
The lanthanide contraction is responsible for the fact that.
A. Zn and Y have about the same radii
B. Zr and Nb have similar oxidation state
C. Zr and Hf have about the same radii
D. Zr and Zn have the same oxidation state
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Lanthanides are groups of elements which are present in the f- block and are also known as inner transition elements. The atomic number of this group of inner transition elements ranges from 58 to 71. These Lanthanides exhibit a special phenomenon known as Lanthanide contraction.
Complete Step-by-Step answer:
Lanthanide contraction basically corresponds to the situation where the atomic radii of the elements in the Lanthanide series decreases drastically from left to right. Now we need to understand that f – block elements are placed in a designated zone inside the d – block. So once the last element of the lanthanide series, we do not move to the next period, but continue to place the d – block elements in the same period.
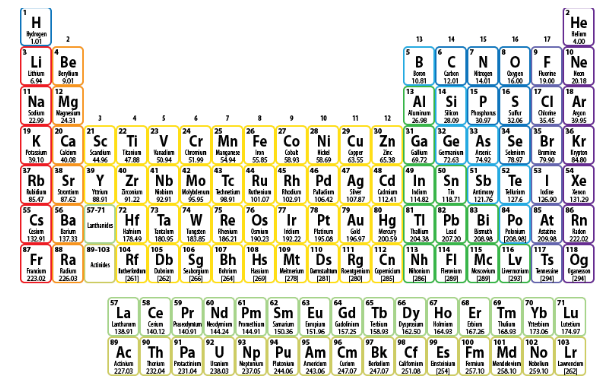
A general trend that is observed is that the atomic radius of elements decreases as we move from left to right in a period. But due to Lanthanide contraction, this trend is not observed. After the last element of lanthanide series, the atomic radius again increases when we move forward in the same period in the d – block.
Also, another observed trend is that as we move down a group, the atomic radius of the elements goes on increasing. But Lanthanide contraction causes an anomaly in this trend as well.
Such a phenomenon causes Zr and Hf to have about the same radii, as we can observe from the periodic table above.
Hence, Option C is the correct option.
Note: Lanthanide contraction is caused because of the poor shielding effect of f – orbital. This results in a greater nuclear change acting on the outer electrons and increases the force of attraction. This causes the outer electrons to be pulled strongly towards the nucleus, thus causing the rapid decrease in the radii of Lanthanides.
Complete Step-by-Step answer:
Lanthanide contraction basically corresponds to the situation where the atomic radii of the elements in the Lanthanide series decreases drastically from left to right. Now we need to understand that f – block elements are placed in a designated zone inside the d – block. So once the last element of the lanthanide series, we do not move to the next period, but continue to place the d – block elements in the same period.

A general trend that is observed is that the atomic radius of elements decreases as we move from left to right in a period. But due to Lanthanide contraction, this trend is not observed. After the last element of lanthanide series, the atomic radius again increases when we move forward in the same period in the d – block.
Also, another observed trend is that as we move down a group, the atomic radius of the elements goes on increasing. But Lanthanide contraction causes an anomaly in this trend as well.
Such a phenomenon causes Zr and Hf to have about the same radii, as we can observe from the periodic table above.
Hence, Option C is the correct option.
Note: Lanthanide contraction is caused because of the poor shielding effect of f – orbital. This results in a greater nuclear change acting on the outer electrons and increases the force of attraction. This causes the outer electrons to be pulled strongly towards the nucleus, thus causing the rapid decrease in the radii of Lanthanides.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Amino Acids and Peptides Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding important Concepts and Tips

Electricity and Magnetism Explained: Key Concepts & Applications

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




