
Shown below are four possible synthesis of Propionaldehyde. Which one would not work?
(A) 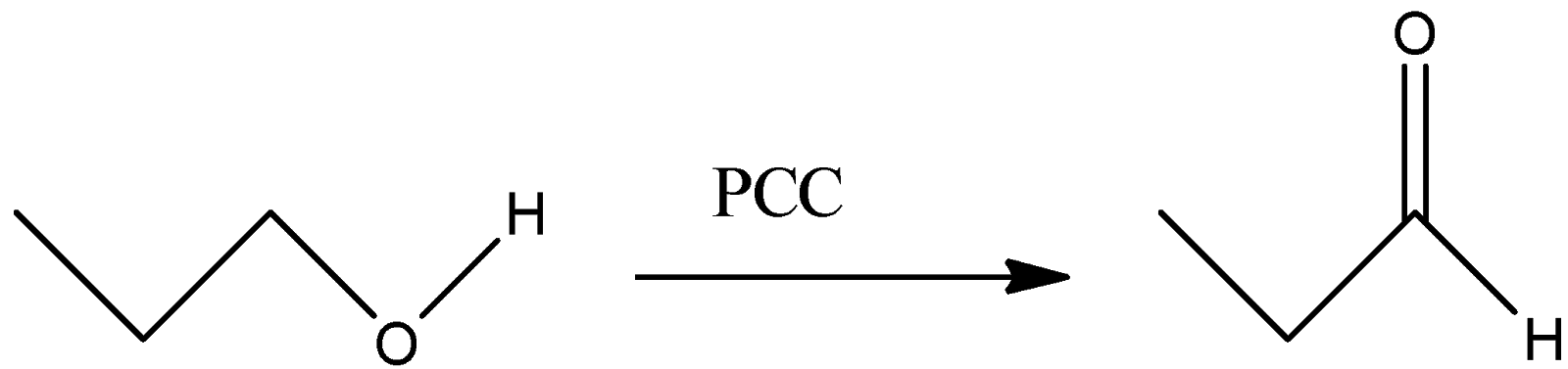
(B) 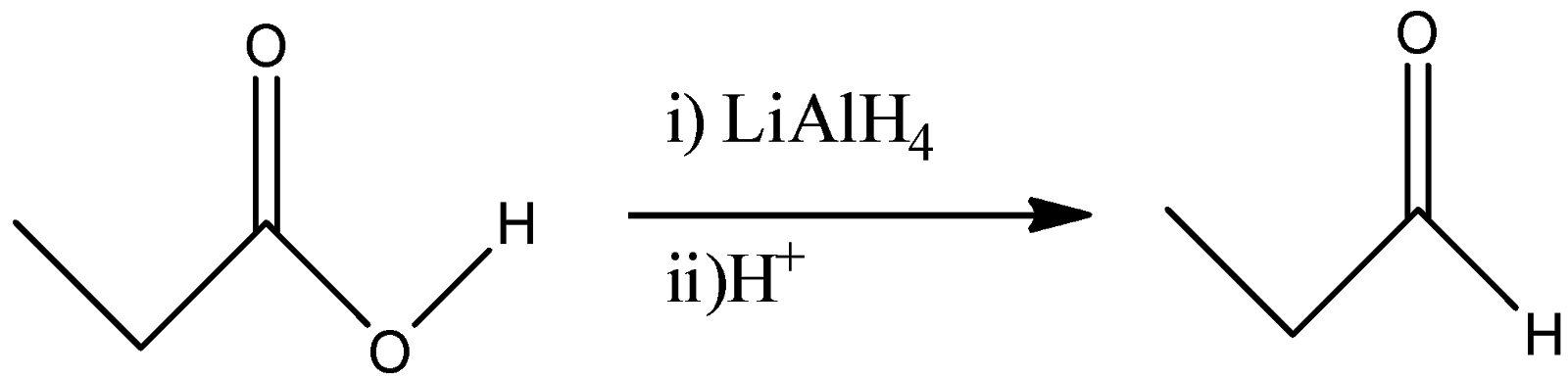
(C) 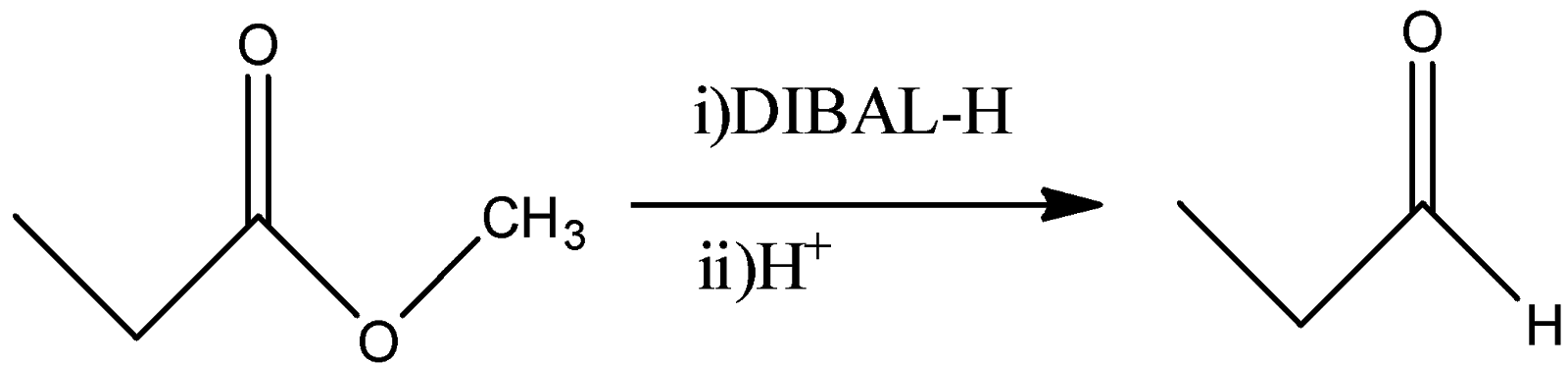
(D) 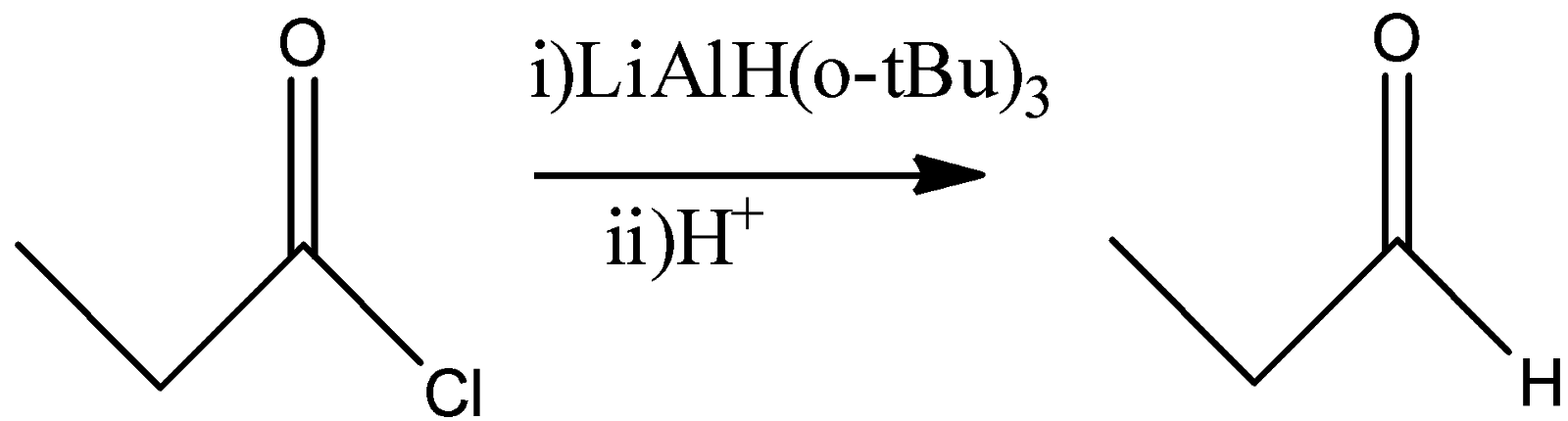
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: PCC is a mild oxidizing agent. $LiAl{H_4}$ is a very strong reducing agent and it can donate four hydrides. $LiAlH{(o - tBu)_3}{\text{ and DIBAL - H}}$ can only donate one hydride from its molecule.
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s see all the reactions one-by-one to find out which one will not work.
