
The total number of optically active compounds formed in the following reaction is?
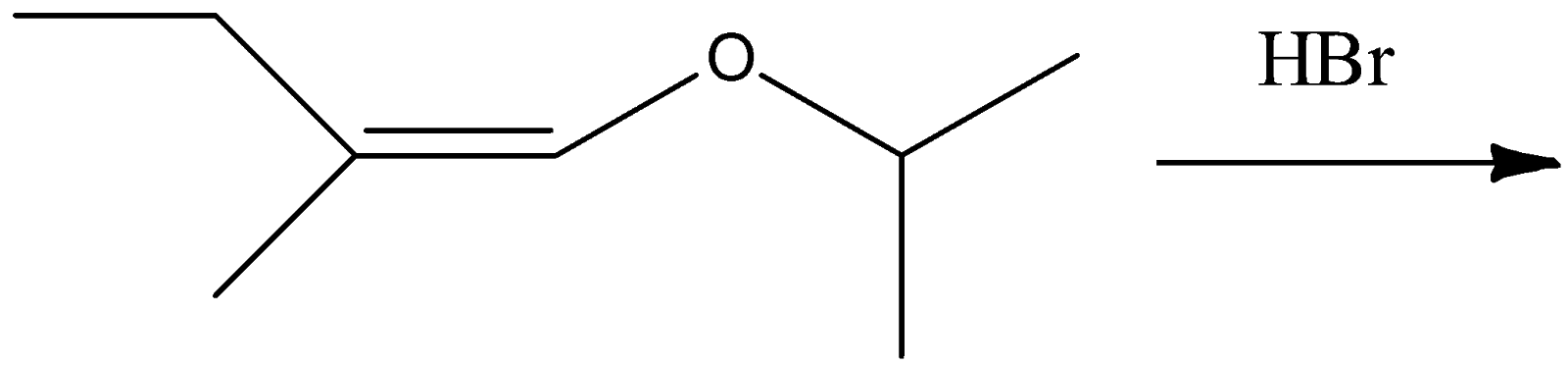
(A) Zero
(B) Six
(C) Four
(D) Two
Answer
240.3k+ views
Hint: This is an additional reaction to the alkene functional groups. A compound that has a chiral carbon can show optical isomerism. If an atom which can donate its lone pairs is bonded to the vinylic carbon, then it can give resonance structures.
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s see what will be the product of this reaction with an explanation.
It is an additional reaction where the addition of Hydrobromic acid is done at two carbons having a double bond. However, there is an oxygen atom which is directly bonded to the vinylic carbon. It will give resonance structures and will direct the position of the incoming electrophile. Let’s see how the addition will occur.
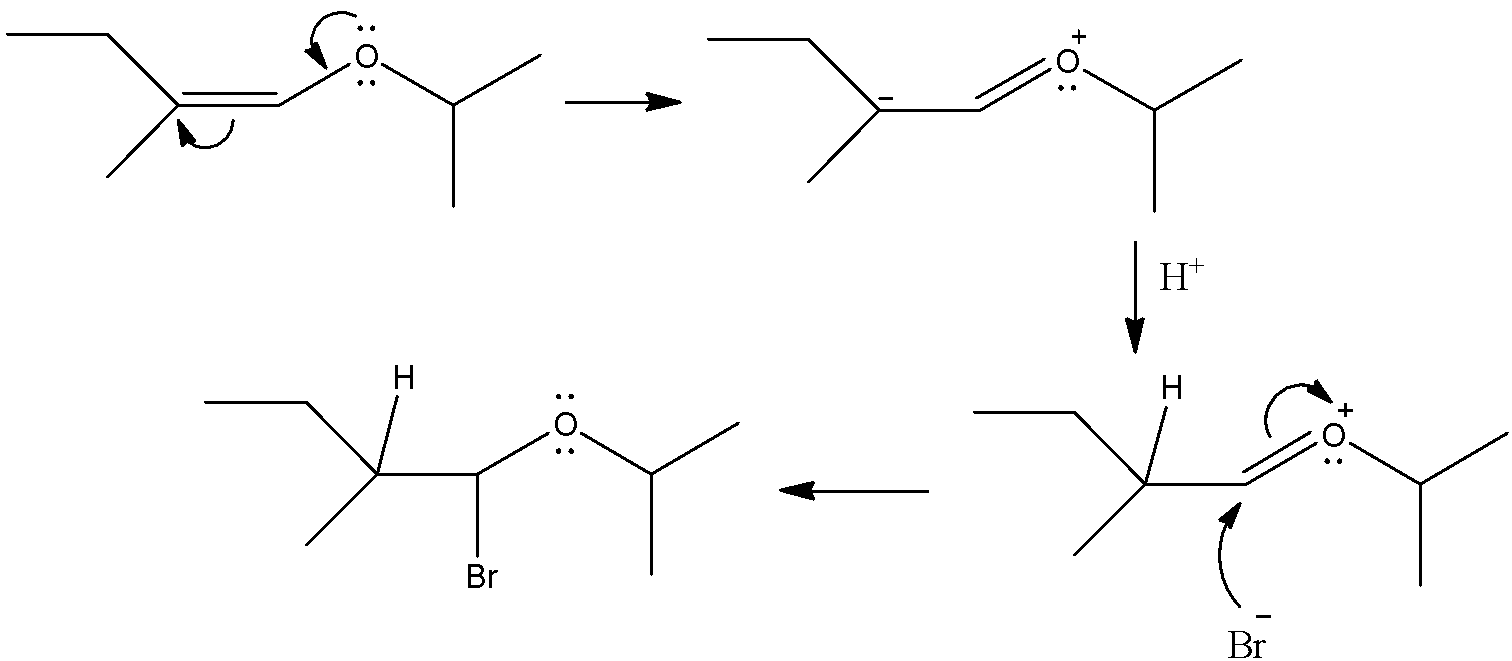
So, we can see that first oxygen will give its lone pair to the vinylic carbon and there will be a carbanion formed after the breakage of C-C double bond. This will attack on the proton and make a sigma bond with it. Then, the bromine atom which is an