
The orbital diagram shows the electronic configuration of the nitrogen atom. Which rule does not support this?
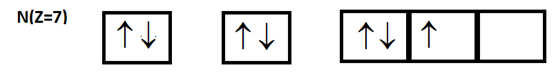
$1s^2$ $2s^2$ $2p^3$
A. Aufbau Principle
B. Hund’s rule
C. Pauli’s exclusion principle
D. None of these
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The orbitals are filled by electrons in the order of their increasing energy. Also, electron pairing cannot occur until each orbital of a given subshell is singly occupied or contains one electron each.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that the filling of electrons into the orbitals of different atoms take place according to the following three rules:
Aufbau principle: ‘Aufbau’ is a German word which means ‘building up’. The building up of orbitals means the filling up of orbitals with electrons. Basically, this principle dictates the manner in which electrons are filled in the atomic orbitals of an atom in ground state. It states that electrons are filled into atomic orbitals in the increasing order of orbital energy. In the above given diagram, we can clearly see that orbitals are filled in order of their increasing energy or we can say that the Aufbau principle is being followed.
Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity: This rule deals with filling of electrons into degenerate (equal) orbitals of the same subshell. This rule states that the lowest energy electronic configuration, the ground state, in any subshell is the one with the greatest number of parallel electron spins or in simple language we can say that no pairing of electrons will occur in any orbital, unless each of them are singly filled. In the above given diagram, we can clearly see that all 2p orbitals are not singly filled first. So, the above electronic configuration does not follow Hund’s rule.
Pauli’s exclusion principle-This rule states that “an orbital can have maximum two electrons and these must have opposite spin”. In the above diagram, we can clearly see that each orbital has either 1 or 2 electrons and in case of 2 electrons both have opposite spins. So, the above electronic configuration follows Pauli’s exclusion principle.
Therefore, from above points, we can clearly say that option B is the correct option.
Note: It should be remembered that orbitals should be singly filled and in an orbital both electrons cannot have same spins.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that the filling of electrons into the orbitals of different atoms take place according to the following three rules:
Aufbau principle: ‘Aufbau’ is a German word which means ‘building up’. The building up of orbitals means the filling up of orbitals with electrons. Basically, this principle dictates the manner in which electrons are filled in the atomic orbitals of an atom in ground state. It states that electrons are filled into atomic orbitals in the increasing order of orbital energy. In the above given diagram, we can clearly see that orbitals are filled in order of their increasing energy or we can say that the Aufbau principle is being followed.
Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity: This rule deals with filling of electrons into degenerate (equal) orbitals of the same subshell. This rule states that the lowest energy electronic configuration, the ground state, in any subshell is the one with the greatest number of parallel electron spins or in simple language we can say that no pairing of electrons will occur in any orbital, unless each of them are singly filled. In the above given diagram, we can clearly see that all 2p orbitals are not singly filled first. So, the above electronic configuration does not follow Hund’s rule.
Pauli’s exclusion principle-This rule states that “an orbital can have maximum two electrons and these must have opposite spin”. In the above diagram, we can clearly see that each orbital has either 1 or 2 electrons and in case of 2 electrons both have opposite spins. So, the above electronic configuration follows Pauli’s exclusion principle.
Therefore, from above points, we can clearly say that option B is the correct option.
Note: It should be remembered that orbitals should be singly filled and in an orbital both electrons cannot have same spins.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




