
The inner surface of a cone coated by a reflecting layer formed a conical mirror. A thin incandescent filament is stretched in the cone along its axis. determine the minimum angle of the cone for which the rays emitted by the filament will be reflected from the conical surface not more than once.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The concept used to solve this problem is the laws of reflection and the geometry of a conical mirror. To find the minimum angle of the cone, we will use the angle of incidence and angle of reflection, and the relationship between them.
Complete answer:
Let us consider a specific filament luminous point \[A\] and the arbitrary ray \[AB\] that emerges from it. Through the beam and the filament, we draw a plane. From geometrical reasoning, it follows that the specified ray, with all potential reflections:
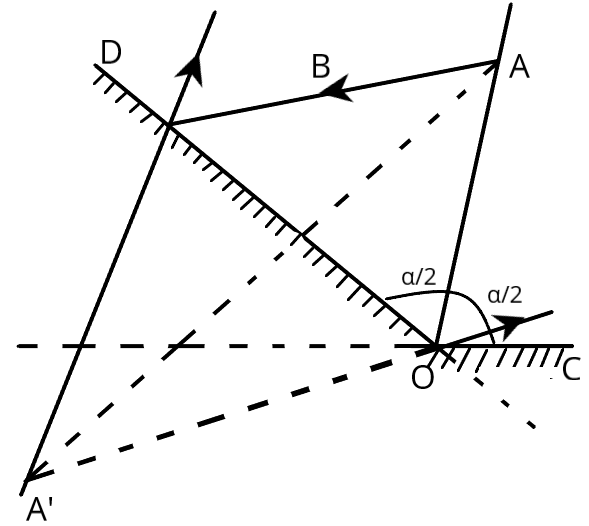
After the initial reflection at the conical surface, the beam \[AB\]will move as if it had come from point\[A'\], creating a virtual image of point\[A\]. In order for any of the rays that are coming from the point\[A\]or the second generator of the cone that are lying in the plane of the beam to ever contact the mirror. And the point \[A'\]must be lower than the straight line \[OC\]which is indicating that Point \[O\]is the vertex of the conical surface.
One will notice this if \[\angle A'OD + \angle AOD + \angle AOC = 3\dfrac{\alpha }{2} > 180^\circ \]
Consequently, \[{\alpha _{\min }} \geqslant 120^\circ \]
As a result, the minimum angle \[\alpha \]of the cone at which the filament's rays will reflect from the conical surface just once is \[{\alpha _{\min }} \geqslant 120^\circ \].
Note: It is important to remember that the angle of incidence and angle of reflection are equal for a conical mirror, and that the critical angle for total internal reflection is equal to the semi-vertex angle of the cone.reflecting mirror has corrosion resistance because the reflecting layer is shielded by a protective layer.
Complete answer:
Let us consider a specific filament luminous point \[A\] and the arbitrary ray \[AB\] that emerges from it. Through the beam and the filament, we draw a plane. From geometrical reasoning, it follows that the specified ray, with all potential reflections:

After the initial reflection at the conical surface, the beam \[AB\]will move as if it had come from point\[A'\], creating a virtual image of point\[A\]. In order for any of the rays that are coming from the point\[A\]or the second generator of the cone that are lying in the plane of the beam to ever contact the mirror. And the point \[A'\]must be lower than the straight line \[OC\]which is indicating that Point \[O\]is the vertex of the conical surface.
One will notice this if \[\angle A'OD + \angle AOD + \angle AOC = 3\dfrac{\alpha }{2} > 180^\circ \]
Consequently, \[{\alpha _{\min }} \geqslant 120^\circ \]
As a result, the minimum angle \[\alpha \]of the cone at which the filament's rays will reflect from the conical surface just once is \[{\alpha _{\min }} \geqslant 120^\circ \].
Note: It is important to remember that the angle of incidence and angle of reflection are equal for a conical mirror, and that the critical angle for total internal reflection is equal to the semi-vertex angle of the cone.reflecting mirror has corrosion resistance because the reflecting layer is shielded by a protective layer.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Why does capacitor block DC and allow AC class 12 physics JEE_Main

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

CBSE Class 12 Physics Set 2 (55/2/2) 2025 Question Paper & Solutions

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Units and Measurements Mock Test for JEE Main 2025-26 Preparation

Chemistry Question Papers for JEE Main, NEET & Boards (PDFs)




