
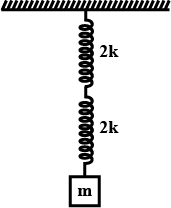
The time period of oscillation of the block as shown in figure is:
(A) $2 \pi \sqrt{\dfrac{m}{2 k}}$
(B) $\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{m}{k}}$
(C) $4 \pi \sqrt{\dfrac{m}{k}}$
(D) $2 \pi \sqrt{\dfrac{m}{k}}$
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: We should know that the time required by a body exhibiting periodic motion to complete one period is known as the time period. The S.I. unit is second. The number of times a body exhibits unique motion (each period) in one second is known as frequency. Oscillation refers to any periodic motion moving at a distance about the equilibrium position and repeating itself over and over for a period of time. Example the oscillation up and down of a spring, the oscillation side by side of a spring. The oscillation swinging side by side of a pendulum.
Complete step by step answer
As seen from the diagram the two springs are in series to each other. So, in this situation the force on each string is the same but the displacement on each string is different.
Thus, we can write that:
$x=x_{1}+x_{2} \quad F_{1}=-k_{1} x_{1}$
Hence the time period is given as:
$\Rightarrow T=2 \pi \sqrt{\dfrac{L}{g_{e f f}}}=2 \pi \sqrt{\dfrac{L}{g+a}} F_{2}=-k_{2} x_{2}$
Thus, we can write that:
$\dfrac{1}{k_{s}}=\dfrac{1}{k_{1}}+\dfrac{1}{k_{2}} \dfrac{F}{k_{1}}=x_{1}$
$\Rightarrow k_{s}=\dfrac{k_{1} k_{2}}{k_{1}+k_{2}} \dfrac{F}{k_{2}}=x_{2}$
Hence the formula of the time period is given as:
$T=2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{m(2k+2k)}{2k\times 2k}}=2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{m}{k}}$
So, we can say that the time period of oscillation is given as $2 \pi \sqrt{\dfrac{m}{k}}$.
Hence the correct answer is option D.
Note We can conclude that for something to oscillate, energy needs to move back and forth between two forms. For example, in a pendulum, energy moves between potential energy and kinetic energy. This movement of energy between the two forms is what causes the oscillation. There are many types of electronic oscillators, but they all operate according to the same basic principle: an oscillator always employs a sensitive amplifier whose output is fed back to the input in phase. Thus, the signal regenerates and sustains itself. This is known as positive feedback. A normal mode of an oscillating system is a pattern of motion in which all parts of the system move sinusoidally with the same frequency and with a fixed phase relation. These fixed frequencies of the normal modes of a system are known as its natural frequencies or resonant frequencies.
Complete step by step answer
As seen from the diagram the two springs are in series to each other. So, in this situation the force on each string is the same but the displacement on each string is different.
Thus, we can write that:
$x=x_{1}+x_{2} \quad F_{1}=-k_{1} x_{1}$
Hence the time period is given as:
$\Rightarrow T=2 \pi \sqrt{\dfrac{L}{g_{e f f}}}=2 \pi \sqrt{\dfrac{L}{g+a}} F_{2}=-k_{2} x_{2}$
Thus, we can write that:
$\dfrac{1}{k_{s}}=\dfrac{1}{k_{1}}+\dfrac{1}{k_{2}} \dfrac{F}{k_{1}}=x_{1}$
$\Rightarrow k_{s}=\dfrac{k_{1} k_{2}}{k_{1}+k_{2}} \dfrac{F}{k_{2}}=x_{2}$
Hence the formula of the time period is given as:
$T=2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{m(2k+2k)}{2k\times 2k}}=2\pi \sqrt{\dfrac{m}{k}}$
So, we can say that the time period of oscillation is given as $2 \pi \sqrt{\dfrac{m}{k}}$.
Hence the correct answer is option D.
Note We can conclude that for something to oscillate, energy needs to move back and forth between two forms. For example, in a pendulum, energy moves between potential energy and kinetic energy. This movement of energy between the two forms is what causes the oscillation. There are many types of electronic oscillators, but they all operate according to the same basic principle: an oscillator always employs a sensitive amplifier whose output is fed back to the input in phase. Thus, the signal regenerates and sustains itself. This is known as positive feedback. A normal mode of an oscillating system is a pattern of motion in which all parts of the system move sinusoidally with the same frequency and with a fixed phase relation. These fixed frequencies of the normal modes of a system are known as its natural frequencies or resonant frequencies.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Derive an expression for maximum speed of a car on class 11 physics JEE_Main

Understanding Elastic Collisions in Two Dimensions

Class 11 JEE Main Physics Mock Test 2025

Other Pages
NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory (2025-26)

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Define thermal expansion for alpha beta and gamma A class 11 physics JEE_Main

Happy New Year Wishes 2026 – 100+ Messages, Quotes, Shayari, Images & Status in All Languages

Valentine Week 2026 List | Valentine Week Days, Dates & Meaning




