
Rank the following in the order of decreasing rate of solvolysis with aqueous ethanol (faster$\to $ slowest)
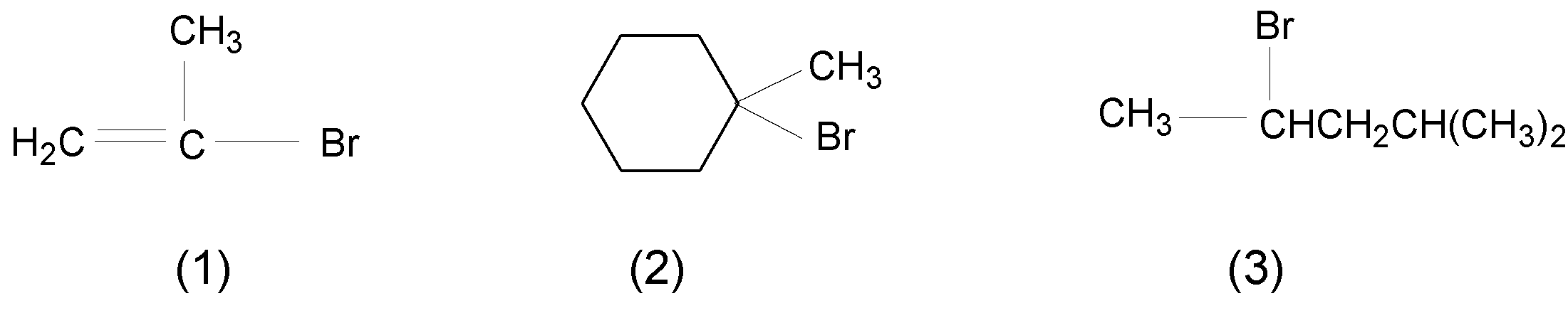
A. $\text{2gt1gt3}$
B. $\text{1gt2gt3}$
C. $\text{2gt3gt1}$
D. $\text{1gt3gt2}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Solvolysis reaction is the type of ${{S}_{{{N}^{1}}}}$ reaction, where solvent acts as a nucleophile. The rate of solvolysis reaction depends on the stability of carbocation, forming in the rate-determining step. The stability of carbocation increases from primary to tertiary $({{1}^{{\mathrm O}}}<{{2}^{O}}<{{3}^{{\mathrm O}}})$.
Complete step by step solution:
First, in the rate-determining step, cleavage of the polar covalent bond $(C-Br)$facilitates the leaving group $(Br)$ to be departed. Hence a carbocation is produced when $Br$leaves the substrate. A nucleophile which is the solvent present in the system (here aqueous methanol) attacks the carbocation in the second step. Thus the rate of solvolysis depends on the rate-determining step of ${{S}_{{{N}^{1}}}}$reaction I,e, the stability of carbocation. The higher the stable carbocation is formed the higher will be the rate of solvolysis reaction.
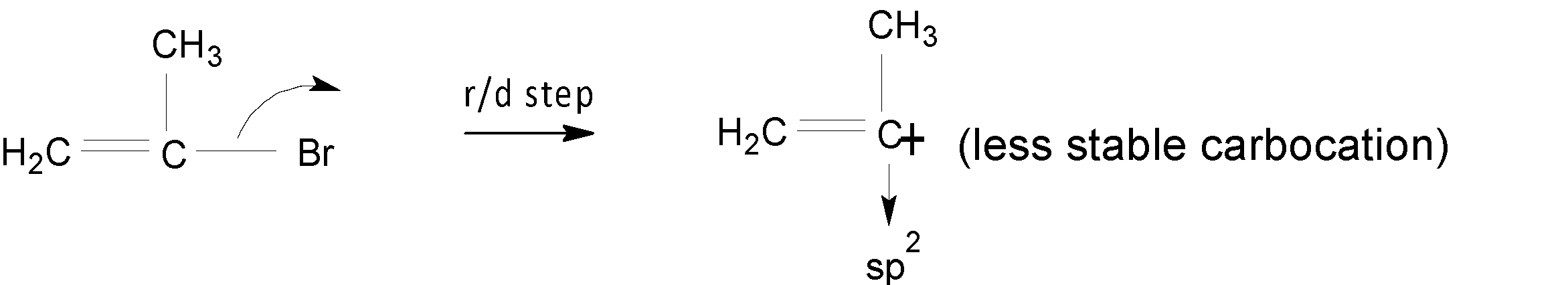
When the compound $(1)$ undergoes a solvolysis reaction, a less stable carbocation is formed because a positive charge on $s{{p}^{2}}$ the carbon atom is not a stable one.
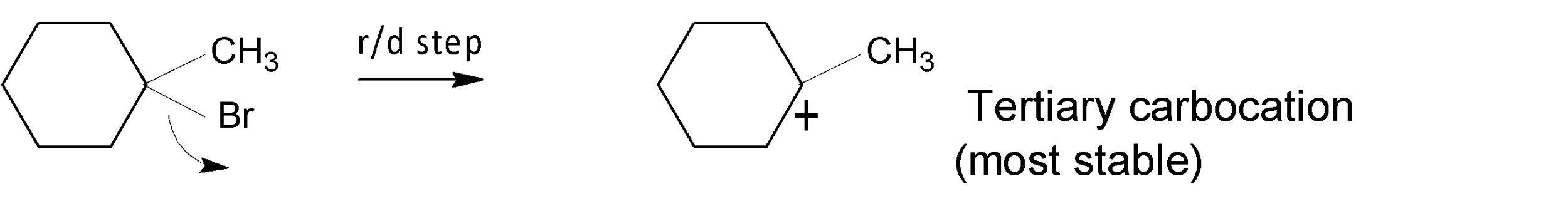
In the case of the compound $(2)$, a highly stable tertiary$({{3}^{{\mathrm O}}})$ carbocation is generated in the rate-determining step and undergoes a rapid solvolysis reaction.
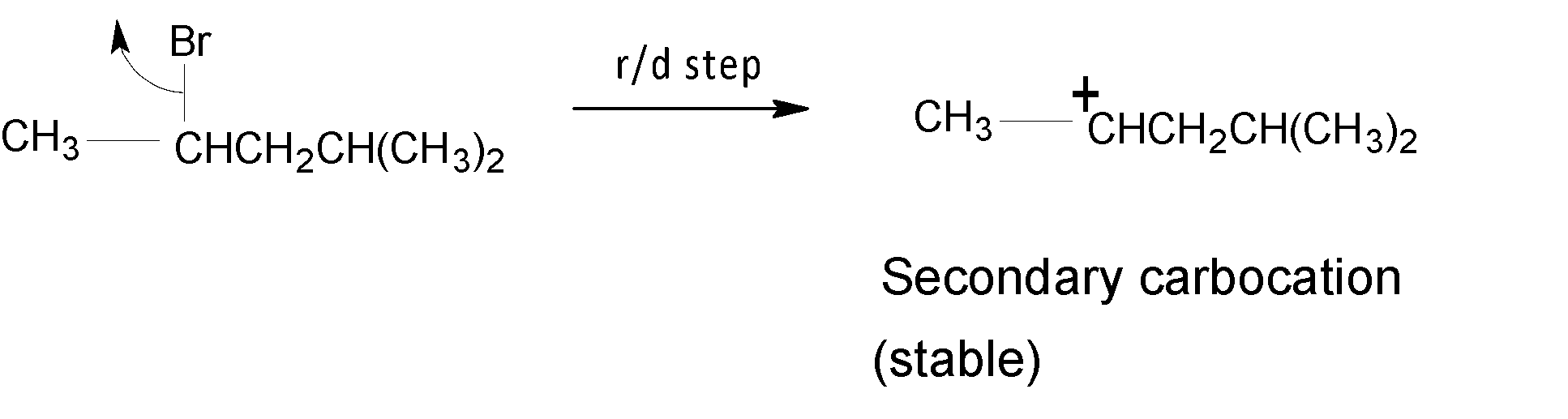
A stable secondary $({{2}^{{\mathrm O}}})$ carbocation is formed when the compound $(3)$ loses its leaving group in the rate-determining step. Hence undergoes solvolysis at a moderate rate among the three compounds.
Therefore, the decreasing order of solvolysis reaction is $2>3>1$$[2gt3gt1gt]$, as stability of carbocation increases from primary to tertiary.
