
Resonance energy per benzene ring decreases in the order
A . Naphthalene > benzene > Anthracene > Phenanthrene
B . Benzene > Naphthalene > Anthracene > Phenanthrene
C . Benzene > Naphthalene > Phenanthrene > Anthracene
D . All have equal resonance energy
Answer
239.4k+ views
Hint: For polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons stability can be said to be proportional to resonance energy per benzene rings. So knowing the number of benzene rings each of the mentioned options are having, we can figure out the stability.
Complete step-by-step answer:
> The theoretical difference in molecular energy between resonance hybrid and the most stable resonance contributor is ( if the resonance contributor existed as a real molecule) is known as the resonance energy. We can also say that the stability gained by electron delocalization due to resonance versus the absence of such delocalization.
> Greater the resonance energy more will be the stability of the compound. This is because of the following two reasons:
- The contributing structures are all equivalent.
The number of contributing structures of roughly compatible energy is greater.
1) Here is the structure of Benzene :
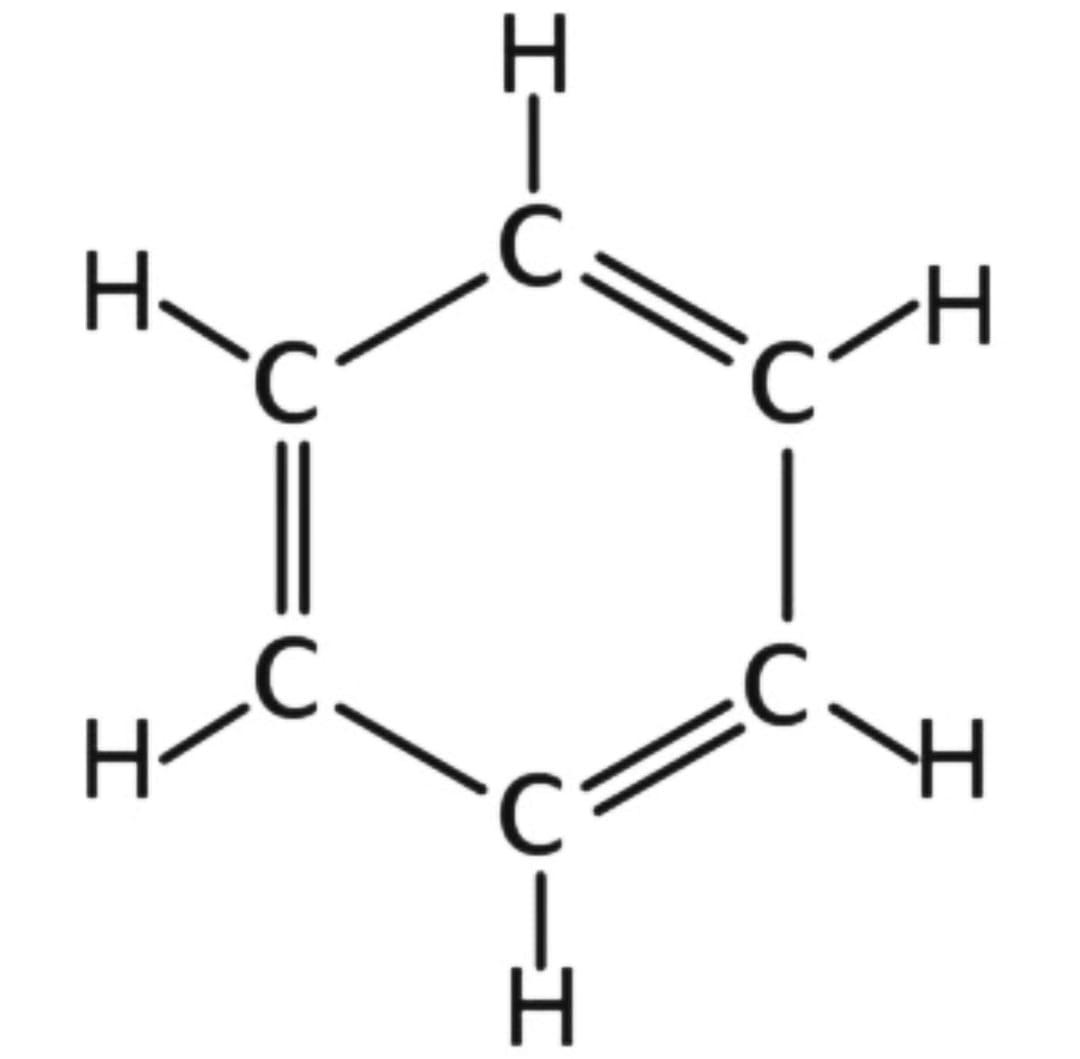
The resonance energy of benzene is 36 Kcal/mol, because there is one benzene ring.
