
Represent graphically the variation of the electric field with distance, for a uniformly charged plane sheet.
Answer
241.8k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question, we should know that the space around an electric charge where the electric force can be experienced is called the electric field, and here we will use the general formula of electric field due to uniformly charged plane sheet and then draw the graph with Electric field versus the distance from the plane sheet.
Complete answer:
For a uniformly charged plane sheet having surface charge density of $\sigma $ then electric field due to uniformly charged plane sheet at any distance from it is calculated using
$E = \dfrac{\sigma }{{2{ \in _0}}}$
where,
${ \in _0} = 8.854 \times {10^{ - 12}}{N^{ - 1}}{C^2}{m^{ - 2}}$ is known as the relative permittivity of free space.
So, we see that electric field due to uniformly charged plane sheet is independent of the distance let’s say ‘r’ so, Graph will be a straight line parallel to the X-axis where Distance r is represented on X-axis and magnitude of electric field E is represented on Y-axis so, The graph is shown below as
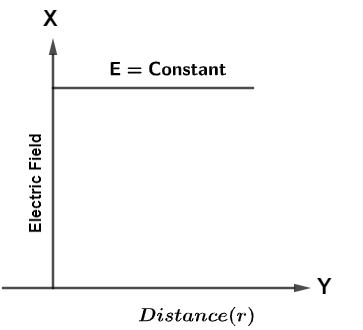
Hence, the electric field always remains constant for a given uniformly charged plane sheet with respect to distance from the plane sheet.
Note: The surface charge density is calculated as the total charge divided by the surface area of the object and when the charge is distributed equally in each section of the object means the charge per unit area is the same all over the surface of the object it’s called object has uniformly charged.
Complete answer:
For a uniformly charged plane sheet having surface charge density of $\sigma $ then electric field due to uniformly charged plane sheet at any distance from it is calculated using
$E = \dfrac{\sigma }{{2{ \in _0}}}$
where,
${ \in _0} = 8.854 \times {10^{ - 12}}{N^{ - 1}}{C^2}{m^{ - 2}}$ is known as the relative permittivity of free space.
So, we see that electric field due to uniformly charged plane sheet is independent of the distance let’s say ‘r’ so, Graph will be a straight line parallel to the X-axis where Distance r is represented on X-axis and magnitude of electric field E is represented on Y-axis so, The graph is shown below as

Hence, the electric field always remains constant for a given uniformly charged plane sheet with respect to distance from the plane sheet.
Note: The surface charge density is calculated as the total charge divided by the surface area of the object and when the charge is distributed equally in each section of the object means the charge per unit area is the same all over the surface of the object it’s called object has uniformly charged.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

JEE Main Mock Test 2025: Properties of Solids and Liquids

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

CBSE Class 10 Sanskrit Set 4 52 Question Paper 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




