
The alcohol that produces turbidity immediately with Lucas reagent at room temperature.
A. \[1 - hydroxy{\text{ }}butane\]
B. \[2 - hydroxy{\text{ }}butane\]
C. \[2 - hydroxy - 2 - methyl{\text{ }}propane\]
D. \[1 - hydroxy - 2 - methyl{\text{ }}propane\]
Answer
240.3k+ views
Hint: Alcohols react with Lucas reagent \[\left( {ZnC{l_2}/Conc.{\text{ }}HCl} \right)\]in the nucleophilic substitution mechanism.
Different types of alcohol react differently with Lucas reagent.
So, this problem is basically based on the concept of reactivity of different types of alcohols with Lucas reagent.
Complete step by step answer:
As we all know, Lucas reagent is used to differentiate between Primary (\[{1^0}\]) Secondary (\[{{\text{2}}^0}\]) and Tertiary(\[{{\text{3}}^0}\]) alcohols.
Now we will see Lucas reagent reacts differently with different types of alcohols-
\[{1^0}\] Alcohols \[\xrightarrow[{{\text{Conc}}{\text{.}}\;{\text{HCl}}}]{{{\text{ZnC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}}}\]Precipitate forms after \[10{\text{ }}minutes\]
\[{{\text{2}}^0}\] Alcohols \[\xrightarrow[{{\text{Conc}}{\text{.}}\;{\text{HCl}}}]{{{\text{ZnC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}}}\] Precipitate forms within \[5 - 10{\text{ }}minutes\]
\[{{\text{3}}^0}\] Alcohols \[\xrightarrow[{{\text{Conc}}{\text{.}}\;{\text{HCl}}}]{{{\text{ZnC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}}}\] Precipitate forms immediately
Now we will see the mechanism of the reaction-
If the nucleophilic substitution gets completed in two steps, \[i.e.\]\[S_N^{{\text{ 1}}}\] mechanism-
\[{\text{R - OH }}\xrightarrow{{}}{\text{ }}{{\text{R}}^ + }{\text{ }}\xrightarrow{{{X^ - }}}\;{\text{R - X (Racemic mixture)}}\]
If the nucleophilic substitution gets completed in one step, i.e. \[S_N^{{\text{ 2}}}\] mechanism-
\[{{\text{X}}^ - }{\text{ + R - OH }}\xrightarrow[{}]{{}}{\text{ [X - - - R - - - OH] }}\xrightarrow[{}]{{}}\,{\text{X - R}}\]
Schematic representation of \[S_N^{{\text{ 1}}}\] mechanism-
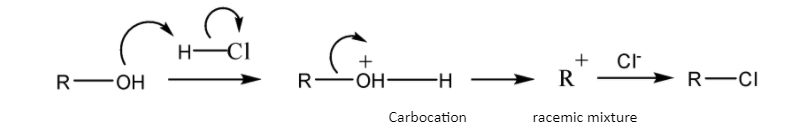
Schematic representation of \[S_N^{{\text{ 2}}}\] mechanism-
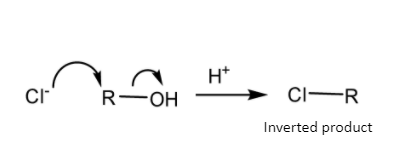
So, the\[S_N^{{\text{ 1}}}\] mechanism gives a carbocation during the course of reaction but the \[S_N^{{\text{ 2}}}\] mechanism gets completed in one step so it does not give any such carbocation during the course of reaction.
The reactivity of alcohols in the \[S_N^{{\text{ 1}}}\] mechanism -\[{{\text{3}}^0}\]- alcohol >\[{\text{ }}{{\text{2}}^0}\]- alcohol >\[{1^0}\]- alcohol
The reactivity of alcohols in the \[S_N^{{\text{ 2}}}\] mechanism - \[{1^0}\]- alcohol>\[{\text{ }}{{\text{2}}^0}\]- alcohol>\[{{\text{3}}^0}\]- alcohol
So, Lucas reagent reacts with alcohols in \[S_N^{{\text{ 1}}}\] mechanism, where the \[{{\text{3}}^0}\]-alcohol reacts immediately.
Now, the structures of the given options-
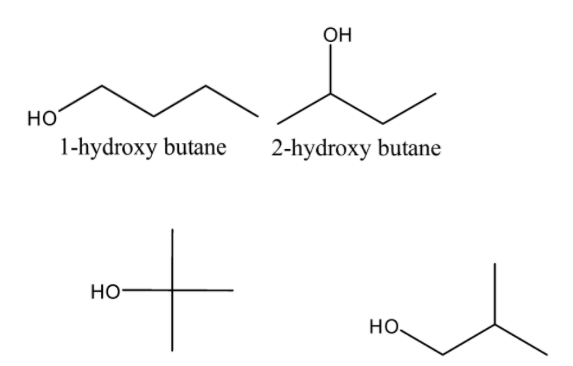
From the above structures, it is clear that Option-\[C\] \[i.e.2 - hydroxy - 2 - methyl\]propane is a tertiary alcohol.
So option-C is the correct answer.
Note: Remember, \[S_N^{{\text{ 1}}}\] mechanism gives a carbocation in the\[{1^{st}}step\], which subsequently reacts with the nucleophile resulting the racemic mixture. Because a carbocation has one vacant p-orbital which can accept the nucleophile using both the lobes of the p-orbital. So, the rate of reaction depends on the stability of the carbocation.
On the other hand, in \[S_N^{{\text{ 2}}}\]mechanism, no such carbocation forms. So, the rate of reaction depends on the availability of the Carbon atom of the substrate molecule.
Different types of alcohol react differently with Lucas reagent.
So, this problem is basically based on the concept of reactivity of different types of alcohols with Lucas reagent.
Complete step by step answer:
As we all know, Lucas reagent is used to differentiate between Primary (\[{1^0}\]) Secondary (\[{{\text{2}}^0}\]) and Tertiary(\[{{\text{3}}^0}\]) alcohols.
Now we will see Lucas reagent reacts differently with different types of alcohols-
\[{1^0}\] Alcohols \[\xrightarrow[{{\text{Conc}}{\text{.}}\;{\text{HCl}}}]{{{\text{ZnC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}}}\]Precipitate forms after \[10{\text{ }}minutes\]
\[{{\text{2}}^0}\] Alcohols \[\xrightarrow[{{\text{Conc}}{\text{.}}\;{\text{HCl}}}]{{{\text{ZnC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}}}\] Precipitate forms within \[5 - 10{\text{ }}minutes\]
\[{{\text{3}}^0}\] Alcohols \[\xrightarrow[{{\text{Conc}}{\text{.}}\;{\text{HCl}}}]{{{\text{ZnC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}}}\] Precipitate forms immediately
Now we will see the mechanism of the reaction-
If the nucleophilic substitution gets completed in two steps, \[i.e.\]\[S_N^{{\text{ 1}}}\] mechanism-
\[{\text{R - OH }}\xrightarrow{{}}{\text{ }}{{\text{R}}^ + }{\text{ }}\xrightarrow{{{X^ - }}}\;{\text{R - X (Racemic mixture)}}\]
If the nucleophilic substitution gets completed in one step, i.e. \[S_N^{{\text{ 2}}}\] mechanism-
\[{{\text{X}}^ - }{\text{ + R - OH }}\xrightarrow[{}]{{}}{\text{ [X - - - R - - - OH] }}\xrightarrow[{}]{{}}\,{\text{X - R}}\]
Schematic representation of \[S_N^{{\text{ 1}}}\] mechanism-

