
The total number of contributing structures showing hyperconjugation (involving $C - H$ bonds) for the following carbocation is:
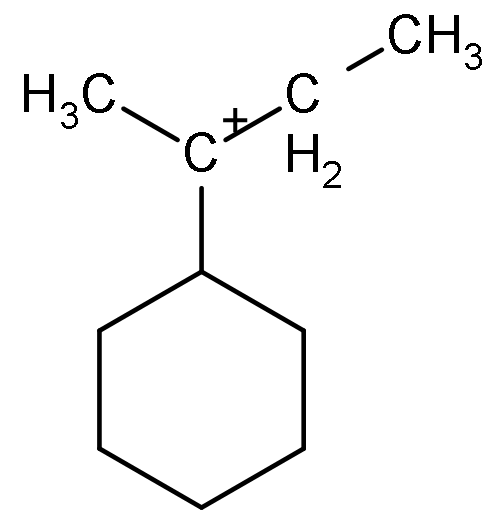
(A) 4
(B) 5
(C) 6
(D) 7
Answer
240.3k+ views
Hint: For this problem, we have to count the total number of alpha hydrogens that are attached to the alpha carbons because the number of hyperconjugation structures is directly proportional to the number of alpha hydrogen present in the structure.
Complete step by step solution:
- In the given question, we have to explain the total number of contributing structures which will show hyperconjugation.
- Now, firstly we should know about the hyperconjugation as it is a process in which the delocalisation of the electron will take place.
- The delocalisation of the electron takes place between the sigma or single bond and pi bond or non-bonding lone pair.
- So, to calculate the total number of conjugating structures, the compound must have the alpha hydrogen.
- Now, alpha hydrogen is the hydrogen which is directly attached to the alpha carbon and alpha carbon is the carbon which is directly attached to the functional group or carbocation.
- Also, we know that the total number of hyperconjugation structures is directly proportional to the total number of alpha hydrogen atoms present in the structure.
- So, in the given compound as we can see that there is three alpha carbon that is attached to the carbocation directly.
- And out of the left alpha carbon has three alpha hydrogen, right alpha carbon has two alpha hydrogen and the alpha carbon that is present below the carbocation has one alpha carbocation.
- So, the total number of alpha-hydrogen will be $3 + 2 + 1 = 5$.
Therefore, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note: Hyperconjugation is different from that of the resonance because in hyperconjugation the delocalisation of the sigma and non-bonding electron takes place whereas in resonance the delocalisation of the pi electrons takes place only.
Complete step by step solution:
- In the given question, we have to explain the total number of contributing structures which will show hyperconjugation.
- Now, firstly we should know about the hyperconjugation as it is a process in which the delocalisation of the electron will take place.
- The delocalisation of the electron takes place between the sigma or single bond and pi bond or non-bonding lone pair.
- So, to calculate the total number of conjugating structures, the compound must have the alpha hydrogen.
- Now, alpha hydrogen is the hydrogen which is directly attached to the alpha carbon and alpha carbon is the carbon which is directly attached to the functional group or carbocation.
- Also, we know that the total number of hyperconjugation structures is directly proportional to the total number of alpha hydrogen atoms present in the structure.
- So, in the given compound as we can see that there is three alpha carbon that is attached to the carbocation directly.
- And out of the left alpha carbon has three alpha hydrogen, right alpha carbon has two alpha hydrogen and the alpha carbon that is present below the carbocation has one alpha carbocation.
- So, the total number of alpha-hydrogen will be $3 + 2 + 1 = 5$.
Therefore, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note: Hyperconjugation is different from that of the resonance because in hyperconjugation the delocalisation of the sigma and non-bonding electron takes place whereas in resonance the delocalisation of the pi electrons takes place only.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions - 2025-26