anion will attack the vinylic carbon and will make a sigma bond with it. The double bond between the carbon and oxygen will be broken and the positive charge on the oxygen atom will be neutralized.
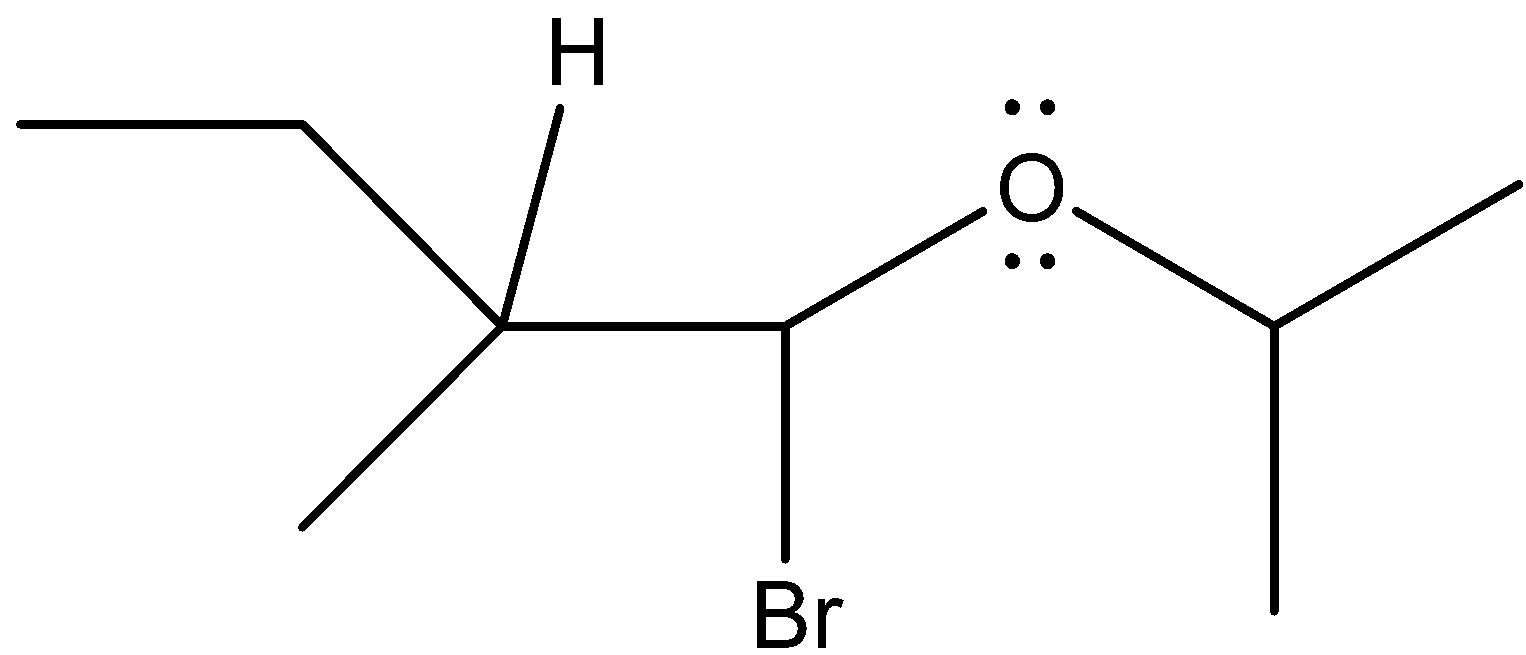
So, our final product can be written as
Now, see all the carbon atoms’ configuration.
- The carbon atom that has four different substituents connected with it by four single bonds, then the carbon is said to be chiral carbon.
In our product, carbon-bearing bromine atoms and the carbon bonded to that carbon is chiral because they have four different groups attached to fulfil their valency of 4 electrons.
-Any compound that has a chiral carbon, has optical isomers.
So, the number of optical isomers produced during this reaction as products=\[{{n}^{2}}\]
Here, n= number of chiral atoms
=\[{{(2)}^{2}}\]
=4
So, we can say that 4 optical isomers will be produced during this reaction. Their structures are as shown below.
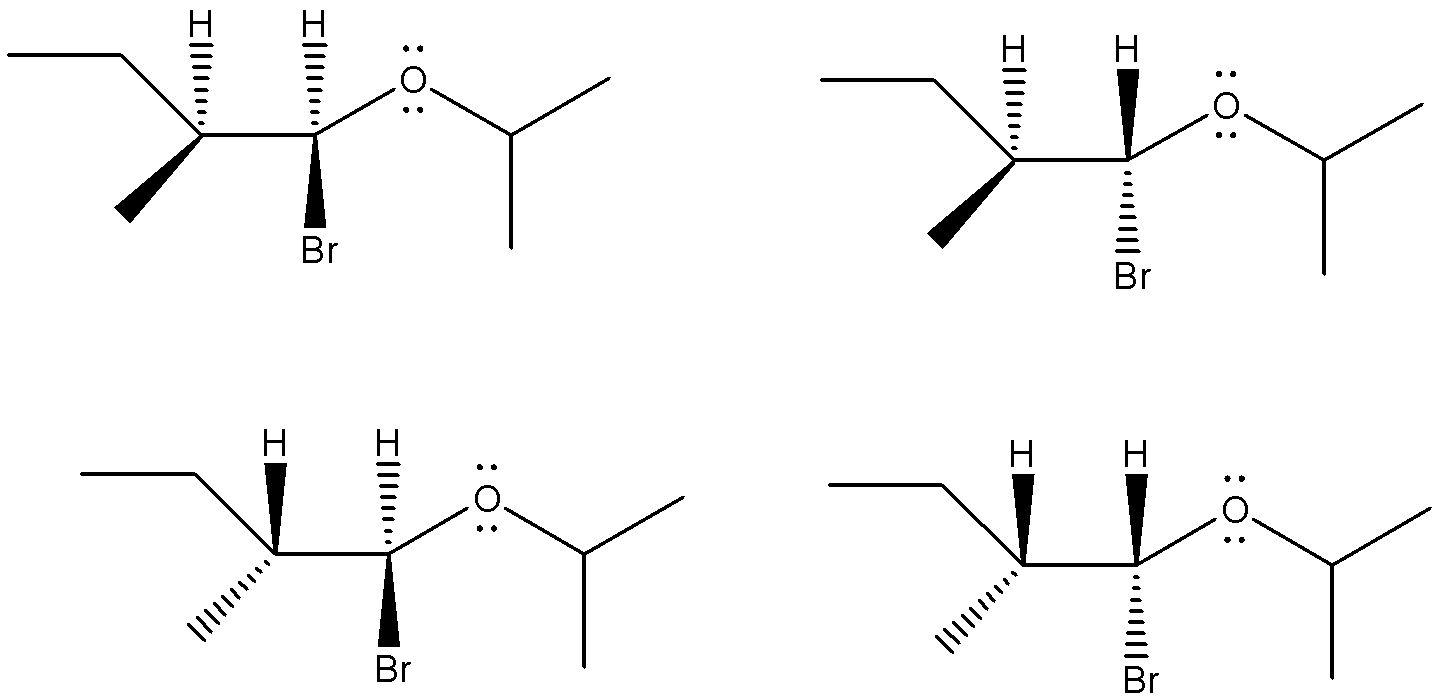
So, the correct answer is (C).
