
When primary amine is heated with CS2 in presence of excess mercuric chloride, it gives isothiocyanate. This reaction is called
A Hofmann bromide reaction
B Hofmann mustard oil reaction
C Carbylamine reaction
D Perkin reaction
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint The substance that causes the black precipitate to form is almost completely insoluble in water. Cinnabar and metacinnabar are the two crystal forms of the dimorphic chemical. When it is used as a pigment, it is also known as vermillion.
Complete solution
In the Hofmann mustard oil reaction, isothiocyanates are created when primary amines are heated with alcoholic carbon disulfide and subsequently heated with excessive mercuric chloride. The reaction produces a strong odour that is brought on by these isothiocyanates. This odour is reminiscent of mustard oil.
A test to distinguish between primary, secondary, and tertiary amines is the Hofmann mustard oil reaction.
Now, let's examine how each amine responds to the Hoffman mustard oil test.
I) None of the reagents react with tertiary amines.
ii) Dithiocarbamic acids are created when secondary amines and carbon disulfide interact. However, it does not interact with the mercuric chloride in the following step.
When primary amines are treated with carbon disulfide and then heated with too much mercury chloride, isothiocyanates are produced that give off a strong odour akin to that of mustard oil.
We notice that a dark, insoluble precipitate forms during the process. Actually, during the process, HgS is produced as this insoluble precipitate.
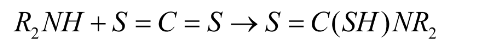
The correct option is (b) .
Note It should be noted that this test is employed to differentiate between primary, secondary, and tertiary amines. It's crucial to keep in mind that aromatic primary amines can pass this test as well. As a result, this test is unable to differentiate between aromatic and aliphatic amines.
Complete solution
In the Hofmann mustard oil reaction, isothiocyanates are created when primary amines are heated with alcoholic carbon disulfide and subsequently heated with excessive mercuric chloride. The reaction produces a strong odour that is brought on by these isothiocyanates. This odour is reminiscent of mustard oil.
A test to distinguish between primary, secondary, and tertiary amines is the Hofmann mustard oil reaction.
Now, let's examine how each amine responds to the Hoffman mustard oil test.
I) None of the reagents react with tertiary amines.
ii) Dithiocarbamic acids are created when secondary amines and carbon disulfide interact. However, it does not interact with the mercuric chloride in the following step.
When primary amines are treated with carbon disulfide and then heated with too much mercury chloride, isothiocyanates are produced that give off a strong odour akin to that of mustard oil.
We notice that a dark, insoluble precipitate forms during the process. Actually, during the process, HgS is produced as this insoluble precipitate.
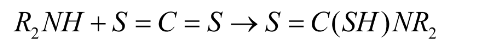
The correct option is (b) .
Note It should be noted that this test is employed to differentiate between primary, secondary, and tertiary amines. It's crucial to keep in mind that aromatic primary amines can pass this test as well. As a result, this test is unable to differentiate between aromatic and aliphatic amines.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




