
Two bodies of the same mass are moving with the same speed, but in different directions in a plane. They have a completely inelastic collision and move together thereafter with a final speed which is half of their initial speed. The angle between the initial velocities of the two bodies (in degree) is ________.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: We are given two bodies having the same mass moving with same velocity but in different directions in a single plane. After having an inelastic collision, they have a final speed which is half of the initial speed. We have to find the angle between the initial velocities of the two bodies. We will be using conservation of momentum to find out.
Complete step by step solution:
Let the two bodies have \[m\] and velocity \[v\]. Let the angle made by their initial velocities be \[\theta \]and let the final velocity be \[V\]. Let us first draw a figure, that is representing the scenario given in question
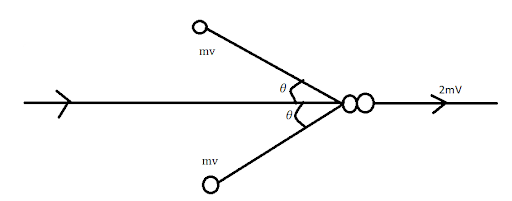
Here it is given that
\[V = \dfrac{v}{2}\]
On applying conservation of momentum on \[x\]axis, we get
\[mv\cos \theta + mv\cos \theta = 2mV \\ \Rightarrow 2mv\cos \theta = 2m\dfrac{v}{2} \\ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = \dfrac{1}{2} \\ \Rightarrow \theta = {60^ \circ } \]
The angle between initial velocities is
\[2\theta = 2 \times 60 = {120^ \circ } \\ \]
Therefore the angle between initial velocities of two bodies is \[{120^ \circ }\].
Note: Students may make mistakes while applying the conservation of momentum. Instead of cosine, they may use sine which is wrong. While applying conservation of momentum, we have taken values of momentum for two bodies on the \[x\] axis, so in our equation the cosine term came. Students should not get confused over here as it is known for a line making angle with axes, on \[x\] axis , cosine comes and on \[y\] axis, sine comes.
Complete step by step solution:
Let the two bodies have \[m\] and velocity \[v\]. Let the angle made by their initial velocities be \[\theta \]and let the final velocity be \[V\]. Let us first draw a figure, that is representing the scenario given in question

Here it is given that
\[V = \dfrac{v}{2}\]
On applying conservation of momentum on \[x\]axis, we get
\[mv\cos \theta + mv\cos \theta = 2mV \\ \Rightarrow 2mv\cos \theta = 2m\dfrac{v}{2} \\ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = \dfrac{1}{2} \\ \Rightarrow \theta = {60^ \circ } \]
The angle between initial velocities is
\[2\theta = 2 \times 60 = {120^ \circ } \\ \]
Therefore the angle between initial velocities of two bodies is \[{120^ \circ }\].
Note: Students may make mistakes while applying the conservation of momentum. Instead of cosine, they may use sine which is wrong. While applying conservation of momentum, we have taken values of momentum for two bodies on the \[x\] axis, so in our equation the cosine term came. Students should not get confused over here as it is known for a line making angle with axes, on \[x\] axis , cosine comes and on \[y\] axis, sine comes.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




