
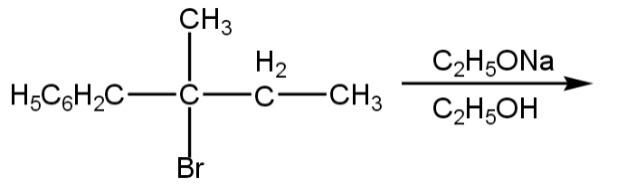
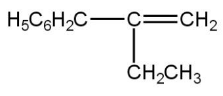
The major product of the following reaction is:
(A)
(B)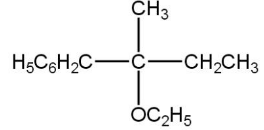
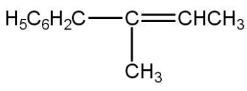
(C)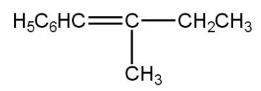
(D)
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: Given compound name is \[\left( 2-bromo-2-methyl\text{ }butyl \right)\] benzene and sodium ethoxide (\[{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}ONa\]) which acts as a strong nucleophile reagent and also a strong base and thus, it tend to donate electron or seek cation. The reaction between both the compounds is followed by a substitution reaction (one nucleophile will substitute for another nucleophile).
Complete Step by Step Solution:
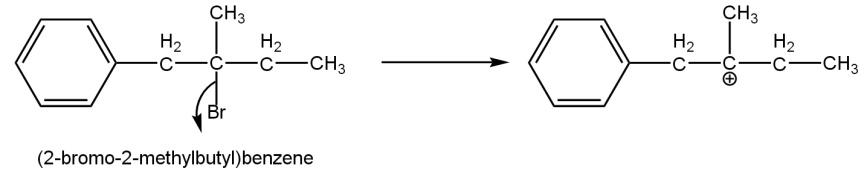
In a given compound \[\left( 2-bromo-2-methyl\text{ }butyl \right)\], bromine’s electronegativity is quite high as compared to carbon to which it is bonded. Due to its high electronegativity, it tends to attract a bond pair of electrons towards itself and become negatively charged. This results in creation of three-degree carbonation such as
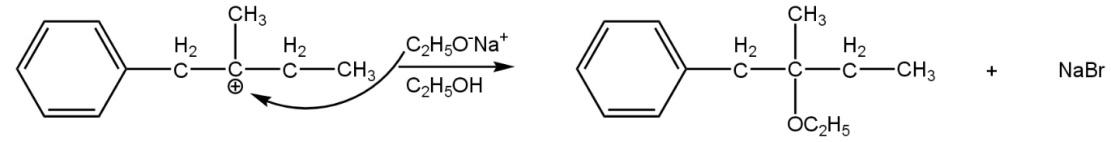
The resultant compound is unstable because it is a charge compound and not neutral compound and it tends to get neutral by the attack of another nucleophile. Sodium ethoxide (\[{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}ONa\]) and ethanol (\[{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH\]) are strong nucleophilic reagents (electron-rich), attack on it and side product will be\[NaBr\](attacked by sodium ethoxide) or\[HBr\] (attack by ethanol) such as
The major product is obtained by nucleophile substitution in this reaction and products obtained by elimination reaction are minor.
Thus, the correct option is A.
Note: Bromine (leaving group) is a good nucleophile due to which substitution reaction is preferred. If in the place of bromine, a strong and bulky base is present then an elimination reaction takes place and the major product will be obtained by elimination reaction and not by a substitution reaction. Also, neutral species are more stable than charged species.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In a given compound \[\left( 2-bromo-2-methyl\text{ }butyl \right)\], bromine’s electronegativity is quite high as compared to carbon to which it is bonded. Due to its high electronegativity, it tends to attract a bond pair of electrons towards itself and become negatively charged. This results in creation of three-degree carbonation such as

The resultant compound is unstable because it is a charge compound and not neutral compound and it tends to get neutral by the attack of another nucleophile. Sodium ethoxide (\[{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}ONa\]) and ethanol (\[{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH\]) are strong nucleophilic reagents (electron-rich), attack on it and side product will be\[NaBr\](attacked by sodium ethoxide) or\[HBr\] (attack by ethanol) such as

The major product is obtained by nucleophile substitution in this reaction and products obtained by elimination reaction are minor.
Thus, the correct option is A.
Note: Bromine (leaving group) is a good nucleophile due to which substitution reaction is preferred. If in the place of bromine, a strong and bulky base is present then an elimination reaction takes place and the major product will be obtained by elimination reaction and not by a substitution reaction. Also, neutral species are more stable than charged species.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




