
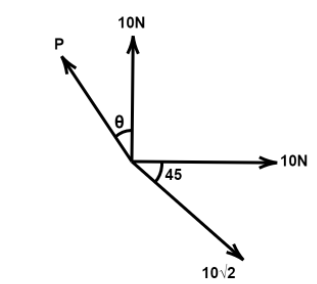
Three vectors acts at a point O as shown in the figure, for the given values of P and $\theta $ the correct options are:-
(A) Resultant is null vector if $\theta = 0,P = 10\sqrt 2 $
(B) Resultant is $10N$if$\theta = 90^\circ,P = 10N$
(C) Resultant is $30\hat iN$if $\theta = \dfrac{{3\pi }}{2},P = 10N$in magnitude
(D) All are correct.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint A vector can be resolved into its components along the x and y axes. When they lie on the same axis, the vectors can be added or subtracted like normal numbers. The resultant of a vector can be found by adding two vectors.
Complete step by step solution
From the figure, it is clear that all the three vectors lie in a 2D plane. The correct option can be found by putting the value of P and $\theta $in each option. Suppose a vector makes angle $\theta $from an axis then the two components of this vector can be found by-
Multiplying the magnitude of the vector with the cos of the angle it makes with the axis. (for the base axis)
Multiplying the magnitude of the vector with the sin of the angle it makes with the axis. (for the perpendicular axis)
Resultant of two vectors is given by-
$\Rightarrow$ $\left| {\vec R} \right| = \sqrt {{{\vec A}^2} + {{\vec B}^2} + 2AB\cos \theta } $
For two perpendicular vectors, $\cos 90^\circ = 0$
$\left| {\vec R} \right| = \sqrt {{{\vec A}^2} + {{\vec B}^2}} $
For A, $\theta = 0,P = 10\sqrt 2 $
The first step is to resolve all the components into $\hat i$ and $\hat j$components. Let those values be $x$ and $y$respectively. Then,
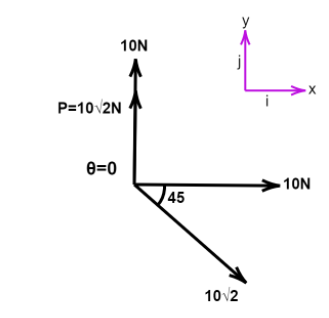
$\Rightarrow$ $x\hat i = 10\hat i + 10\sqrt 2 \cos 45^\circ \hat i$
$\Rightarrow$ $\left\{ {\cos 45^\circ = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right\}$
$\Rightarrow$ $x\hat i = 10\hat i + 10\hat i = 20\hat i$
$y\hat j = 10\hat j + 10\sqrt 2 \hat j - 10\sqrt 2 \sin 45^\circ $
$\Rightarrow$ $y\hat j = 10\sqrt 2 \hat j$
$\Rightarrow$ $\left\{ {\sin 45^\circ = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right\}$
Resultant $\vec R = \sqrt {{{(x\hat i)}^2} + {{(y\hat j)}^2}} $
$\Rightarrow$ $\vec R = \sqrt {{{(20\hat i)}^2} + {{(10\sqrt 2 \hat j)}^2}} $
$\Rightarrow$ $\vec R = \sqrt {400 + 200} $
$\vec R = \sqrt {600} = 10\sqrt 6 $
Resultant is not a null vector, statement is false.
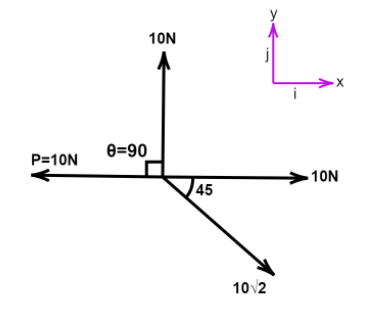
For B, $\theta = 90^\circ,P = 10N$
$x\hat i = 10\hat i + 10\sqrt 2 \cos 45^\circ \hat i - 10\hat i$
$\Rightarrow$ $\left\{ {\cos 45^\circ = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right\}$
$\Rightarrow$ $x\hat i = 10\hat i + 10\hat i - 10\hat i = 10\hat i$
$\Rightarrow$ $y\hat j = 10\hat j - 10\sqrt 2 \sin 45^\circ \hat j$
$\left\{ {\sin 45^\circ = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right\}$
$y\hat j = 10\hat j - 10\hat j$
$y\hat j = 0$
Resultant, $\vec R = \sqrt {{{(x\hat i)}^2} + {{(y\hat j)}^2}} $
$\Rightarrow$ $\vec R = \sqrt {{{(10\hat i)}^2} + {{(0\hat j)}^2} + } $
$\Rightarrow$ $\vec R = \sqrt {100} $
$\vec R = 10$
Resultant is $10N$, statement is true.

