
The intermediate during the addition of HCl to propene in the presence of peroxide is
A) \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\mathop {\rm{C}}\limits^{\rm{ \bullet }} {\rm{HC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{Cl}}\]
B) \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\mathop {\rm{C}}\limits^{\rm{ + }} {\rm{HC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\]
C) \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}\mathop {\rm{C}}\limits^{\rm{ \bullet }} {{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}\]
D) \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_2}\mathop {\rm{C}}\limits^{\rm{ + }} {{\rm{H}}_2}\]
Answer
232.5k+ views
Hint: The reaction intermediates are short-lived and highly reactive species formed due to heterolytic and homolytic fission of bonds. Some reaction intermediates are carbocations, nitrenes, benzyne, etc.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Let's understand what a carbocation is. A carbocation defines a species carrying the positively charged atom of carbon. The positive charge on the carbon atom is due to the electron pair attraction by the electronegative atom bonded to that carbon atom.
Let's understand the peroxide effect in detail. When an alkene undergoes a reaction with HBr in peroxide, the reaction gives a product contrary to Markovnikov's rule. But, there is no effect of peroxide on HCl and HI.
Here, propene undergoes a reaction with HCl in the presence of peroxide. The reaction happens the following way:
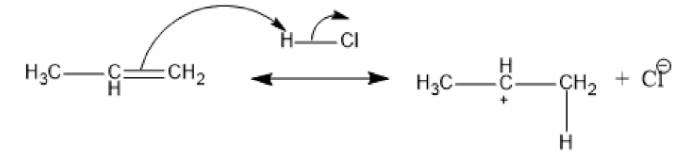
Fig: Formation of carbocation
The above reaction shows that the H-Cl bond breaks and the formation of a stable carbocation take place. The secondary carbocation is the one in which the positively charged carbon atom is bonded to two other carbon atoms. And secondary carbocation is formed because of its more stability than primary carbocation.
Hence, option B is right.
Note: When an asymmetrical alkene undergoes a reaction with a hydrogen halide, the addition of H atoms takes place at the Carbon atom of the double bond to which more numbers of hydrogen atoms are boned. And the halogen atom adds to the other atoms of the double bond.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Let's understand what a carbocation is. A carbocation defines a species carrying the positively charged atom of carbon. The positive charge on the carbon atom is due to the electron pair attraction by the electronegative atom bonded to that carbon atom.
Let's understand the peroxide effect in detail. When an alkene undergoes a reaction with HBr in peroxide, the reaction gives a product contrary to Markovnikov's rule. But, there is no effect of peroxide on HCl and HI.
Here, propene undergoes a reaction with HCl in the presence of peroxide. The reaction happens the following way:

Fig: Formation of carbocation
The above reaction shows that the H-Cl bond breaks and the formation of a stable carbocation take place. The secondary carbocation is the one in which the positively charged carbon atom is bonded to two other carbon atoms. And secondary carbocation is formed because of its more stability than primary carbocation.
Hence, option B is right.
Note: When an asymmetrical alkene undergoes a reaction with a hydrogen halide, the addition of H atoms takes place at the Carbon atom of the double bond to which more numbers of hydrogen atoms are boned. And the halogen atom adds to the other atoms of the double bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Amino Acids and Peptides Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding important Concepts and Tips

Electricity and Magnetism Explained: Key Concepts & Applications

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




