
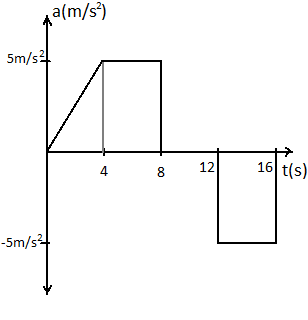
The acceleration of a train between two stations is shown in the figure. The maximum speed of the train is:
A) $60m{s^{ - 1}}$
B) $30m{s^{ - 1}}$
C) $120m{s^{ - 1}}$
D) $90m{s^{ - 1}}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Define acceleration and try to recall the mathematical expression of acceleration. From the graph and from the relation between velocity and acceleration we can easily estimate the maximum speed the train can reach.
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s have some nostalgia and revisit our classes of kinematics. Our physics teacher was yelling that acceleration is the rate of change of velocity.
For a small change in velocity \[dv\] over a time $dt$ acceleration of a body can be represented mathematically as,
$a = \dfrac{{dv}}{{dt}}$ ……….. (1)
Further simplifying,
$ \Rightarrow dv = a \times dt$
For the maximum velocity, we can integrate both sides of the above equation.
Taking integration both sides, we get
$ \Rightarrow v = \int {adt} $ ………. (2)
This is the expression for velocity in terms of acceleration.
Now we know that integrating a function/ curve, we get the area under that function/ curve. Thus from equation (2), we can conclude that the area under the acceleration-time graph is defined as the velocity of the train/ moving object.
Now from the diagram given in the question, we can see that after $12s$ mark, the acceleration of the train is negative, so in order to calculate the maximum velocity, we can take the area under the graph before the 12s mark.
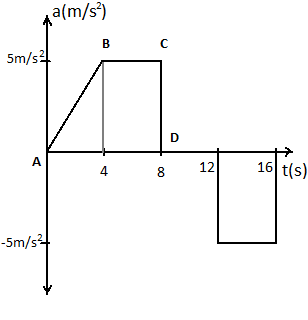
From the above diagram the area of the section $ABCD$ gives us the maximum velocity.
Area of $ABCD$ is the sum of area of right angled $\vartriangle ABE$ and the rectangle $BCDE$.
Area of $\vartriangle ABE$ is $\dfrac{1}{2} \times 4 \times 5 = 10$
Area of rectangle $BCDE$ is $5 \times 4 = 20$
Thus the maximum velocity of the train would be $10 + 20 = 30m{s^{ - 1}}$
So the correct answer is option B.
Note: Using this technique we can solve problems where we are provided with a graph in simple kinematics, for example, in a velocity time graph, the area under the graph represents the displacement of the moving body. Because the rate of change of displacement is defined as velocity.
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s have some nostalgia and revisit our classes of kinematics. Our physics teacher was yelling that acceleration is the rate of change of velocity.
For a small change in velocity \[dv\] over a time $dt$ acceleration of a body can be represented mathematically as,
$a = \dfrac{{dv}}{{dt}}$ ……….. (1)
Further simplifying,
$ \Rightarrow dv = a \times dt$
For the maximum velocity, we can integrate both sides of the above equation.
Taking integration both sides, we get
$ \Rightarrow v = \int {adt} $ ………. (2)
This is the expression for velocity in terms of acceleration.
Now we know that integrating a function/ curve, we get the area under that function/ curve. Thus from equation (2), we can conclude that the area under the acceleration-time graph is defined as the velocity of the train/ moving object.
Now from the diagram given in the question, we can see that after $12s$ mark, the acceleration of the train is negative, so in order to calculate the maximum velocity, we can take the area under the graph before the 12s mark.

From the above diagram the area of the section $ABCD$ gives us the maximum velocity.
Area of $ABCD$ is the sum of area of right angled $\vartriangle ABE$ and the rectangle $BCDE$.
Area of $\vartriangle ABE$ is $\dfrac{1}{2} \times 4 \times 5 = 10$
Area of rectangle $BCDE$ is $5 \times 4 = 20$
Thus the maximum velocity of the train would be $10 + 20 = 30m{s^{ - 1}}$
So the correct answer is option B.
Note: Using this technique we can solve problems where we are provided with a graph in simple kinematics, for example, in a velocity time graph, the area under the graph represents the displacement of the moving body. Because the rate of change of displacement is defined as velocity.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




