
Primary amines can be converted into alcohols by the action of
(A) Alkali
(B) Nitrous acid
(C) Reducing agent
(D) Oxidising agent
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Primary amines are the amines in which the N of $N{{H}_{2}}$ group is attached to only one carbon. In the conversion of primary amines to alcohol, the amine $(-N{{H}_{2}})$ functional group is replaced by a hydroxyl ($-OH$) group.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
A primary amine can be converted into alcohol by the action of nitrous acid ($NaN{{O}_{2}}$ +$HCl$) on it. When nitrous acid ($NaN{{O}_{2}}$ +$HCl$) is treated with primary amines at a low temperature (273K – 278K), it gives rise to diazonium salt. When this diazonium salt is hydrolysed or treated with dilute acid, it forms alcohol. Along with the alcohol, side products like nitrogen (${{N}_{2}}$ ) gas and hydrochloric acid ($HCl$ ) are also formed.
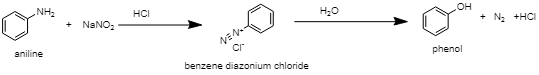
Correct Option: (B) Nitrous acid.
Additional Information: Alcohols have a wide range of applications in our daily lives. The paper we use for writing, the sugar we eat, and the sanitizers that we use to disinfect our hands are all made up of compounds that contain hydroxyl groups. The alcohols are soluble in water due to their ability to form hydrogen bonds in water. However, this solubility decreases with an increase in the size of alkyl or aryl groups.
Note: The well-known trihydric alcohol, glycerol ($C{{H}_{2}}(OH)-C{{H}_{2}}(OH)-C{{H}_{2}}(OH)$ )(IUPAC Name-Propane-1,2,3-triol) has various uses. It is used for the treatment of constipation. It can also be used as a solvent for flavours and food colours and for improving the performance of athletes.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
A primary amine can be converted into alcohol by the action of nitrous acid ($NaN{{O}_{2}}$ +$HCl$) on it. When nitrous acid ($NaN{{O}_{2}}$ +$HCl$) is treated with primary amines at a low temperature (273K – 278K), it gives rise to diazonium salt. When this diazonium salt is hydrolysed or treated with dilute acid, it forms alcohol. Along with the alcohol, side products like nitrogen (${{N}_{2}}$ ) gas and hydrochloric acid ($HCl$ ) are also formed.

Correct Option: (B) Nitrous acid.
Additional Information: Alcohols have a wide range of applications in our daily lives. The paper we use for writing, the sugar we eat, and the sanitizers that we use to disinfect our hands are all made up of compounds that contain hydroxyl groups. The alcohols are soluble in water due to their ability to form hydrogen bonds in water. However, this solubility decreases with an increase in the size of alkyl or aryl groups.
Note: The well-known trihydric alcohol, glycerol ($C{{H}_{2}}(OH)-C{{H}_{2}}(OH)-C{{H}_{2}}(OH)$ )(IUPAC Name-Propane-1,2,3-triol) has various uses. It is used for the treatment of constipation. It can also be used as a solvent for flavours and food colours and for improving the performance of athletes.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

AssertionIn electrolytic refining of metal impure metal class 12 chemistry JEE_Main

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Solutions Hindi Medium (2025-26)

CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Set 1 56/2/1 2025: Question Paper, Answers & Analysis

CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Set 3 2025 with Answers

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses




