
The cyclic process forms a circle on a PV diagram as shown in the figure. The work done by the gas is:
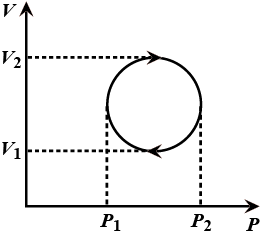
(A) $\dfrac{\pi}{4}\left(P_{2}-P_{1}\right)^{2}$
(B) $\dfrac{\pi}{4}\left(V_{2}-V_{1}\right)^{2}$
(C) $\dfrac{\pi}{2}\left(P_{2}-P_{1}\right)\left(V_{2}-V_{1}\right)$
(D) $\dfrac{\pi}{4}\left(P_{2}-P_{1}\right)\left(V_{2}-V_{1}\right)$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: We know that in a cyclic process, the system starts and returns to the same thermodynamic state. If the cycle goes clockwise, the system does work. A cyclic process is the underlying principle for an engine. If the cycle goes counter clockwise, work is done on the system every cycle. Hence, the work done by the system in a cyclic transformation is equal to the heat absorbed by the system. The net work involved in a cyclic process is the area enclosed in a P-V diagram. If the cycle goes clockwise, the system does work. If the cycle goes anticlockwise, then the work is done on the system every cycle. Although in both the process the system reaches its initial state but there is a little difference. All the cyclic processes are Reversible but not all reversible processes are cyclic. In a cyclic process the system needs to follow the complete cycle to reach the initial state.
Complete step by step answer
We know that work, in physics, is a measure of energy transfer that occurs when an object is moved over a distance by an external force at least part of which is applied in the direction of the displacement. If the force is being exerted at an angle $\theta$ to the displacement, the work done is $W=f d \cos \theta$. One joule is defined as the amount of work done when a force of one newton is exerted through a distance of one meter. In the English system of units, where force is measured in pounds, work is measured in a unit called the foot-pound. The product of force and the amount of displacement in the direction of that force: it is the means by which energy is transferred from one object or system to another.
The work done is an area enclosed in the loop.
The loop is a circle.
Hence the diameters $\mathrm{P}_{2}-\mathrm{P}_{1}=\mathrm{V}_{2}-\mathrm{V}_{1}$
Area of circle $=\dfrac{\pi \mathrm{D}^{2}}{4}$ $\mathrm{D}^{2}=\left(\mathrm{P}_{2}-\mathrm{P}_{1}\right)^{2}=\left(\mathrm{V}_{2}-\mathrm{V}_{1}\right)^{2}=\left(\mathrm{P}_{2}-\mathrm{P}_{1}\right)\left(\mathrm{V}_{2}-\mathrm{V}_{1}\right)$
So, the correct answers are option A, option C and Option D.
Note We know that the change in energy in a cyclic process is zero, since the initial and final states are the same. The work done and the quantity of heat gained in such a process are therefore the same with opposite signs $(\mathrm{R}=-\mathrm{Q})$. An isochoric process, also called a constant-volume process, an isovolumetric process, or an isometric process, is a thermodynamic process during which the volume of the closed system undergoing such a process remains constant. An isothermal process is that process in which the temperature of the system remains constant. During the derivation of the formula for work done by a thermodynamic system during an isothermal process we found that work done is equal to $\mathrm{nRT}$ In $(\mathrm{V} 2 / \mathrm{V} 1)$ or $\mathrm{nRT}$ In $(\mathrm{P} 1 / \mathrm{P} 2),$ where $\mathrm{n}$ is the no. Entropy is defined as the degree of randomness or measure of disorder .Entropy is a state Function because it depends only on the initial and final thermodynamic states and not on the path followed.
Complete step by step answer
We know that work, in physics, is a measure of energy transfer that occurs when an object is moved over a distance by an external force at least part of which is applied in the direction of the displacement. If the force is being exerted at an angle $\theta$ to the displacement, the work done is $W=f d \cos \theta$. One joule is defined as the amount of work done when a force of one newton is exerted through a distance of one meter. In the English system of units, where force is measured in pounds, work is measured in a unit called the foot-pound. The product of force and the amount of displacement in the direction of that force: it is the means by which energy is transferred from one object or system to another.
The work done is an area enclosed in the loop.
The loop is a circle.
Hence the diameters $\mathrm{P}_{2}-\mathrm{P}_{1}=\mathrm{V}_{2}-\mathrm{V}_{1}$
Area of circle $=\dfrac{\pi \mathrm{D}^{2}}{4}$ $\mathrm{D}^{2}=\left(\mathrm{P}_{2}-\mathrm{P}_{1}\right)^{2}=\left(\mathrm{V}_{2}-\mathrm{V}_{1}\right)^{2}=\left(\mathrm{P}_{2}-\mathrm{P}_{1}\right)\left(\mathrm{V}_{2}-\mathrm{V}_{1}\right)$
So, the correct answers are option A, option C and Option D.
Note We know that the change in energy in a cyclic process is zero, since the initial and final states are the same. The work done and the quantity of heat gained in such a process are therefore the same with opposite signs $(\mathrm{R}=-\mathrm{Q})$. An isochoric process, also called a constant-volume process, an isovolumetric process, or an isometric process, is a thermodynamic process during which the volume of the closed system undergoing such a process remains constant. An isothermal process is that process in which the temperature of the system remains constant. During the derivation of the formula for work done by a thermodynamic system during an isothermal process we found that work done is equal to $\mathrm{nRT}$ In $(\mathrm{V} 2 / \mathrm{V} 1)$ or $\mathrm{nRT}$ In $(\mathrm{P} 1 / \mathrm{P} 2),$ where $\mathrm{n}$ is the no. Entropy is defined as the degree of randomness or measure of disorder .Entropy is a state Function because it depends only on the initial and final thermodynamic states and not on the path followed.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