For C, $\theta = \dfrac{{3\pi }}{2},P = 10N$
$\Rightarrow$ $x\hat i = 10\hat i + 10\sqrt 2 \cos 45^\circ \hat i + 10\hat i$ $\Rightarrow$ $\left\{ {\cos 45^\circ = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right\}$
$\Rightarrow$ $x\hat i = 10\hat i + 10\hat i + 10\hat i = 30\hat i$
$y\hat j = 10\hat j - 10\sqrt 2 \sin 45^\circ \hat j$
$\left\{ {\sin 45^\circ = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right\}$
$y\hat j = 10\hat j - 10\hat j = 0$
Resultant, $\vec R = \sqrt {{{(x\hat i)}^2} + {{(y\hat j)}^2}} $
$\Rightarrow$ $\vec R = \sqrt {{{(30\hat i)}^2} + {{(0\hat j)}^2}} $
$\Rightarrow$ $\vec R = \sqrt {900} = 30$
Resultant is $30N$, since all the other components get cancelled out, the direction of this vector is on along x axis or $\hat i$, this statement is also true.
Hence the correct answers are option (B) and (C)
Note To find the resultant of multiple vectors, the best method is to resolve them into their x, y and z components and then find the resultant, this reduces the extra steps which would otherwise be required to find the angle made by the intermediate resultant vectors in the procedure.
Complete step by step solution
From the figure, it is clear that all the three vectors lie in a 2D plane. The correct option can be found by putting the value of P and $\theta $in each option. Suppose a vector makes angle $\theta $from an axis then the two components of this vector can be found by-
Multiplying the magnitude of the vector with the cos of the angle it makes with the axis. (for the base axis)
Multiplying the magnitude of the vector with the sin of the angle it makes with the axis. (for the perpendicular axis)
Resultant of two vectors is given by-
$\Rightarrow$ $\left| {\vec R} \right| = \sqrt {{{\vec A}^2} + {{\vec B}^2} + 2AB\cos \theta } $
For two perpendicular vectors, $\cos 90^\circ = 0$
$\left| {\vec R} \right| = \sqrt {{{\vec A}^2} + {{\vec B}^2}} $
For A, $\theta = 0,P = 10\sqrt 2 $
The first step is to resolve all the components into $\hat i$ and $\hat j$components. Let those values be $x$ and $y$respectively. Then,

$\Rightarrow$ $x\hat i = 10\hat i + 10\sqrt 2 \cos 45^\circ \hat i$
$\Rightarrow$ $\left\{ {\cos 45^\circ = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right\}$
$\Rightarrow$ $x\hat i = 10\hat i + 10\hat i = 20\hat i$
$y\hat j = 10\hat j + 10\sqrt 2 \hat j - 10\sqrt 2 \sin 45^\circ $
$\Rightarrow$ $y\hat j = 10\sqrt 2 \hat j$
$\Rightarrow$ $\left\{ {\sin 45^\circ = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right\}$
Resultant $\vec R = \sqrt {{{(x\hat i)}^2} + {{(y\hat j)}^2}} $
$\Rightarrow$ $\vec R = \sqrt {{{(20\hat i)}^2} + {{(10\sqrt 2 \hat j)}^2}} $
$\Rightarrow$ $\vec R = \sqrt {400 + 200} $
$\vec R = \sqrt {600} = 10\sqrt 6 $
Resultant is not a null vector, statement is false.

For B, $\theta = 90^\circ,P = 10N$
$x\hat i = 10\hat i + 10\sqrt 2 \cos 45^\circ \hat i - 10\hat i$
$\Rightarrow$ $\left\{ {\cos 45^\circ = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right\}$
$\Rightarrow$ $x\hat i = 10\hat i + 10\hat i - 10\hat i = 10\hat i$
$\Rightarrow$ $y\hat j = 10\hat j - 10\sqrt 2 \sin 45^\circ \hat j$
$\left\{ {\sin 45^\circ = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right\}$
$y\hat j = 10\hat j - 10\hat j$
$y\hat j = 0$
Resultant, $\vec R = \sqrt {{{(x\hat i)}^2} + {{(y\hat j)}^2}} $
$\Rightarrow$ $\vec R = \sqrt {{{(10\hat i)}^2} + {{(0\hat j)}^2} + } $
$\Rightarrow$ $\vec R = \sqrt {100} $
$\vec R = 10$
Resultant is $10N$, statement is true.

For C, $\theta = \dfrac{{3\pi }}{2},P = 10N$
$\Rightarrow$ $x\hat i = 10\hat i + 10\sqrt 2 \cos 45^\circ \hat i + 10\hat i$ $\Rightarrow$ $\left\{ {\cos 45^\circ = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right\}$
$\Rightarrow$ $x\hat i = 10\hat i + 10\hat i + 10\hat i = 30\hat i$
$y\hat j = 10\hat j - 10\sqrt 2 \sin 45^\circ \hat j$
$\left\{ {\sin 45^\circ = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right\}$
$y\hat j = 10\hat j - 10\hat j = 0$
Resultant, $\vec R = \sqrt {{{(x\hat i)}^2} + {{(y\hat j)}^2}} $
$\Rightarrow$ $\vec R = \sqrt {{{(30\hat i)}^2} + {{(0\hat j)}^2}} $
$\Rightarrow$ $\vec R = \sqrt {900} = 30$
Resultant is $30N$, since all the other components get cancelled out, the direction of this vector is on along x axis or $\hat i$, this statement is also true.
Hence the correct answers are option (B) and (C)
Note To find the resultant of multiple vectors, the best method is to resolve them into their x, y and z components and then find the resultant, this reduces the extra steps which would otherwise be required to find the angle made by the intermediate resultant vectors in the procedure.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




