
The most stable canonical structure among the given structure is:
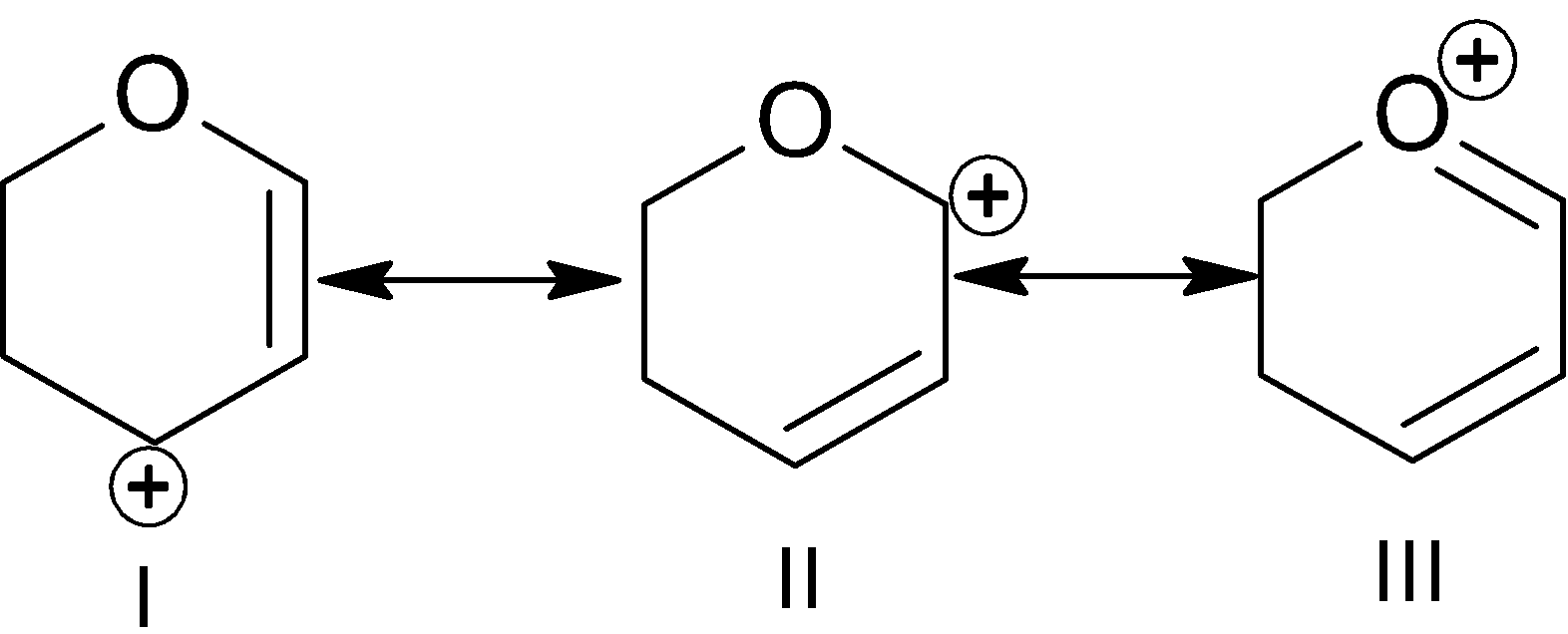
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. All are equally stable
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: There are many factors for deciding stability of canonical structures like resonance is the major factor, inductive effect, number of \[\pi \] bonds, \[\pi \]-lone pair conjugation, position of charges etc. So, by using these effects we can check the stability order of canonical structures.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Canonical structures are a way of representing or describing the delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions like in phosphate ions. Here all three are resonance structures. In this example many effects work like inductive effect, number of \[\pi \]bonds, positive charge - lone pair conjugation, position of charge etc.
In the 1st structure \[-I\] effect of oxygen, incomplete octet of cation.
In the 2nd structure \[-I\] effect of oxygen, incomplete octet of cation.
In the 3rd structure \[\pi \] bonds are more than 1st and 2nd, octet is complete, and positive charge is present on the most electronegative element which makes it highly unstable.
Conclusion from the above three factors is that the 3rd structure is unstable than other 2 structures because of positive charge on the most electronegative atom. In the 1st part \[-I\] effect is less than the 2nd part which makes cation less stable than the 1st part.
So, the stability order is:
$III < II < I$
So, “A” is the correct answer.
Note: You should know which effect is dominating where. In the 3rd structure there is positive charge on the most electronegative atom.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Canonical structures are a way of representing or describing the delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions like in phosphate ions. Here all three are resonance structures. In this example many effects work like inductive effect, number of \[\pi \]bonds, positive charge - lone pair conjugation, position of charge etc.
In the 1st structure \[-I\] effect of oxygen, incomplete octet of cation.
In the 2nd structure \[-I\] effect of oxygen, incomplete octet of cation.
In the 3rd structure \[\pi \] bonds are more than 1st and 2nd, octet is complete, and positive charge is present on the most electronegative element which makes it highly unstable.
Conclusion from the above three factors is that the 3rd structure is unstable than other 2 structures because of positive charge on the most electronegative atom. In the 1st part \[-I\] effect is less than the 2nd part which makes cation less stable than the 1st part.
So, the stability order is:
$III < II < I$
So, “A” is the correct answer.
Note: You should know which effect is dominating where. In the 3rd structure there is positive charge on the most electronegative atom.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




