
The cyclopentadienyl cation is antiaromatic while the cyclopentadienyl anion is aromatic. If true enter 1, else enter 0.
Answer
241.8k+ views
Hint: (1) A compound is said to be aromatic if it is cyclic and has planar ring, and also it must have cyclic delocalized pi-electron clouds lying above and below the plane of the ring.
(2) It must also follow Huckel’s $(4n+2)\pi$ electron rule where n is any integer.
(3) For antiaromaticity, the rule is that the molecule must have ${\text{4n\pi }}$ electrons where n is any integer.
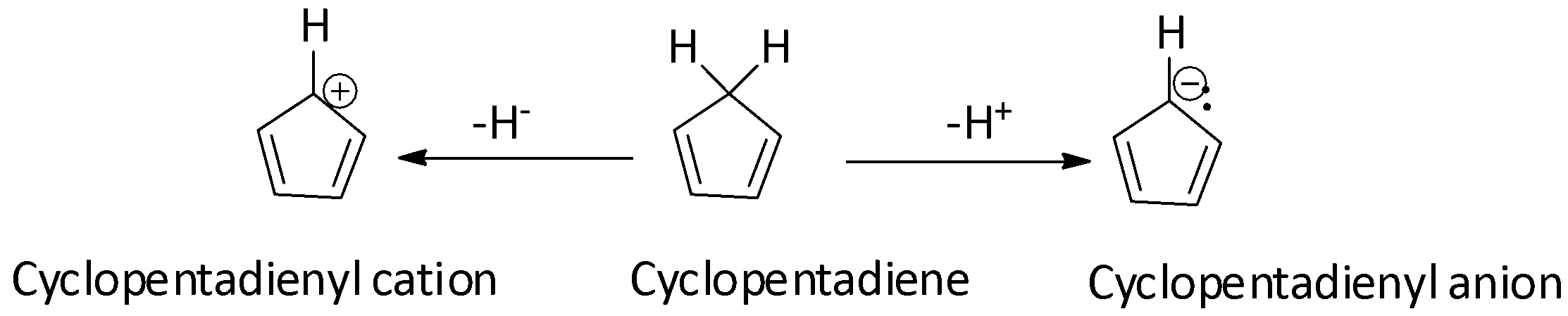
Complete step-by-step answer: Both the cyclopentadienyl cation and cyclopentadienyl anion are formed from cyclopentadiene by the loss of a hydride ion and the abstraction of a proton respectively. Cyclopentadiene is not an aromatic compound because of the presence of a ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ hybridized ring carbon on its ring due to which it does not contain an uninterrupted cyclic pi-electron cloud. When a hydride anion $\left( {{{\text{H}}^{\text{ - }}}} \right)$ is removed from the ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ hybridized ring carbon of cyclopentadiene, the cyclopentadienyl cation will be formed and the hybridization of the ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ hybridized ring carbon will be changed from ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$to${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}$. As a result of this conversion of hybridization, the cyclopentadienyl cation formed will be planar and will contain a cyclic pi-electron cloud above and below the ring. However, it fails to meet the Huckel’s rule of aromaticity as it does not have $(4n+2)\pi$ electrons and so it is not aromatic. But, it does have ${\text{4n\pi }}$ electrons (n is equal to 1 as there are 4 pi electrons). Hence, it is antiaromatic.
When a proton is abstracted from the ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ hybridized ring carbon of cyclopentadiene, the cyclopentadienyl anion is formed and the hybridization of the ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ hybridized ring carbon will be changed from ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ to ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}$. As a result of this conversion of hybridization, the cyclopentadienyl anion formed will be planar and will contain a cyclic pi-electron cloud above and below the ring. Moreover, it also satisfies the Huckel’s rule for aromaticity as it has $(4n+2)\pi$ electrons (n is equal to 1 as there are 6 pi electrons) and so it is aromatic. Thus, the cyclopentadienyl anion is an aromatic compound.
Thus, the given statement is true and so 1.
Note: In the $(4n+2)\pi$ rule, n is not a property of the molecule. This rule is applied just to generate a series: n is equal to 2, 6, 10, 14 etc. and if our pi electron value matches any number in this series, then it possesses aromaticity.
(2) It must also follow Huckel’s $(4n+2)\pi$ electron rule where n is any integer.
(3) For antiaromaticity, the rule is that the molecule must have ${\text{4n\pi }}$ electrons where n is any integer.
Complete step-by-step answer: Both the cyclopentadienyl cation and cyclopentadienyl anion are formed from cyclopentadiene by the loss of a hydride ion and the abstraction of a proton respectively. Cyclopentadiene is not an aromatic compound because of the presence of a ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ hybridized ring carbon on its ring due to which it does not contain an uninterrupted cyclic pi-electron cloud. When a hydride anion $\left( {{{\text{H}}^{\text{ - }}}} \right)$ is removed from the ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ hybridized ring carbon of cyclopentadiene, the cyclopentadienyl cation will be formed and the hybridization of the ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ hybridized ring carbon will be changed from ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$to${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}$. As a result of this conversion of hybridization, the cyclopentadienyl cation formed will be planar and will contain a cyclic pi-electron cloud above and below the ring. However, it fails to meet the Huckel’s rule of aromaticity as it does not have $(4n+2)\pi$ electrons and so it is not aromatic. But, it does have ${\text{4n\pi }}$ electrons (n is equal to 1 as there are 4 pi electrons). Hence, it is antiaromatic.
When a proton is abstracted from the ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ hybridized ring carbon of cyclopentadiene, the cyclopentadienyl anion is formed and the hybridization of the ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ hybridized ring carbon will be changed from ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ to ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}$. As a result of this conversion of hybridization, the cyclopentadienyl anion formed will be planar and will contain a cyclic pi-electron cloud above and below the ring. Moreover, it also satisfies the Huckel’s rule for aromaticity as it has $(4n+2)\pi$ electrons (n is equal to 1 as there are 6 pi electrons) and so it is aromatic. Thus, the cyclopentadienyl anion is an aromatic compound.

Thus, the given statement is true and so 1.
Note: In the $(4n+2)\pi$ rule, n is not a property of the molecule. This rule is applied just to generate a series: n is equal to 2, 6, 10, 14 etc. and if our pi electron value matches any number in this series, then it possesses aromaticity.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




