
Reaction of\[B{r_2}\] on ethylene in presence of NaCl gives
A.\[{\rm{BrC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{ - C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{Br}}\]
B.\[ClC{H_2} - C{H_2}Br\]
C. Both A and B
D. None of these
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: Alkenes react with bromine in the cold with pure liquid bromine, or with a solution of bromine in an organic solvent like tetrachloromethane. The reaction of ethylene with molecular bromine is an instance of electrophilic addition.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Ethylene reacts with bromine in an organic solvent like tetrachloromethane.
The double bond present in ethylene breaks down, and a bromine atom is connected to each carbon.
The bromine which was initially red-brown lost its colour to provide a colourless liquid.
In this reaction, ethylene gets converted to 1,2-dibromoethane.
The reaction is an instance of electrophilic addition.
Bromine is an extremely "polarizable" molecule and when it moves toward the pi bond in the ethene, it causes an induced dipole in the bromine molecule.
Step-1
One of the bromine atoms gets connected to both carbon atoms, with a positive charge on the bromine atom. A bromonium ion is constructed.
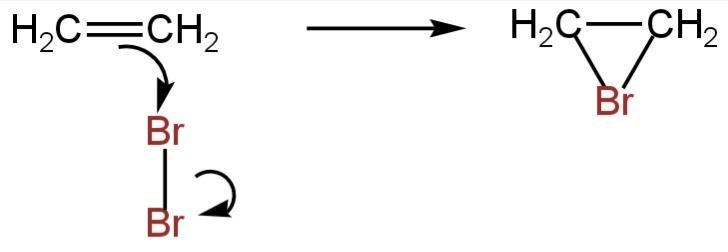
Image: Formation of bromonium ion
Step-2
The bromonium ion is then attacked from the back by another bromide ion. 1,2-dibromoethane is formed as a product.
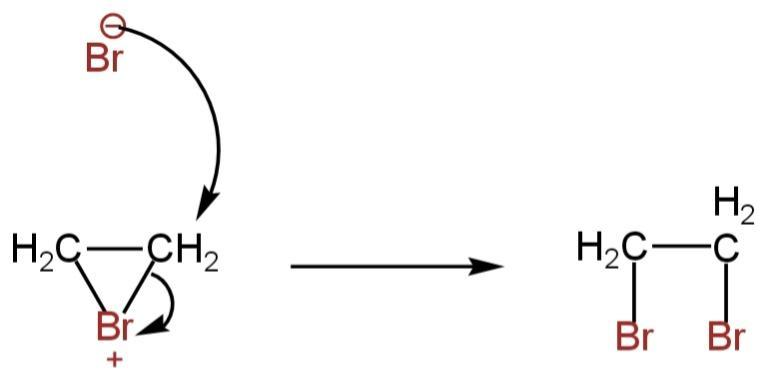
Image: Attack of bromide ion.
So, the product in this reaction is 1,2-dibromoethane.
But NaCl is also present in the medium which will produce chloride ions. This chloride ion will displace one bromide ion giving rise to 1-bromo-2-chloroethene.
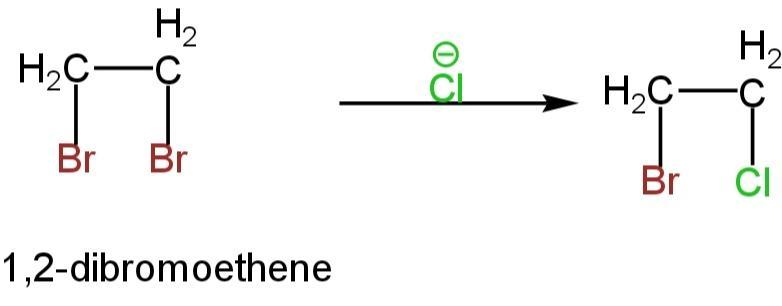
Image: Formation of 1-bromo-2-chloroethene
So, both \[ClC{H_2} - C{H_2}Br\] and \[{\rm{BrC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{ - C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{Br}}\]are formed.
So, both A and B will be formed.
So, option C is correct.
Note: We learned that a displacement reaction is the one in which the atom or a group of atoms is replaced by another atom in a molecule. Chlorine is more reactive than bromine. So, chloride ion displaces bromine ion in 1,2-dibromoethane. A less reactive halogen can't replace a more reactive halogen.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Ethylene reacts with bromine in an organic solvent like tetrachloromethane.
The double bond present in ethylene breaks down, and a bromine atom is connected to each carbon.
The bromine which was initially red-brown lost its colour to provide a colourless liquid.
In this reaction, ethylene gets converted to 1,2-dibromoethane.
The reaction is an instance of electrophilic addition.
Bromine is an extremely "polarizable" molecule and when it moves toward the pi bond in the ethene, it causes an induced dipole in the bromine molecule.
Step-1
One of the bromine atoms gets connected to both carbon atoms, with a positive charge on the bromine atom. A bromonium ion is constructed.

Image: Formation of bromonium ion
Step-2
The bromonium ion is then attacked from the back by another bromide ion. 1,2-dibromoethane is formed as a product.

Image: Attack of bromide ion.
So, the product in this reaction is 1,2-dibromoethane.
But NaCl is also present in the medium which will produce chloride ions. This chloride ion will displace one bromide ion giving rise to 1-bromo-2-chloroethene.

Image: Formation of 1-bromo-2-chloroethene
So, both \[ClC{H_2} - C{H_2}Br\] and \[{\rm{BrC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{ - C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{Br}}\]are formed.
So, both A and B will be formed.
So, option C is correct.
Note: We learned that a displacement reaction is the one in which the atom or a group of atoms is replaced by another atom in a molecule. Chlorine is more reactive than bromine. So, chloride ion displaces bromine ion in 1,2-dibromoethane. A less reactive halogen can't replace a more reactive halogen.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




