
The IUPAC name of the insecticide lindane is:
(A) Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane
(B) Benzene hexachloride
(C) Hexachloran
(D) 1,2,3.4,5,6-hexachlorocyclohexane
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: IUPAC nomenclature is used to make an international standard of naming molecules to help in communication. By this IUPAC nomenclature each structure is given a unique name and structure.
Complete step by step solution:
In IUPAC nomenclature, the root word is basically the number of total carbons in a longest chain of that compound.
… and so on.
The primary suffix is basically used to differentiate between the saturated compounds( Alkanes) and unsaturated compounds (Alkene and Alkynes).
If there are more than one suffix. Then one of those suffixes is considered a secondary suffix.
Example: Methanol (Alkanol) , here ‘ol’ is a secondary suffix.
The primary prefixes are basically used to differentiate between cyclic compound and noncyclic or chain compound. For cyclic compound prefix s ‘cyclo’ . If there are any side chains or groups are present then secondary prefixes like ‘methyl’, ‘ethyl’ are used.
The structure of lindane is ,
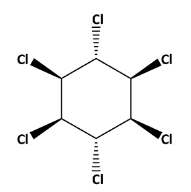
The IUPAC name of lindane is gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane. It is also called benzene hexachloride.
In this structure two chlorine atom are cis to each other are at gamma position that is why gamma is written in the IUPAC name.
It is a cyclic compound so “cyclo” prefix is used. Six carbon is present in the ring so “hex” is the word root. And “ane” is used as the primary suffix.
There are six chlorine atoms present that is why “hexa chloro” is added in the name.
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note: In agricultural science lindane is used as an insecticide on fruit, vegetables etc. It has uses in pharmaceutical treatment too. primary prefixes are used to indicate the origin of the compound in IUPAC nomenclature and suffixes are used to indicate the functional group of that molecule.
Complete step by step solution:
In IUPAC nomenclature, the root word is basically the number of total carbons in a longest chain of that compound.
| No. of carbons | Root word |
| 1 | meth |
| 2 | eth |
| 3 | prop |
| 4 | but |
| 5 | pent |
… and so on.
The primary suffix is basically used to differentiate between the saturated compounds( Alkanes) and unsaturated compounds (Alkene and Alkynes).
| Compound | Suffix |
| Alkane | ane |
| Alkene | Ene |
| Alkyne | Yne |
If there are more than one suffix. Then one of those suffixes is considered a secondary suffix.
Example: Methanol (Alkanol) , here ‘ol’ is a secondary suffix.
The primary prefixes are basically used to differentiate between cyclic compound and noncyclic or chain compound. For cyclic compound prefix s ‘cyclo’ . If there are any side chains or groups are present then secondary prefixes like ‘methyl’, ‘ethyl’ are used.
The structure of lindane is ,

The IUPAC name of lindane is gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane. It is also called benzene hexachloride.
In this structure two chlorine atom are cis to each other are at gamma position that is why gamma is written in the IUPAC name.
It is a cyclic compound so “cyclo” prefix is used. Six carbon is present in the ring so “hex” is the word root. And “ane” is used as the primary suffix.
There are six chlorine atoms present that is why “hexa chloro” is added in the name.
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note: In agricultural science lindane is used as an insecticide on fruit, vegetables etc. It has uses in pharmaceutical treatment too. primary prefixes are used to indicate the origin of the compound in IUPAC nomenclature and suffixes are used to indicate the functional group of that molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




