
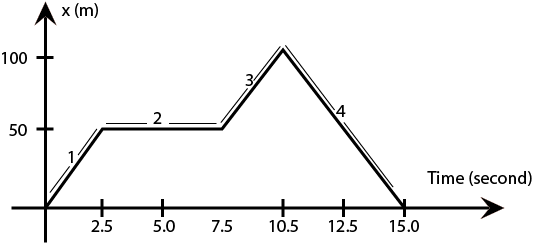
The figure shows the graph of the x-coordinate of a particle going along the x-axis as a function of time. Find (a) the average velocity during 0 to 10 seconds. (b) instantaneous velocity 2, 5, 8 and 12 sec.
(A) (a)1Mm/sec, (b) 20m/sec, zero, 20m/sec, -20m/sec.
(B) (a)20m/sec, (b) 15m/sec, zero, -10m/sec, 15m/sec.
(C) (a)15m/sec, (b) 15m/sec, 10m/sec, -15m/sec, 20m/sec.
(D) (a)25m/sec, (b) 10m/sec, -10m/sec, zero, 20m/sec.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint First, we will calculate displacement of an object from 0 to 10 seconds. Then we will calculate average velocity using the displacement value in formula $\bar \vee = \dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}}$ .
\[{V_{inst}} = \] slope of the graph is used to calculate instantaneous velocity.
Complete step by step solution:
Average velocity: It is defined as the rate of change of velocity of an object. It tells us how much displacement is done by an object in a specific time range.
Average velocity during 0 to 10 seconds = (total displacement) / (total time taken
\[ = \dfrac{{(100 - 0)}}{{10}}\]
=10m/sec
Instantaneous velocity = slope of graph
= change in y axis / change in x axis
Velocity at a particular instant is known as instantaneous velocity. Formula $\mathop {\lim }\limits_{t \to 0}^{} \dfrac{{\Delta x}}{{\Delta t}}$ is used in numerical calculations.
At 2 sec = slope of (1) $ = \dfrac{{50 - 0}}{{2.5 - 0}}$
=20m/sec
At 5 sec = slope of (2) $ = \dfrac{{50 - 50}}{{7.5 - 2.5}}$
= zero
At 8 sec = slope of (3) $ = \dfrac{{100 - 50}}{{10.5 - 7.5}}$
$ = \dfrac{{50}}{{2.5}}$
= 20m/sec
At 12 sec = slope of (4) $ = \dfrac{{0 - 100}}{{15 - 10}}$
$ = \dfrac{{ - 100}}{5}$
=-20m/sec
so, we are left with only one correct option I.e. (A) part.
Note:
Instantaneous velocity can be positive, zero, negative whereas average velocity should be positive always. We cannot use $\mathop {\lim }\limits_{t \to 0}^{} \dfrac{{\Delta x}}{{\Delta t}}$ to calculate instantaneous velocity. Since, we get average velocity as 10m/s
\[{V_{inst}} = \] slope of the graph is used to calculate instantaneous velocity.
Complete step by step solution:
Average velocity: It is defined as the rate of change of velocity of an object. It tells us how much displacement is done by an object in a specific time range.
Average velocity during 0 to 10 seconds = (total displacement) / (total time taken
\[ = \dfrac{{(100 - 0)}}{{10}}\]
=10m/sec
Instantaneous velocity = slope of graph
= change in y axis / change in x axis
Velocity at a particular instant is known as instantaneous velocity. Formula $\mathop {\lim }\limits_{t \to 0}^{} \dfrac{{\Delta x}}{{\Delta t}}$ is used in numerical calculations.
At 2 sec = slope of (1) $ = \dfrac{{50 - 0}}{{2.5 - 0}}$
=20m/sec
At 5 sec = slope of (2) $ = \dfrac{{50 - 50}}{{7.5 - 2.5}}$
= zero
At 8 sec = slope of (3) $ = \dfrac{{100 - 50}}{{10.5 - 7.5}}$
$ = \dfrac{{50}}{{2.5}}$
= 20m/sec
At 12 sec = slope of (4) $ = \dfrac{{0 - 100}}{{15 - 10}}$
$ = \dfrac{{ - 100}}{5}$
=-20m/sec
so, we are left with only one correct option I.e. (A) part.
Note:
Instantaneous velocity can be positive, zero, negative whereas average velocity should be positive always. We cannot use $\mathop {\lim }\limits_{t \to 0}^{} \dfrac{{\Delta x}}{{\Delta t}}$ to calculate instantaneous velocity. Since, we get average velocity as 10m/s
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




