
Structure of ammonia is:
A) Trigonal
B) Tetrahedral
C) Pyramidal
D)Trigonal pyramidal
Answer
239.7k+ views
Hint: The VSEPR theory helps in the prediction of the shape of molecules. This theory predicts shape on the basis of lone pairs and bond pairs surrounding the central atom. Here, we will use the VSEPR theory to identify ammonia's shape.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Let's discuss the structure of ammonia. The ammonia is written by the formula of \[{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\]. The nitrogen atom forms three bond pairs with the hydrogen atom. The count of valence electrons of the N atom in ammonia is five, and three electrons are used in the formation of covalent bonds with H atoms. And one lone pair is present.
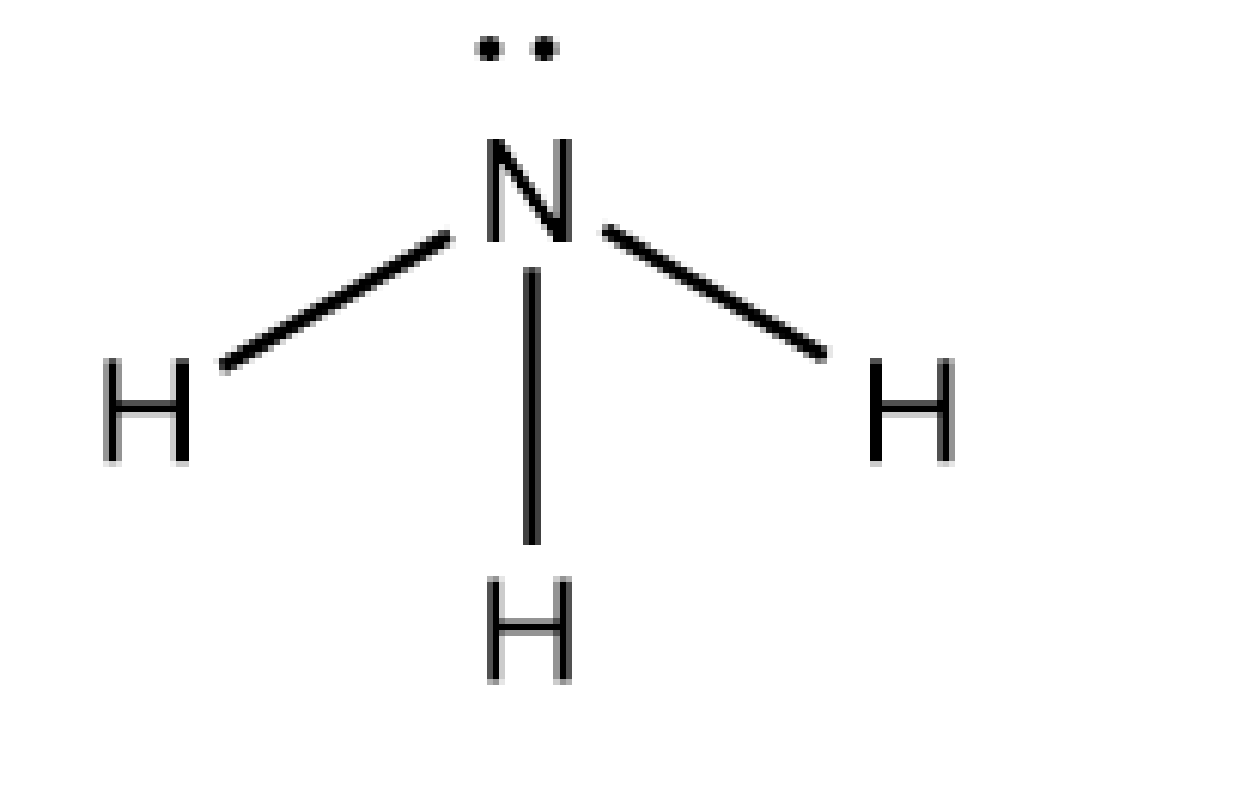
Image: Structure of ammonia
Let's discuss the electron pair geometry of ammonia. As the molecule has three numbers of bond pairs and one lone pair, the electron pair geometry of ammonia is tetrahedral. As one lone pair and three numbers of bond pairs are present, the molecular shape of the ammonia molecule is trigonal bipyramidal.
Hence, option D is right.
Additional Information: Ammonia is a gas that has no colour. It possesses a distinct smell. It is a nitrogenous waste among aquatic organisms. It is an important component of many fertilisers. The pure form of ammonia can be directly applied to soil for fertility.
Note: If the electron pair geometry is tetrahedral, there are three possibilities, if no lone pair is present, then the shape of the molecule is tetrahedral. If one lone pair is present, the shape is trigonal bipyramidal (ammonia) and if two lone pairs are present, the shape is bent.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Let's discuss the structure of ammonia. The ammonia is written by the formula of \[{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\]. The nitrogen atom forms three bond pairs with the hydrogen atom. The count of valence electrons of the N atom in ammonia is five, and three electrons are used in the formation of covalent bonds with H atoms. And one lone pair is present.

Image: Structure of ammonia
Let's discuss the electron pair geometry of ammonia. As the molecule has three numbers of bond pairs and one lone pair, the electron pair geometry of ammonia is tetrahedral. As one lone pair and three numbers of bond pairs are present, the molecular shape of the ammonia molecule is trigonal bipyramidal.
Hence, option D is right.
Additional Information: Ammonia is a gas that has no colour. It possesses a distinct smell. It is a nitrogenous waste among aquatic organisms. It is an important component of many fertilisers. The pure form of ammonia can be directly applied to soil for fertility.
Note: If the electron pair geometry is tetrahedral, there are three possibilities, if no lone pair is present, then the shape of the molecule is tetrahedral. If one lone pair is present, the shape is trigonal bipyramidal (ammonia) and if two lone pairs are present, the shape is bent.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26




