
The monomers of biodegradable polymer, nylon 2-nylon 6 are:
A. glycine + adipic acid
B. glycol + phthalic acid
C. phenol + urea
D. glycine + amino caproic acid
Answer
241.8k+ views
Hint: Nylon 2-nylon 6 is a condensation polymer. It is a result of polyamide copolymerization of two monomers, one has both amino group and carboxylic acid and another is a derivative of amino acid lysine.
Complete step by step answer:
Polymerization is a process in which small molecules, known as monomers combine chemically to produce a very large network molecule which is called a polymer.
Monomers are the molecules that are bonded to other molecules to form a polymer.
There are two monomers of Nylon 2-nylon 6 named as Glycine $\left( \text{Gly} \right)$ with chemical formula $\left( {{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{NC}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{COOH} \right)$ and Amino caproic acid has the chemical formula $\left( {{\text{C}}_{6}}{{\text{H}}_{13}}{{\text{O}}_{2}}\text{N} \right)$. The reaction of both gives the polymer nylon 2-nylon 6 after removal of water molecules from the reactants.
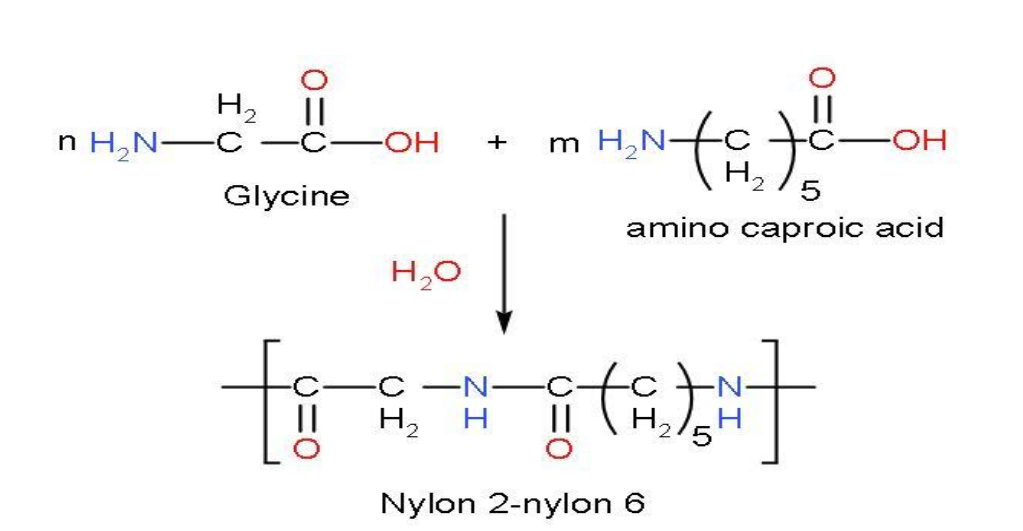
A condensation polymerization is in which monomers react with each other to form larger structural units while releasing water or methanol as by-product.
Biodegradable polymers are a type of polymer that breaks down by bacterial decomposition to result in natural by-products such as gases $\left( \text{C}{{\text{O}}_{2}},{{\text{N}}_{2}} \right)$, water and biomass.
The correct answer of this question is the monomers of biodegradable polymer, nylon 2-nylon 6 are glycine and amino caproic acid.
option ‘d’ is correct
Additional Information:
Applications of Nylon 2-nylon 6 are:
(1) It is used in synthesis of artificial fibers.
(2) Used to make strings of musical instruments and threads in bristles for toothbrushes.
Note:
Glycine is the only achiral amino acid. As glycine has two groups attached to it as the same which is two hydrogen atoms are attached to it. But the coming compounds of amino acids groups will have one hydrogen atom to be replaced with other groups. Like, Alanine has methyl group instead of hydrogen atom; $\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{CHN}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{COOH}$.
Complete step by step answer:
Polymerization is a process in which small molecules, known as monomers combine chemically to produce a very large network molecule which is called a polymer.
Monomers are the molecules that are bonded to other molecules to form a polymer.
There are two monomers of Nylon 2-nylon 6 named as Glycine $\left( \text{Gly} \right)$ with chemical formula $\left( {{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{NC}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{COOH} \right)$ and Amino caproic acid has the chemical formula $\left( {{\text{C}}_{6}}{{\text{H}}_{13}}{{\text{O}}_{2}}\text{N} \right)$. The reaction of both gives the polymer nylon 2-nylon 6 after removal of water molecules from the reactants.

A condensation polymerization is in which monomers react with each other to form larger structural units while releasing water or methanol as by-product.
Biodegradable polymers are a type of polymer that breaks down by bacterial decomposition to result in natural by-products such as gases $\left( \text{C}{{\text{O}}_{2}},{{\text{N}}_{2}} \right)$, water and biomass.
The correct answer of this question is the monomers of biodegradable polymer, nylon 2-nylon 6 are glycine and amino caproic acid.
option ‘d’ is correct
Additional Information:
Applications of Nylon 2-nylon 6 are:
(1) It is used in synthesis of artificial fibers.
(2) Used to make strings of musical instruments and threads in bristles for toothbrushes.
Note:
Glycine is the only achiral amino acid. As glycine has two groups attached to it as the same which is two hydrogen atoms are attached to it. But the coming compounds of amino acids groups will have one hydrogen atom to be replaced with other groups. Like, Alanine has methyl group instead of hydrogen atom; $\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{CHN}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{COOH}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

JEE Main Correction Window 2026 Session 1 Dates Announced - Edit Form Details, Dates and Link

Other Pages
NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Set 2 (56/5/2) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis

CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Set 3 56/4/3 2025 Question Paper PDF & Answer Key

CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Set 3 2025 with Answers

What is Glucose in Chemistry? Structure, Properties & Uses