2) Here is the structure of Naphthalene :
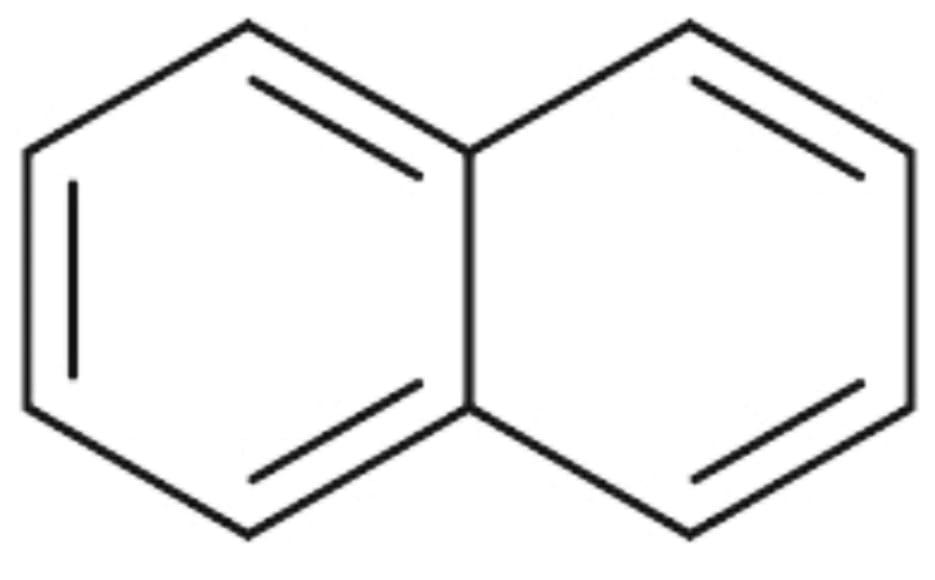
The resonance energy of Naphthalene is 30.5 Kcal/mol. There are two aromatic rings in Naphthalene.
3) The structure of Phenanthrene :
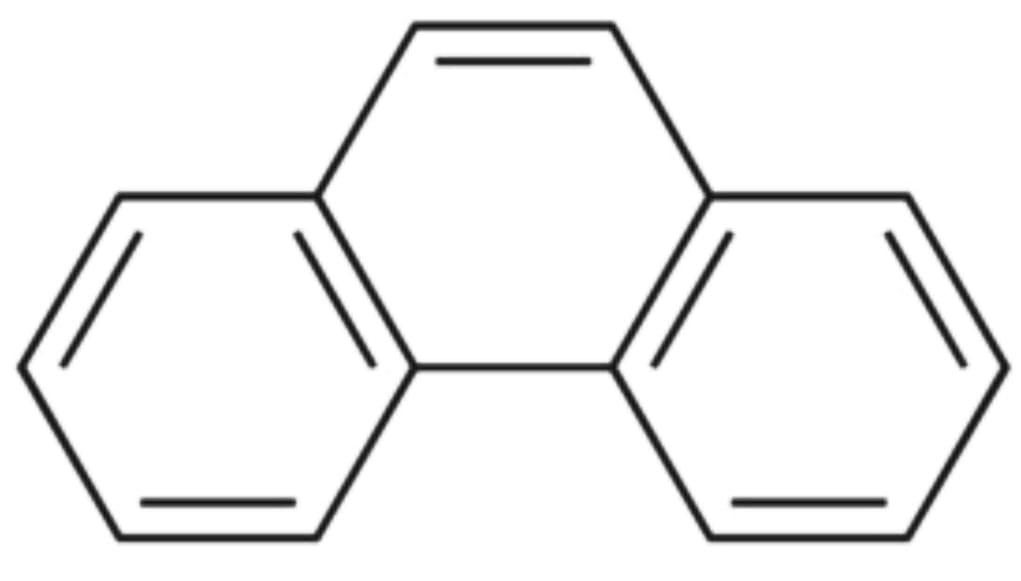
The resonance energy of Phenanthrene is 30.3 Kcal/mol. There are three aromatic rings in Phenanthrene.