Thus, Option (c) is correct.
Note: In the solvolysis reaction solvent plays an important role, it not only facilitates the formation of carbocation but also speeds up the reaction. The polar protic solvent is preferred. Water and alcohol are the most common solvent in solvolysis reactions.
Complete step by step solution:
First, in the rate-determining step, cleavage of the polar covalent bond $(C-Br)$facilitates the leaving group $(Br)$ to be departed. Hence a carbocation is produced when $Br$leaves the substrate. A nucleophile which is the solvent present in the system (here aqueous methanol) attacks the carbocation in the second step. Thus the rate of solvolysis depends on the rate-determining step of ${{S}_{{{N}^{1}}}}$reaction I,e, the stability of carbocation. The higher the stable carbocation is formed the higher will be the rate of solvolysis reaction.
When the compound $(1)$ undergoes a solvolysis reaction, a less stable carbocation is formed because a positive charge on $s{{p}^{2}}$ the carbon atom is not a stable one.

In the case of the compound $(2)$, a highly stable tertiary$({{3}^{{\mathrm O}}})$ carbocation is generated in the rate-determining step and undergoes a rapid solvolysis reaction.

A stable secondary $({{2}^{{\mathrm O}}})$ carbocation is formed when the compound $(3)$ loses its leaving group in the rate-determining step. Hence undergoes solvolysis at a moderate rate among the three compounds.

Therefore, the decreasing order of solvolysis reaction is $2>3>1$$[2gt3gt1gt]$, as stability of carbocation increases from primary to tertiary.
Thus, Option (c) is correct.
Note: In the solvolysis reaction solvent plays an important role, it not only facilitates the formation of carbocation but also speeds up the reaction. The polar protic solvent is preferred. Water and alcohol are the most common solvent in solvolysis reactions.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