Note: Note that as oxygen is there which is directly bonded to the vinylic carbon. This will result in a product such that an anti-Markovnikov type of addition has occurred to the double bond. So, here anti-Markovnikov product is obtained even though peroxide is not present and that is because of the structure of the reactant.
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s see what will be the product of this reaction with an explanation.
It is an additional reaction where the addition of Hydrobromic acid is done at two carbons having a double bond. However, there is an oxygen atom which is directly bonded to the vinylic carbon. It will give resonance structures and will direct the position of the incoming electrophile. Let’s see how the addition will occur.

So, we can see that first oxygen will give its lone pair to the vinylic carbon and there will be a carbanion formed after the breakage of C-C double bond. This will attack on the proton and make a sigma bond with it. Then, the bromine atom which is an anion will attack the vinylic carbon and will make a sigma bond with it. The double bond between the carbon and oxygen will be broken and the positive charge on the oxygen atom will be neutralized.

So, our final product can be written as
Now, see all the carbon atoms’ configuration.
- The carbon atom that has four different substituents connected with it by four single bonds, then the carbon is said to be chiral carbon.
In our product, carbon-bearing bromine atoms and the carbon bonded to that carbon is chiral because they have four different groups attached to fulfil their valency of 4 electrons.
-Any compound that has a chiral carbon, has optical isomers.
So, the number of optical isomers produced during this reaction as products=\[{{n}^{2}}\]
Here, n= number of chiral atoms
=\[{{(2)}^{2}}\]
=4
So, we can say that 4 optical isomers will be produced during this reaction. Their structures are as shown below.

So, the correct answer is (C).
Note: Note that as oxygen is there which is directly bonded to the vinylic carbon. This will result in a product such that an anti-Markovnikov type of addition has occurred to the double bond. So, here anti-Markovnikov product is obtained even though peroxide is not present and that is because of the structure of the reactant.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2026 PDF Download (All Sets) with Answer Key

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More