4) The structure of Anthracene :
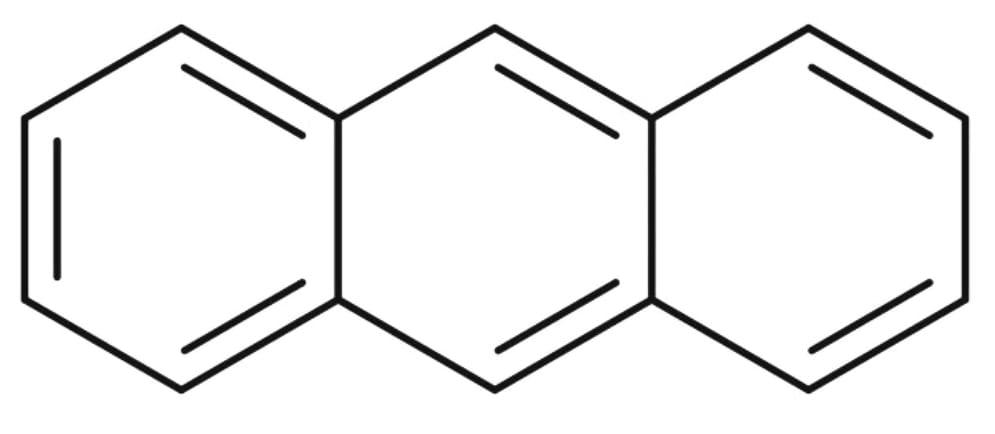
The resonance energy of Anthracene is 28 Kcal/mol. There are three aromatic rings in Anthracene.
Therefore the order of resonance energy as per the benzene ring in the decreasing order is : Benzene > Naphthalene > Phenanthrene > Anthracene. So the correct answer is Option C.
Additional Information:
The resonance energy of a compound is a measure of the extra stability of the conjugated system compared to the bonding number of isolated double bonds.
Note: We know that stability can be compared only for isomeric or related compounds. In case of unsaturated hydrocarbons, it is compared only when they give the same hydrogenated products.
Complete step-by-step answer:
> The theoretical difference in molecular energy between resonance hybrid and the most stable resonance contributor is ( if the resonance contributor existed as a real molecule) is known as the resonance energy. We can also say that the stability gained by electron delocalization due to resonance versus the absence of such delocalization.
> Greater the resonance energy more will be the stability of the compound. This is because of the following two reasons:
- The contributing structures are all equivalent.
The number of contributing structures of roughly compatible energy is greater.
1) Here is the structure of Benzene :

The resonance energy of benzene is 36 Kcal/mol, because there is one benzene ring.
2) Here is the structure of Naphthalene :

The resonance energy of Naphthalene is 30.5 Kcal/mol. There are two aromatic rings in Naphthalene.
3) The structure of Phenanthrene :

The resonance energy of Phenanthrene is 30.3 Kcal/mol. There are three aromatic rings in Phenanthrene.
4) The structure of Anthracene :

The resonance energy of Anthracene is 28 Kcal/mol. There are three aromatic rings in Anthracene.
Therefore the order of resonance energy as per the benzene ring in the decreasing order is : Benzene > Naphthalene > Phenanthrene > Anthracene. So the correct answer is Option C.
Additional Information:
The resonance energy of a compound is a measure of the extra stability of the conjugated system compared to the bonding number of isolated double bonds.
Note: We know that stability can be compared only for isomeric or related compounds. In case of unsaturated hydrocarbons, it is compared only when they give the same hydrogenated products.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 - Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques - 2025-26




