
The ammonium ion is
(a) Tetrahedral
(b) Trigonal pyramidal
(c) Square planar
(d) Square pyramidal
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The shape and structure of any given molecule can be predicted by the concept of hybridization. If a series of molecules possesses \[s{p^3}\], \[s{p^2}\], and \[s{p^{}}\]hybridization, then the geometry will be tetrahedral, planar and linear respectively.
Complete step by step solution:The hybridization for any given molecule can be calculated in the following two ways:
(A) By using the following formula
\[Hybridization(H) = \frac{{V + M - C + A}}{2}\] (Eq.1)
Whereas V=number of valence electrons on the central atom
M= number of monovalent atoms
C= charge on the cation
A=charge on anion
(B) By counting the total number of sigma bonds and lone pairs:
If the sum of the sigma bond is two, then the hybridization will be \[s{p^{}}\]with linear geometry.
If the sum of the sigma bond is three, then the hybridization will be \[s{p^2}\] with planar geometry.
If the sum of the sigma bond is four, then the hybridization will be \[s{p^3}\]with tetrahedral geometry.
If the sum of the sigma bond is five, then the hybridization will be \[s{p^3}d\]with trigonal bipyramidal geometry.
If the sum of the sigma bond is six, then the hybridization will be \[s{p^3}{d^2}\]with octahedral geometry.
Now see the structure of ammonium ion (\[N{H_4}^ + \]) which is known as the protonated ammonia molecule.
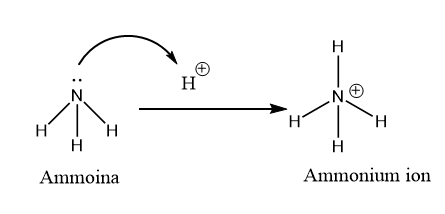
Image: Protonation of the ammonia molecule.
Now we can use \[Hybridization(H) = \frac{{V + M - C + A}}{2}\]equation.
\[Hybridization(H) = \frac{{5 + 4 - 1}}{2} = \frac{8}{2} = 4\]
The value of 4 will be equal to \[s{p^3}\] hybridization and the geometry will be tetrahedral.
We can also count sigma bonds in ammonium ions. There are a total four sigma bonds present in ammonium molecules. Therefore, the hybridization will be \[s{p^3}\].
Therefore, from the above discussion, it is quite clear that option (a) will be the correct answer.
Note: All the \[N - H\]bonds in ammonium ions have the same bond length.
The ammonium ion and methane molecules have identical structures i.e., tetrahedral structures.
The ammonium ion has a +1 formal charge.
Complete step by step solution:The hybridization for any given molecule can be calculated in the following two ways:
(A) By using the following formula
\[Hybridization(H) = \frac{{V + M - C + A}}{2}\] (Eq.1)
Whereas V=number of valence electrons on the central atom
M= number of monovalent atoms
C= charge on the cation
A=charge on anion
(B) By counting the total number of sigma bonds and lone pairs:
If the sum of the sigma bond is two, then the hybridization will be \[s{p^{}}\]with linear geometry.
If the sum of the sigma bond is three, then the hybridization will be \[s{p^2}\] with planar geometry.
If the sum of the sigma bond is four, then the hybridization will be \[s{p^3}\]with tetrahedral geometry.
If the sum of the sigma bond is five, then the hybridization will be \[s{p^3}d\]with trigonal bipyramidal geometry.
If the sum of the sigma bond is six, then the hybridization will be \[s{p^3}{d^2}\]with octahedral geometry.
Now see the structure of ammonium ion (\[N{H_4}^ + \]) which is known as the protonated ammonia molecule.

Image: Protonation of the ammonia molecule.
Now we can use \[Hybridization(H) = \frac{{V + M - C + A}}{2}\]equation.
\[Hybridization(H) = \frac{{5 + 4 - 1}}{2} = \frac{8}{2} = 4\]
The value of 4 will be equal to \[s{p^3}\] hybridization and the geometry will be tetrahedral.
We can also count sigma bonds in ammonium ions. There are a total four sigma bonds present in ammonium molecules. Therefore, the hybridization will be \[s{p^3}\].
Therefore, from the above discussion, it is quite clear that option (a) will be the correct answer.
Note: All the \[N - H\]bonds in ammonium ions have the same bond length.
The ammonium ion and methane molecules have identical structures i.e., tetrahedral structures.
The ammonium ion has a +1 formal charge.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




