
The force required to keep a body in uniform circular motion is ________.
A. centripetal force
B. centrifugal force
C. resistance
D. None of these
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint:
A body moving in a circular pattern is said to be in a circular motion. A particular kind of circular motion called uniform circular motion involves a body moving along a circular path at a constant speed. The body has a fixed central point and is always equally far from it.
Complete step by step solution:
In the question we have been asked about the force that is required to keep a body in a uniform circular motion. A body is said to be in a circular motion when it’s traveling in a circular path. Circular motion is of two types, one is called as non-uniform circular motion and the other is called as the uniform circular motion. In uniform circular motion the body covers equal distance in equal time and moves with a constant speed. A free body diagram of an object in uniform circular motion is shown below:
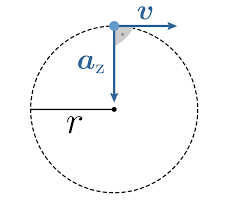
Here ${{a}_{z}}$is the centripetal acceleration, \[v\] is the velocity with which the object is moving and $r$ is the radius of the path. In uniform circular motion only centripetal force is applied as the object is moving with equal speed then the tangential force ceases to zero.
Centrifugal force: When observed from a rotating frame of reference, the centrifugal force, which is an inertial force, appears to affect every object. It is pointed away from the origin of the coordinate system, along an axis that is perpendicular to the axis of rotation.
Hence the correct option is A. centripetal force
Note:
The thing to remember is that the centrifugal force is a non-inertial force. And during the uniform circular motion the tangential force ceases to zero and hence only the centripetal force comes into play to keep an object in uniform circular motion.
A body moving in a circular pattern is said to be in a circular motion. A particular kind of circular motion called uniform circular motion involves a body moving along a circular path at a constant speed. The body has a fixed central point and is always equally far from it.
Complete step by step solution:
In the question we have been asked about the force that is required to keep a body in a uniform circular motion. A body is said to be in a circular motion when it’s traveling in a circular path. Circular motion is of two types, one is called as non-uniform circular motion and the other is called as the uniform circular motion. In uniform circular motion the body covers equal distance in equal time and moves with a constant speed. A free body diagram of an object in uniform circular motion is shown below:

Here ${{a}_{z}}$is the centripetal acceleration, \[v\] is the velocity with which the object is moving and $r$ is the radius of the path. In uniform circular motion only centripetal force is applied as the object is moving with equal speed then the tangential force ceases to zero.
Centrifugal force: When observed from a rotating frame of reference, the centrifugal force, which is an inertial force, appears to affect every object. It is pointed away from the origin of the coordinate system, along an axis that is perpendicular to the axis of rotation.
Hence the correct option is A. centripetal force
Note:
The thing to remember is that the centrifugal force is a non-inertial force. And during the uniform circular motion the tangential force ceases to zero and hence only the centripetal force comes into play to keep an object in uniform circular motion.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




