
Salicylic acid is prepared from phenol by:
A. Reimer-Tiemann reaction
B. Kolbe's reaction
C. Kolbe-electrolysis reaction
D. None of the above
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Reaction of phenol with carbon tetrachloride in aqueous sodium hydroxide gives salicylic acid as the major product.
It is called the Reimer-Tiemann reaction.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the reaction of phenol with carbon tetrachloride in aqueous sodium or potassium hydroxide, salicylic acid is the product.
This reaction occurs at 340 K temperature.
The IUPAC name of Salicylic acid is 2-hydroxybenzoic acid.
The mechanism of the reaction is as follows:
It is an electrophilic substitution reaction.
The first step involves the removal of the proton from phenol in aqueous sodium hydroxide giving sodium phenoxide as the product.
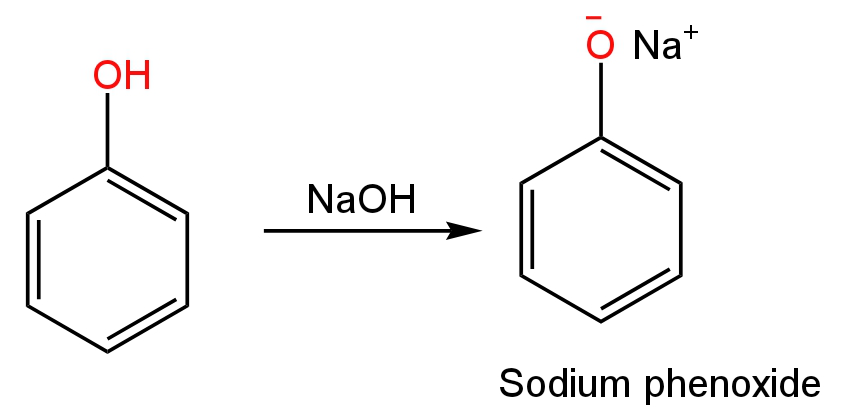
Image: Sodium phenoxide ion formation
The next step involves the attack of carbon tetrachloride at the ortho position of the benzene ring.
This leads to the replacement of three chlorine atoms with three hydroxide ions.
The removal of a molecule of water happens in the following step.
The product when reacted with aqueous sodium hydroxide followed by dilute hydrochloric acid forms 2-Hydroxybenzoic acid or salicylic acid.
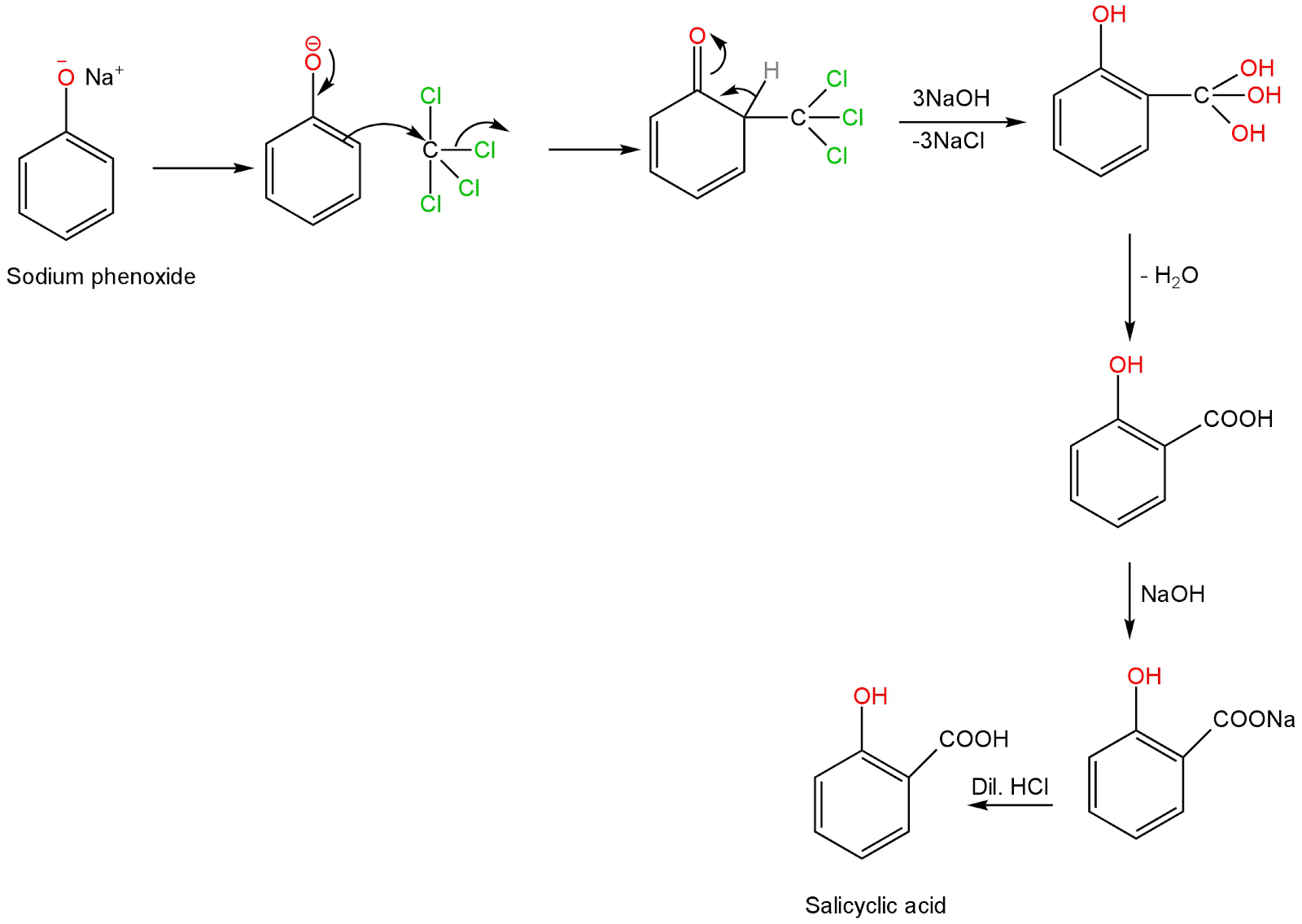
Image: Formation of salicylic acid from sodium phenoxide ion.
So, option A is correct.
Additional Information: Reaction of phenol with chloroform in aqueous sodium or potassium hydroxide at temperature 340 K then hydrolysis of the resulting product forms 2-hydroxybenzaldehyde or salicylaldehyde as the primary product.
Note: Reimer-Tiemann reaction is the production of salicylic acid and salicylaldehyde using phenol as the reactant.
