
The area of triangle $\vartriangle ABC$ is equal to
A. $\frac{1}{2}ab\sin A$
B. $\frac{1}{2}bc\sin A$
C. $\frac{1}{2}ca\sin A$
D. $bc\sin A$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: To prove the formula, we will assume a triangle with sides $a,b,c$$\;$and angles$A,B,C$. We will draw a perpendicular and form a right angled triangle. Then using trigonometric ratios we will find the value of $\sin A$ and then write the equation of height in terms of this angle. Using formula of area of right angled triangle, we will then find the area of the triangle.
Formula used:
$\begin{align}
& Area=\frac{1}{2}\times base\times height \\
& \sin A=\frac{Perpendicular}{Hypotenuse} \\
\end{align}$
Complete step-by-step solution:
We have been given a triangle $\vartriangle ABC$ and we have to determine its area. We know that the area of the triangle whose included angle is$A$then their sides are $b$ and $c$. It’s a formula of the triangle. We will prove this formula.
Let us assume the sides of the triangle $\vartriangle ABC$be $a,b,c$ $\;$and $A,B,C$.
We will draw the diagram of the triangle with height $h$,
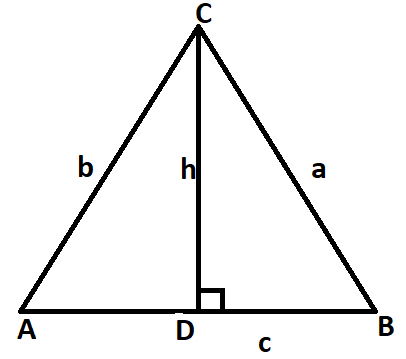
Let the two known sides be $AC$ and $AB$ and the known angle included be $A$.
From the diagram we can see that the triangle $ADC$ is a right angled triangle. Using formula of trigonometry ratio of sine we will find the value of angle $\sin A$.
$\begin{align}
& \sin A=\frac{P}{H} \\
& \sin A=\frac{h}{b} \\
& h=b\sin A \\
\end{align}$
Now we will use formula of the area of the right angled triangle. The base of the triangle is $AB=c$ and we have derived height as $h=b\sin A$. We will substitute these values in the formula of the area of the triangle.
$\begin{align}
& Area=\frac{1}{2}\times AB\times h \\
& =\frac{1}{2}\times c\times b\sin A \\
& =\frac{1}{2}bc\sin A
\end{align}$
The area of the triangle we derived is $Area=\frac{1}{2}bc\sin A$. Hence the option is (B).
Note:
There are three formulas for area of triangle with two sides and an angle between then according to the two different sides and different angles.
$\begin{align}
& Area=\frac{1}{2}bc\sin A \\
& Area=\frac{1}{2}ab\sin C \\
& Area=\frac{1}{2}ac\sin B \\
\end{align}$
Formula used:
$\begin{align}
& Area=\frac{1}{2}\times base\times height \\
& \sin A=\frac{Perpendicular}{Hypotenuse} \\
\end{align}$
Complete step-by-step solution:
We have been given a triangle $\vartriangle ABC$ and we have to determine its area. We know that the area of the triangle whose included angle is$A$then their sides are $b$ and $c$. It’s a formula of the triangle. We will prove this formula.
Let us assume the sides of the triangle $\vartriangle ABC$be $a,b,c$ $\;$and $A,B,C$.
We will draw the diagram of the triangle with height $h$,

Let the two known sides be $AC$ and $AB$ and the known angle included be $A$.
From the diagram we can see that the triangle $ADC$ is a right angled triangle. Using formula of trigonometry ratio of sine we will find the value of angle $\sin A$.
$\begin{align}
& \sin A=\frac{P}{H} \\
& \sin A=\frac{h}{b} \\
& h=b\sin A \\
\end{align}$
Now we will use formula of the area of the right angled triangle. The base of the triangle is $AB=c$ and we have derived height as $h=b\sin A$. We will substitute these values in the formula of the area of the triangle.
$\begin{align}
& Area=\frac{1}{2}\times AB\times h \\
& =\frac{1}{2}\times c\times b\sin A \\
& =\frac{1}{2}bc\sin A
\end{align}$
The area of the triangle we derived is $Area=\frac{1}{2}bc\sin A$. Hence the option is (B).
Note:
There are three formulas for area of triangle with two sides and an angle between then according to the two different sides and different angles.
$\begin{align}
& Area=\frac{1}{2}bc\sin A \\
& Area=\frac{1}{2}ab\sin C \\
& Area=\frac{1}{2}ac\sin B \\
\end{align}$
Recently Updated Pages
Geometry of Complex Numbers Explained

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Amino Acids and Peptides Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding important Concepts and Tips

Electricity and Magnetism Explained: Key Concepts & Applications

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding How a Current Loop Acts as a Magnetic Dipole

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 11 Introduction to Three Dimensional Geometry (2025-26)

Introduction to Three Dimensional Geometry Class 11 Maths Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




