
The following reaction proceeds through the intermediate \[RCOOAg\text{ }+\text{ }B{{r}_{2}}\to RBr+C{{O}_{2}}+\text{ }AgBr\]
(A) \[RCO{{O}^{+}}\]
(B) \[\text{ }\!\!\grave{\ }\!\!\text{ }{{R}^{(+)}}\]
(C) \[B{{r}^{-}}\]
(D) All
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The reaction in which silver salt of carboxylic acid (RCOOAg acyl compound) is reacted with a molecule of halogen (\[B{{r}_{2}}\])to give organic alkyl halide and side product is known as the Hunsdiecker reaction. This reaction mechanism involves the formation of a radical or following radical chain mechanism. The number of carbon in the reactant is not equal to the number of carbon on the product side, thus, this reaction is termed as a decarboxylation reaction.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In the chain initiation step, the bromide molecule undergoes hetero cleavage through induction as the bromide molecule is bonded with a non-polar covalent bond. The negatively charged bromide ion attack the positive part of silver carboxylate to give AgBr and the positively charged bromide ion makes a bond with the negative part of silver carboxylate to give unstable acyl hypobromite (RCOOBr) such as
\[RCO{{O}^{-}}A{{g}^{+}}+\to RCOOBr\text{ }+\text{ }AgBr\]
Now the bond between Br and O (RCOOBr) is not stable or weak. So it undergoes homolytic cleavage (bond electron divided equally because of less electronegativity difference between both elements) to give out two radicals such as
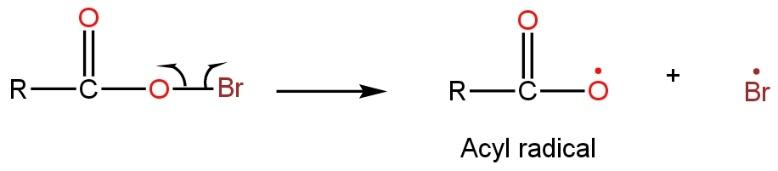
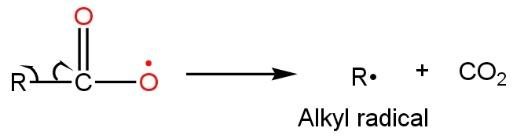
In the chain propagation step, acyl radical lose a molecule of carbon dioxide resulting in the formation of alkyl free radical such as
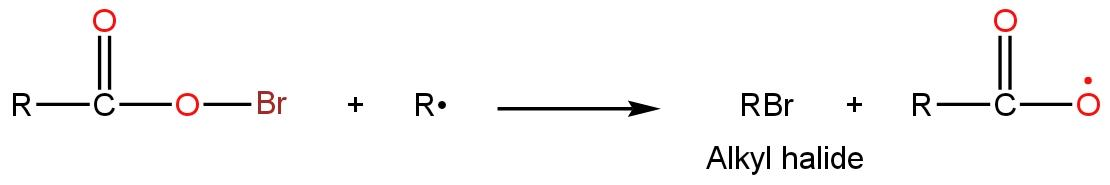
Now in the chain termination step, both radical, alkyl radical, and bromine radical (formed in the initiation step) make bonds with each other to give alkyl halide such as
So, during this reaction all the intermediates given in the options areproduced. Thus, the correct option is D.
Note: Radicals are neutral species. Radicals are of two types, anion radical (\[-ve\]radical) and cation radical (\[+ve\]radical). A species containing radical means it has its own electron (in neutral form) before bonding to any other element (no charge). Radical is a subset of negative charges.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In the chain initiation step, the bromide molecule undergoes hetero cleavage through induction as the bromide molecule is bonded with a non-polar covalent bond. The negatively charged bromide ion attack the positive part of silver carboxylate to give AgBr and the positively charged bromide ion makes a bond with the negative part of silver carboxylate to give unstable acyl hypobromite (RCOOBr) such as
\[RCO{{O}^{-}}A{{g}^{+}}+\to RCOOBr\text{ }+\text{ }AgBr\]
Now the bond between Br and O (RCOOBr) is not stable or weak. So it undergoes homolytic cleavage (bond electron divided equally because of less electronegativity difference between both elements) to give out two radicals such as

In the chain propagation step, acyl radical lose a molecule of carbon dioxide resulting in the formation of alkyl free radical such as

Now in the chain termination step, both radical, alkyl radical, and bromine radical (formed in the initiation step) make bonds with each other to give alkyl halide such as

So, during this reaction all the intermediates given in the options areproduced. Thus, the correct option is D.
Note: Radicals are neutral species. Radicals are of two types, anion radical (\[-ve\]radical) and cation radical (\[+ve\]radical). A species containing radical means it has its own electron (in neutral form) before bonding to any other element (no charge). Radical is a subset of negative charges.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