A)
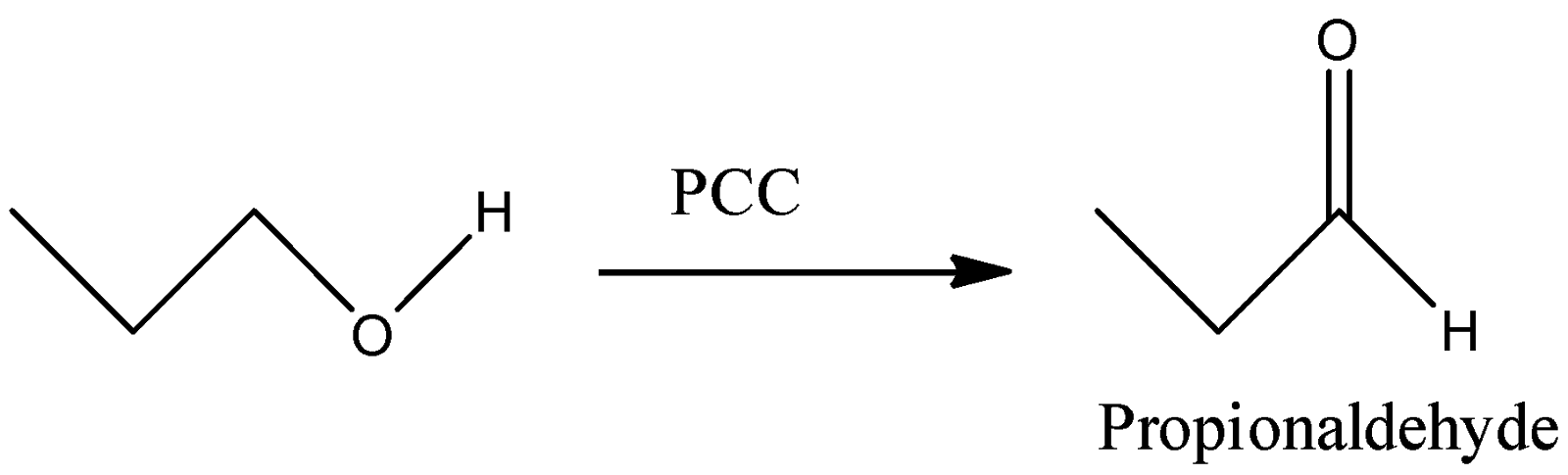
-PCC stands for Pyridinium Chlorochromate. This reagent selectively converts the –OH group to –CHO group. We can see that in the reaction, the hydroxyl group gets converted to the corresponding aldehyde. Thus, this reaction will give Propionaldehyde as a final product.
B)
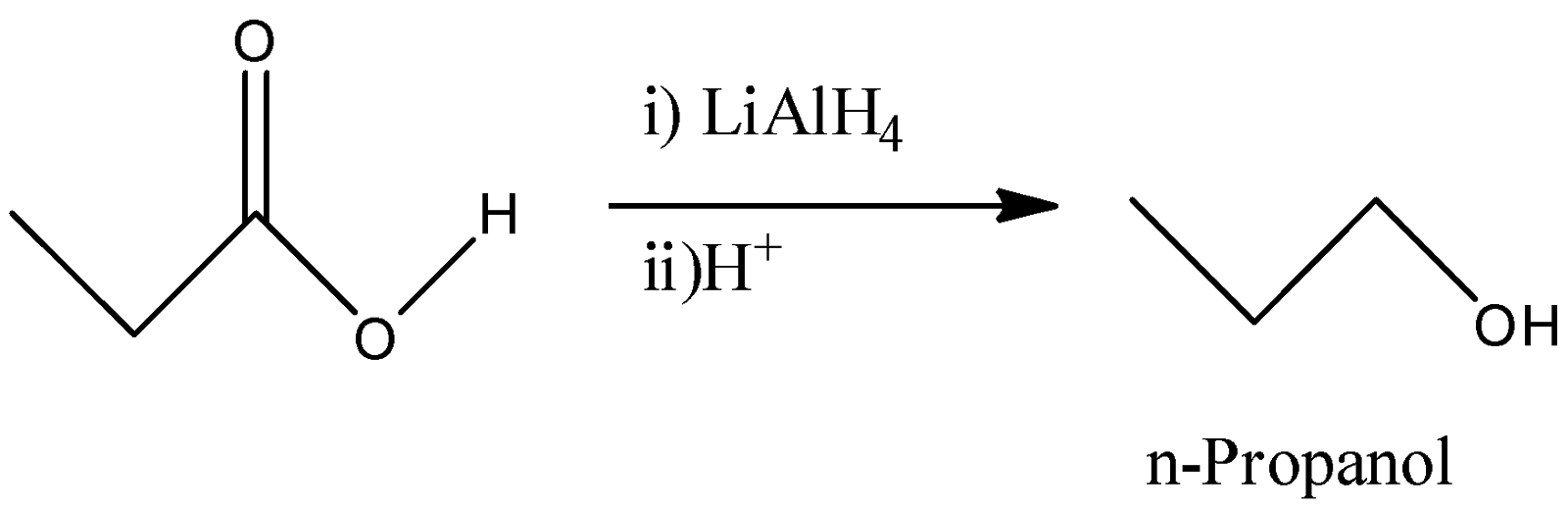
-Lithium aluminium hydride is a strong reducing agent and it reduced the carboxylic acid group to its corresponding hydroxyl derivative. So, propanoic acid will react with $LiAl{H_4}$ to give n-Propanol. So, by this reaction, we will not get Propionaldehyde as a final product.
