar magnet at any point along its axial line is twice the magnetic field at a point along the equatorial line with the same distance.
Formula used:
The formula used to solve this question is given as follows: -
Magnetic dipole moment, $M = ml$
Complete step by step solution:
Initially, the magnetic moment of $P$ and $Q$ is $M$ (given)
We know that $M = ml$ is the magnetic dipole moment of a bar magnet.
Where m = pole strength and l = length of a bar magnet
Now, for magnet $P$, when it is cut along its axial line length remains the same but pole strength becomes halved as: -

Therefore, in this case, magnetic moment will be: ${M_P} = \left( {\dfrac{m}{2}} \right)l = \dfrac{{ml}}{2} = \dfrac{M}{2}$ $\left( {\therefore M = ml} \right)$
Now, for magnet $Q$, when it is cut along its equatorial line pole strength remains the same but length becomes halved as: -

Therefore, in this case, magnetic moment will be: ${M_Q} = m\left( {\dfrac{l}{2}} \right) = \dfrac{{ml}}{2} = \dfrac{M}{2}$
Thus, when the two magnets $P$ and $Q$ is cut according to the question, the resulting magnetic moment of both the magnets will become ${M_P} = {M_Q} = \dfrac{M}{2}$.
Hence, the correct option is (C) Magnetic Moment $\dfrac{M}{2}$.
Therefore, the correct option is C.
Note:
Since this is a problem related to a uniform magnetic field and magnetic dipole moment hence, we should always remember that the direction of magnetic field is the same direction as that of magnetic dipole moment vector due to tiny bar magnet.
Recently Updated Pages
Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Amino Acids and Peptides Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding important Concepts and Tips

Electricity and Magnetism Explained: Key Concepts & Applications

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




