
The number of sigma bonds in tetra cyano ethylene is ______.
(A) 7
(B) 6
(C) 5
(D) 9
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: As the name suggests, the compound tetra cyano ethylene contains four cyano groups and one ethylene group bonded with each other in a specific arrangement. Mostly, the name of the compound tells us about the composition but this is not applicable every time.
Complete step by step solution:
There are two types of covalent bonds between atoms namely sigma bond and a pi bond.
Sigma bonds (σ-bond) are the strongest type of covalent bonds. They are formed when atomic orbitals between atoms overlap head-on with each other. A σ-bond is symmetrical with respect to rotation about the bond axis of the atoms. Common forms of sigma bonds are of four types i.e. \[s + s,{\text{ }}{p_z} + {p_z},{\text{ }}s + {p_z}\; and {\text{ }}{d_z}^2 + {d_z}^2\] where s, p and d are the atomic orbitals of the atoms.
Pi bonds (π bonds) are covalent bonds where two lobes of an orbital on one atom laterally overlap with two lobes of an orbital on another atom. The electron density in each atomic orbital is zero at a shared nodal plane, passing through the two bonded nuclei. Pi Bonds can form in double and triple bonds but do not form in single bonds in most cases.
The compound tetra cyano ethylene also contains several sigma and pi bonds. To find the number, we have to look in its structure.
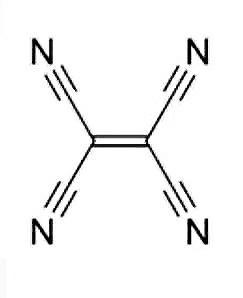
As we can see, there are four nitrogen atoms bonded with carbon with a triple bond. Also, two of the carbons are bonded with a double bond and both of them are connected with the carbon of cyanide with a single bond (two single bonds each).
We know, a triple bond contains 2 pi bonds and 1 sigma bond and a double bond contains a single sigma bond and a pi bond and a single bond contains only 1 sigma bond. Therefore:
Total number of sigma bond from four triple bonds are – 4
Total number of sigma bond from one double bond is – 1
Total number of sigma bond from four single bonds is – 4
Therefore, total number of sigma bonds are = 4+1+4 = 9
So, the correct answer is (D) “9”.
Note: In most of the cases, sigma bond is stronger than pi bonds but in some special cases pi bond may get stronger. One of these cases can be found in coordination compounds.
Complete step by step solution:
There are two types of covalent bonds between atoms namely sigma bond and a pi bond.
Sigma bonds (σ-bond) are the strongest type of covalent bonds. They are formed when atomic orbitals between atoms overlap head-on with each other. A σ-bond is symmetrical with respect to rotation about the bond axis of the atoms. Common forms of sigma bonds are of four types i.e. \[s + s,{\text{ }}{p_z} + {p_z},{\text{ }}s + {p_z}\; and {\text{ }}{d_z}^2 + {d_z}^2\] where s, p and d are the atomic orbitals of the atoms.
Pi bonds (π bonds) are covalent bonds where two lobes of an orbital on one atom laterally overlap with two lobes of an orbital on another atom. The electron density in each atomic orbital is zero at a shared nodal plane, passing through the two bonded nuclei. Pi Bonds can form in double and triple bonds but do not form in single bonds in most cases.
The compound tetra cyano ethylene also contains several sigma and pi bonds. To find the number, we have to look in its structure.

As we can see, there are four nitrogen atoms bonded with carbon with a triple bond. Also, two of the carbons are bonded with a double bond and both of them are connected with the carbon of cyanide with a single bond (two single bonds each).
We know, a triple bond contains 2 pi bonds and 1 sigma bond and a double bond contains a single sigma bond and a pi bond and a single bond contains only 1 sigma bond. Therefore:
Total number of sigma bond from four triple bonds are – 4
Total number of sigma bond from one double bond is – 1
Total number of sigma bond from four single bonds is – 4
Therefore, total number of sigma bonds are = 4+1+4 = 9
So, the correct answer is (D) “9”.
Note: In most of the cases, sigma bond is stronger than pi bonds but in some special cases pi bond may get stronger. One of these cases can be found in coordination compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