C)
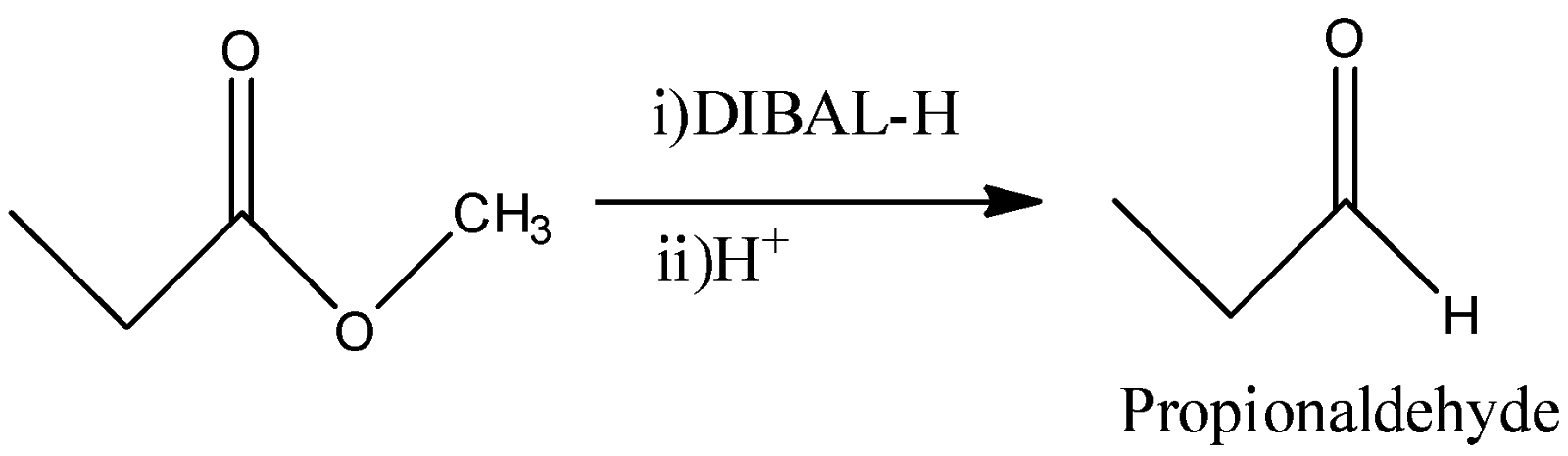
-DIBAL-H stands for Diisobutylaluminumhydride and it has only one hydride. So, if we allow this reaction to happen quantitatively, then it will convert the ester functional group to its corresponding aldehyde as a final product. So, -OR group will be replaced by –H atom. So, Propionaldehyde will be obtained from this reaction.