Schematic representation of \[S_N^{{\text{ 2}}}\] mechanism-

So, the\[S_N^{{\text{ 1}}}\] mechanism gives a carbocation during the course of reaction but the \[S_N^{{\text{ 2}}}\] mechanism gets completed in one step so it does not give any such carbocation during the course of reaction.
The reactivity of alcohols in the \[S_N^{{\text{ 1}}}\] mechanism -\[{{\text{3}}^0}\]- alcohol >\[{\text{ }}{{\text{2}}^0}\]- alcohol >\[{1^0}\]- alcohol
The reactivity of alcohols in the \[S_N^{{\text{ 2}}}\] mechanism - \[{1^0}\]- alcohol>\[{\text{ }}{{\text{2}}^0}\]- alcohol>\[{{\text{3}}^0}\]- alcohol
So, Lucas reagent reacts with alcohols in \[S_N^{{\text{ 1}}}\] mechanism, where the \[{{\text{3}}^0}\]-alcohol reacts immediately.
Now, the structures of the given options-

From the above structures, it is clear that Option-\[C\] \[i.e.2 - hydroxy - 2 - methyl\]propane is a tertiary alcohol.
So option-C is the correct answer.
Note: Remember, \[S_N^{{\text{ 1}}}\] mechanism gives a carbocation in the\[{1^{st}}step\], which subsequently reacts with the nucleophile resulting the racemic mixture. Because a carbocation has one vacant p-orbital which can accept the nucleophile using both the lobes of the p-orbital. So, the rate of reaction depends on the stability of the carbocation.
On the other hand, in \[S_N^{{\text{ 2}}}\]mechanism, no such carbocation forms. So, the rate of reaction depends on the availability of the Carbon atom of the substrate molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 - Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques - 2025-26




