
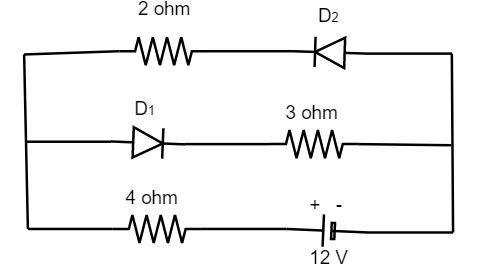
The circuit has two oppositely connected ideal diodes in parallel. What is the current flowing in the circuit?
A) $1.71\,A$
B) $2.0\,A$
C) $2.31\,A$
D) $1.33\,A$
Answer
241.2k+ views
Hint: The diode is forward biased if the positive terminal is connected to $P$ side and the negative terminal is connected to $N$ side of the diode. The condition is opposite for the reverse biased. Calculate the equivalent resistance from the circuit and apply in the ohm’s law to find the value of the current.
Formula used:
The ohm’s law is given by
$V = IR$
Where $V$ is the voltage developed across the circuit, $I$ is the current flowing through the circuit and $R$ is the equivalent resistance of the circuit.
Complete step by step solution:
From the given circuit diagram, it is clear that the diode ${D_1}$ is forward biased and the diode ${D_2}$ is reverse biased in nature. Hence ${D_2}$ has no current flows through it where ${D_1}$ has some amount of current flowing through it due to the changes in the value of the resistance for both. Since no current flows through the diode ${D_2}$, its resistance is not considered for calculating the equivalent resistance of the circuit.
${R_{eq}} = 3 + 4 = 7\,\Omega $
The value of the equivalent resistance is obtained as $7\,\Omega $ .
Using the formula of the ohm’s law,
$V = IR$
Rearranging the above formula, we get
$I = \dfrac{V}{R}$
Substituting the known values in it,
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{12}}{7} = 1.71\,A$
Hence the current of the circuit is calculated as $1.71\,A$ .
Thus the option (A) is correct.
Note: Remember that if the diode in the circuit is reversely biased, then it will have the infinite resistance and so no current flows through it. If the diode is forward biased, the resistance of this diode will be zero and hence maximum current flows through it.
Formula used:
The ohm’s law is given by
$V = IR$
Where $V$ is the voltage developed across the circuit, $I$ is the current flowing through the circuit and $R$ is the equivalent resistance of the circuit.
Complete step by step solution:
From the given circuit diagram, it is clear that the diode ${D_1}$ is forward biased and the diode ${D_2}$ is reverse biased in nature. Hence ${D_2}$ has no current flows through it where ${D_1}$ has some amount of current flowing through it due to the changes in the value of the resistance for both. Since no current flows through the diode ${D_2}$, its resistance is not considered for calculating the equivalent resistance of the circuit.
${R_{eq}} = 3 + 4 = 7\,\Omega $
The value of the equivalent resistance is obtained as $7\,\Omega $ .
Using the formula of the ohm’s law,
$V = IR$
Rearranging the above formula, we get
$I = \dfrac{V}{R}$
Substituting the known values in it,
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{12}}{7} = 1.71\,A$
Hence the current of the circuit is calculated as $1.71\,A$ .
Thus the option (A) is correct.
Note: Remember that if the diode in the circuit is reversely biased, then it will have the infinite resistance and so no current flows through it. If the diode is forward biased, the resistance of this diode will be zero and hence maximum current flows through it.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

JEE Main Mock Test 2025: Properties of Solids and Liquids

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/1/3) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis

CBSE Class 12 Physics Set 2 (55/2/2) 2025 Question Paper & Solutions

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




