
The working of an atomizer depends upon
A. Pascal’s law
B. Bernoulli’s theorem
C. Archimedes principle
D. Boyle’s law
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The Bernoulli’s theorem states that for the streamline flow of an ideal liquid, the total energy of the pressure energy, potential energy and the kinetic energy per unit mass is constant throughout the flow of the liquid.
Complete step by step solution:
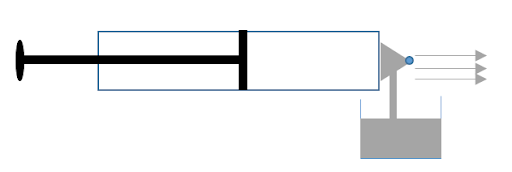
Image: The cross-section of atomizer
According to Bernoulli's theorem, when a liquid is flowing through the frictionless tube then the total energy per unit mass of the liquid is constant throughout the flow of the liquid. The total energy of the flowing liquid is the sum of the potential energy, the pressure energy and the kinetic energy.
\[\dfrac{P}{\rho } + gh + \dfrac{1}{2}{v^2} = C\]
Here, C is the constant.
When the piston is pushed inside the cylinder, the air trapped inside the cylinder starts flowing from higher pressure to lower pressure region with high speed. When it is passing through the tube with high speed, it reaches the point where a pipe is dipped inside the container of liquid which needs to be sprayed, creating a region of low pressure above the liquid.
As we know that the flow of fluid takes place from higher pressure to lower pressure, so the liquid kept in the container got sucked upward and it got sprayed out through the nozzle connected at the end of the cylinder. Hence, the principle which the spray of atomizer is following is Bernoulli’s theorem of conservation of energy.
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note: Some other applications of Bernoulli's theorem is action of carburettor, paint-gun, water-spray in saloons. The flow of the liquid from the container to the exit point of the atomizer also follows the same principle. While the liquid rises in the tube, the gravitational potential energy increases but the pressure energy decreases, which get converted to the kinetic energy of the fluid droplets.
Complete step by step solution:

Image: The cross-section of atomizer
According to Bernoulli's theorem, when a liquid is flowing through the frictionless tube then the total energy per unit mass of the liquid is constant throughout the flow of the liquid. The total energy of the flowing liquid is the sum of the potential energy, the pressure energy and the kinetic energy.
\[\dfrac{P}{\rho } + gh + \dfrac{1}{2}{v^2} = C\]
Here, C is the constant.
When the piston is pushed inside the cylinder, the air trapped inside the cylinder starts flowing from higher pressure to lower pressure region with high speed. When it is passing through the tube with high speed, it reaches the point where a pipe is dipped inside the container of liquid which needs to be sprayed, creating a region of low pressure above the liquid.
As we know that the flow of fluid takes place from higher pressure to lower pressure, so the liquid kept in the container got sucked upward and it got sprayed out through the nozzle connected at the end of the cylinder. Hence, the principle which the spray of atomizer is following is Bernoulli’s theorem of conservation of energy.
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note: Some other applications of Bernoulli's theorem is action of carburettor, paint-gun, water-spray in saloons. The flow of the liquid from the container to the exit point of the atomizer also follows the same principle. While the liquid rises in the tube, the gravitational potential energy increases but the pressure energy decreases, which get converted to the kinetic energy of the fluid droplets.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




