
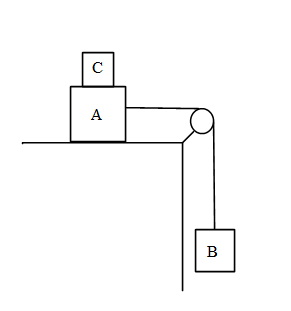
Two masses A and B of 10 kg and 5 kg respectively are connected with a string passing over a frictionless pulley fixed at the corner of a table as in figure. The coefficient of friction of A with the table is 0.2. The minimum mass of C that may be placed on A to prevent it from moving is equal to:
A) 20 kg.
B) 15 kg.
C) 10 kg.
D) 5 kg.
E) 0 kg.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The friction is the resistive force which stops the movement of the body. The friction depends upon the coefficient of friction which is constant for a material and also it depends upon the roughness of the surface.
Formula used:
The formula of the weight is equal to,
$ \Rightarrow W = mg$
Where mass is m and acceleration due to gravity is g.
The formula of the friction is given by,
$ \Rightarrow f = \mu \times R$
Where the coefficient of friction is $\mu $ and the normal reaction is R.
Complete step by step solution:
In this problem it is given that two masses A and B of 10 kg and 5 kg respectively are connected with a string passing over a frictionless pulley fixed at the corner of a table as in figure the coefficient of friction of A with the table is 0.2 and we need to find the minimum mass of C that may be placed on A to prevent it from moving.
The free body diagram of the system.
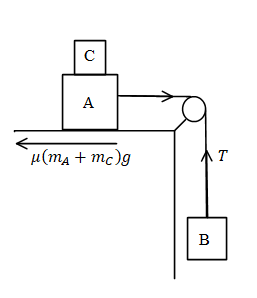
The tension in the string is equal to,
$ \Rightarrow T = {m_B}g$
$ \Rightarrow T = 5 \times 10$
$ \Rightarrow T = 50N$
The force that the combination of block A and C is 50 N.
$ \Rightarrow T = \mu \left( {{m_A} + {m_B}} \right)g$
$ \Rightarrow T = 0 \cdot 2 \times \left( {10 + {m_B}} \right) \times 10$
$ \Rightarrow T = 2 \times \left( {10 + {m_B}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow T = 20 + 2{m_B}$
$ \Rightarrow 50 = 20 + 2{m_B}$
$ \Rightarrow 2{m_B} = 30$
$ \Rightarrow {m_B} = 15kg$
The minimum mass of the block B is equal to 15kg.
The correct answer for this problem is option B.
Note: The students are advised to understand and remember the formula of the friction and also the formula of the weight. The friction force should be equal to the tension of the string so that the combination of block A and C doesn’t move.
Formula used:
The formula of the weight is equal to,
$ \Rightarrow W = mg$
Where mass is m and acceleration due to gravity is g.
The formula of the friction is given by,
$ \Rightarrow f = \mu \times R$
Where the coefficient of friction is $\mu $ and the normal reaction is R.
Complete step by step solution:
In this problem it is given that two masses A and B of 10 kg and 5 kg respectively are connected with a string passing over a frictionless pulley fixed at the corner of a table as in figure the coefficient of friction of A with the table is 0.2 and we need to find the minimum mass of C that may be placed on A to prevent it from moving.
The free body diagram of the system.

The tension in the string is equal to,
$ \Rightarrow T = {m_B}g$
$ \Rightarrow T = 5 \times 10$
$ \Rightarrow T = 50N$
The force that the combination of block A and C is 50 N.
$ \Rightarrow T = \mu \left( {{m_A} + {m_B}} \right)g$
$ \Rightarrow T = 0 \cdot 2 \times \left( {10 + {m_B}} \right) \times 10$
$ \Rightarrow T = 2 \times \left( {10 + {m_B}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow T = 20 + 2{m_B}$
$ \Rightarrow 50 = 20 + 2{m_B}$
$ \Rightarrow 2{m_B} = 30$
$ \Rightarrow {m_B} = 15kg$
The minimum mass of the block B is equal to 15kg.
The correct answer for this problem is option B.
Note: The students are advised to understand and remember the formula of the friction and also the formula of the weight. The friction force should be equal to the tension of the string so that the combination of block A and C doesn’t move.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




