
The monomer used in Novolac; a polymer used in paints is:
A. Butadiene and styrene
B. Phenol and formaldehyde
C. Butadiene and acrylo nitrile
D. Melamine and formaldehyde
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: There are different classes of polymers. Novolac is a phenolic resin type of polymer. It is extensively used in microelectronics.
Complete step by step answer: A polymer is a large molecule formed by continuous linking of many small subunits called Monomers. Basically, it is a repetition of monomers.
Another name for novolac is phenolic resin or phenol formaldehyde resin. As this suggests, the two monomers needed to form novolac are phenol and formaldehyde.
The reaction that occurs is –
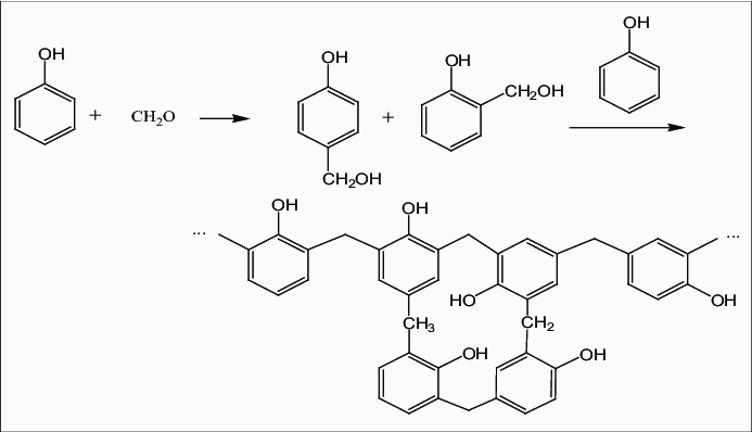
The reaction stops when the formaldehyde reactant is exhausted, often leaving up to 10% of un-reacted phenol.
So, B is the correct option.
Additional information: There are two types of polymers, natural and artificial. Natural polymers are found in plants. Apart from natural and manmade, polymers are classified in various other ways.
Based on the type of monomer used and mechanism of polymerization, there are different types of polymers. Novolac is a cross linked polymer formed by condensation polymerisation. During preparation of novolac, as a general rule phenol gets substituted on both ortho and para positions. But we know that para position is almost twice as reactive as ortho. But there are twice as many ortho sites (two per phenol molecule) so the fractions of ortho-ortho, para-para and ortho-para bridges are approximately equal. In this reaction, a water molecule gets eliminated. Hence the type of polymerization mechanism is condensation. Distillation of the molten resin during manufacturing removes the excess phenol and water.
Note: To remember this easily, we can keep in mind that novolac is a phenolic resin type of polymer. It has a cross linked structure and is formed by condensation polymerization.
Complete step by step answer: A polymer is a large molecule formed by continuous linking of many small subunits called Monomers. Basically, it is a repetition of monomers.
Another name for novolac is phenolic resin or phenol formaldehyde resin. As this suggests, the two monomers needed to form novolac are phenol and formaldehyde.
The reaction that occurs is –

The reaction stops when the formaldehyde reactant is exhausted, often leaving up to 10% of un-reacted phenol.
So, B is the correct option.
Additional information: There are two types of polymers, natural and artificial. Natural polymers are found in plants. Apart from natural and manmade, polymers are classified in various other ways.
Based on the type of monomer used and mechanism of polymerization, there are different types of polymers. Novolac is a cross linked polymer formed by condensation polymerisation. During preparation of novolac, as a general rule phenol gets substituted on both ortho and para positions. But we know that para position is almost twice as reactive as ortho. But there are twice as many ortho sites (two per phenol molecule) so the fractions of ortho-ortho, para-para and ortho-para bridges are approximately equal. In this reaction, a water molecule gets eliminated. Hence the type of polymerization mechanism is condensation. Distillation of the molten resin during manufacturing removes the excess phenol and water.
Note: To remember this easily, we can keep in mind that novolac is a phenolic resin type of polymer. It has a cross linked structure and is formed by condensation polymerization.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

What Is a Galvanometer? Definition, Working, and Uses

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