For the formation of salicylic acid, carbon tetrachloride is used as a reagent and for salicylaldehyde, chloroform is used as a reagent.
It is called the Reimer-Tiemann reaction.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the reaction of phenol with carbon tetrachloride in aqueous sodium or potassium hydroxide, salicylic acid is the product.
This reaction occurs at 340 K temperature.
The IUPAC name of Salicylic acid is 2-hydroxybenzoic acid.
The mechanism of the reaction is as follows:
It is an electrophilic substitution reaction.
The first step involves the removal of the proton from phenol in aqueous sodium hydroxide giving sodium phenoxide as the product.

Image: Sodium phenoxide ion formation
The next step involves the attack of carbon tetrachloride at the ortho position of the benzene ring.
This leads to the replacement of three chlorine atoms with three hydroxide ions.
The removal of a molecule of water happens in the following step.
The product when reacted with aqueous sodium hydroxide followed by dilute hydrochloric acid forms 2-Hydroxybenzoic acid or salicylic acid.

Image: Formation of salicylic acid from sodium phenoxide ion.
So, option A is correct.
Additional Information: Reaction of phenol with chloroform in aqueous sodium or potassium hydroxide at temperature 340 K then hydrolysis of the resulting product forms 2-hydroxybenzaldehyde or salicylaldehyde as the primary product.
Note: Reimer-Tiemann reaction is the production of salicylic acid and salicylaldehyde using phenol as the reactant.
For the formation of salicylic acid, carbon tetrachloride is used as a reagent and for salicylaldehyde, chloroform is used as a reagent.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