D)
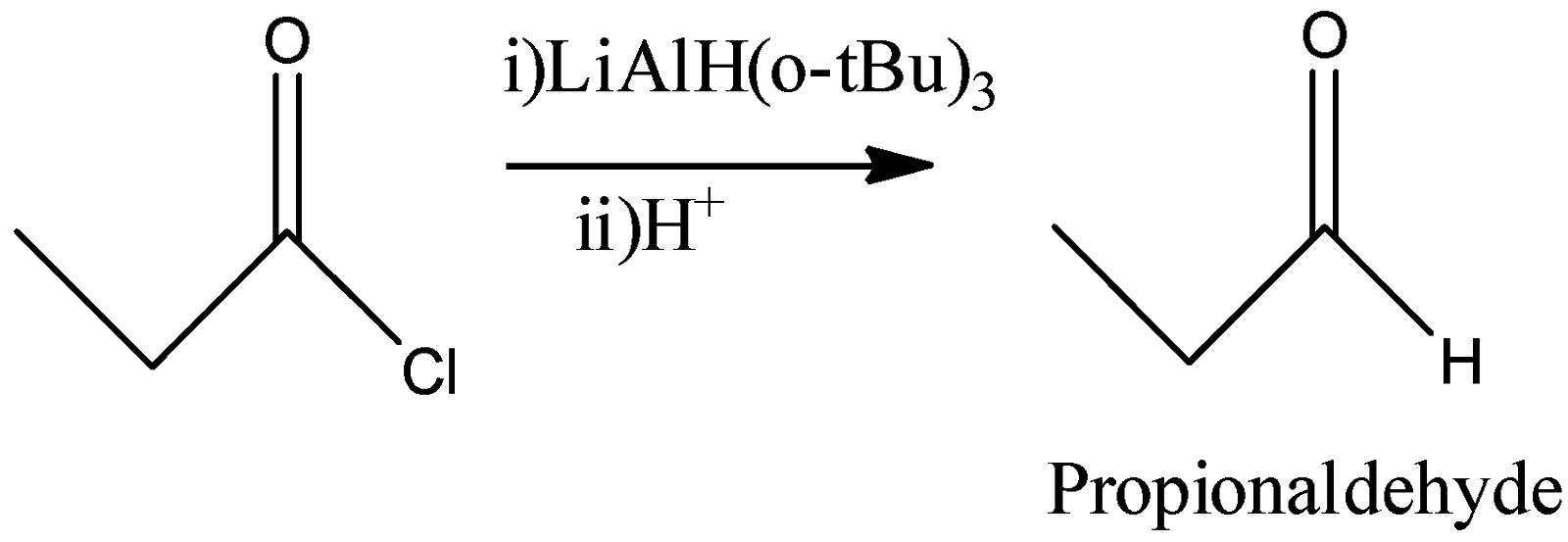
Here, the reagent used is Lithium tertbutoxyaluminumhydride. This reagent also has only one hydride and if allowed to react quantitatively, then it will convert the acid chloride into the corresponding aldehyde by replacing the –Cl by –H atom. So, we will also get Propionaldehyde as a product in this reaction.
So, we can say that correct answer is (B).
Note: Note that as DIBAL-H has only one hydride, it will convert the ester to aldehyde only and it will not reduce the aldehyde further to the alcohol. The same thing is with Lithium tertbutoxyaluminumhydride, it also cannot reduce acid chloride to alcohols and the reaction stops at the formation of aldehyde.
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s see all the reactions one-by-one to find out which one will not work.
A)

-PCC stands for Pyridinium Chlorochromate. This reagent selectively converts the –OH group to –CHO group. We can see that in the reaction, the hydroxyl group gets converted to the corresponding aldehyde. Thus, this reaction will give Propionaldehyde as a final product.
B)

-Lithium aluminium hydride is a strong reducing agent and it reduced the carboxylic acid group to its corresponding hydroxyl derivative. So, propanoic acid will react with $LiAl{H_4}$ to give n-Propanol. So, by this reaction, we will not get Propionaldehyde as a final product.
C)

-DIBAL-H stands for Diisobutylaluminumhydride and it has only one hydride. So, if we allow this reaction to happen quantitatively, then it will convert the ester functional group to its corresponding aldehyde as a final product. So, -OR group will be replaced by –H atom. So, Propionaldehyde will be obtained from this reaction.
D)

Here, the reagent used is Lithium tertbutoxyaluminumhydride. This reagent also has only one hydride and if allowed to react quantitatively, then it will convert the acid chloride into the corresponding aldehyde by replacing the –Cl by –H atom. So, we will also get Propionaldehyde as a product in this reaction.
So, we can say that correct answer is (B).
Note: Note that as DIBAL-H has only one hydride, it will convert the ester to aldehyde only and it will not reduce the aldehyde further to the alcohol. The same thing is with Lithium tertbutoxyaluminumhydride, it also cannot reduce acid chloride to alcohols and the reaction stops at the formation of aldehyde.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




